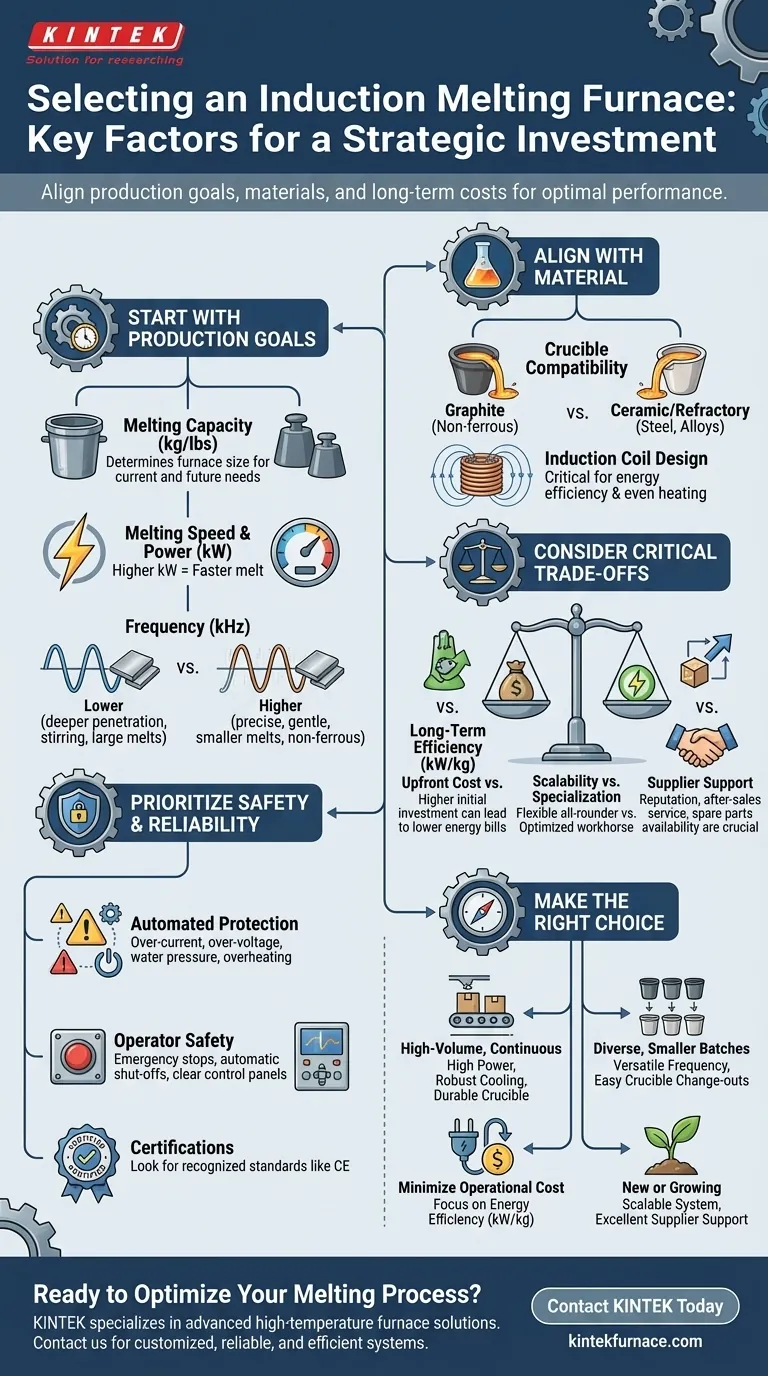
When selecting an induction melting furnace, you must evaluate your specific production requirements against the furnace's technical specifications and long-term operational costs. The most critical factors are the melting capacity and speed you require, the type of metal you will be melting, the system's energy efficiency, and the built-in safety features.
Choosing an induction furnace is not just a technical purchase; it is a strategic investment in your operational core. The goal is to align the furnace's power, frequency, and material compatibility with your specific production goals, ensuring it serves as a reliable and cost-effective asset for years to come.

Start with Your Production Goal: Capacity and Speed
The most fundamental decision revolves around how much metal you need to melt and how fast you need to melt it. This directly informs the required power and frequency of the system.
Defining Your Melting Capacity
Your required melting capacity (measured in kg or lbs) determines the physical size of the furnace and its crucible. This should be based on your typical batch sizes and daily or hourly production targets.
It is crucial to consider not just your current needs but also your potential for future growth.
Matching Power (kW) to Melting Speed
The power supply rating (kW) is the primary driver of melting speed. A higher kilowatt rating delivers more energy into the metal charge, resulting in a faster melt.
A simple rule is that more power equals a faster melt time for a given amount of material. This is a key factor in calculating your throughput (kg/hour).
Understanding the Role of Frequency (kHz)
Operating frequency affects the stirring action and heating efficiency for different metals and melt sizes.
Lower frequencies penetrate deeper and create more vigorous stirring, ideal for larger melts and metals like iron. Higher frequencies are better for smaller melts and non-ferrous metals, offering more precise and gentle heating. Modern systems often feature variable frequency for greater flexibility.
Aligning the Furnace with Your Material
The materials you intend to melt dictate the core components that come into direct contact with the molten metal. Mismatches here can lead to contamination and equipment failure.
The Crucible: Your First Point of Contact
The crucible contains the metal charge and must be chemically compatible with the material at high temperatures.
Graphite crucibles are commonly used for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper. Ceramic or refractory crucibles are required for melting steel and other high-temperature alloys to prevent carbon contamination.
The Induction Coils: The Engine of the System
The water-cooled copper induction coils generate the magnetic field that heats the metal. The design of these coils is critical for energy efficiency and ensuring an even heating pattern throughout the charge.
Proper coil design minimizes electrical resistance and heat loss, directly impacting your operational costs.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making a sound investment.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term Efficiency
A lower-cost furnace may seem attractive, but it often comes with lower energy efficiency (kW/kg). This results in higher electricity bills over the life of the equipment.
Investing in a furnace with better insulation, an optimized coil design, and a modern power supply can yield significant long-term savings that outweigh the higher initial price.
Scalability vs. Specialized Performance
A furnace designed for a single purpose may be highly efficient for that task but lack flexibility. A more scalable or versatile system might handle different metals and batch sizes but may not be perfectly optimized for any single one.
Consider if your operation benefits more from a specialized workhorse or a flexible all-rounder.
The Hidden Costs of Poor Supplier Support
Supplier reputation is not a soft metric; it is a critical risk factor. A supplier with a poor track record for after-sales service can leave you with extended downtime.
Ensure your chosen supplier has positive reviews, provides clear documentation, and offers accessible technical support and spare parts.
Prioritizing Safety and Reliability
An induction furnace is a powerful piece of industrial equipment. Non-negotiable safety and protection systems are essential to protect operators and the investment itself.
Essential Automated Protection Systems
Modern furnaces should include a suite of automated protection features. These include monitoring for over-current, over-voltage, water pressure failure, and overheating.
These systems automatically shut down the furnace before catastrophic failure can occur, ensuring reliability and preventing costly damage.
Operator Safety Features
Key operator safety features include clearly marked emergency stop buttons and automatic shut-off systems that engage if safety parameters are breached.
A well-designed control panel provides clear feedback and simplifies operation, reducing the chance of human error.
The Value of Certifications
Look for furnaces that comply with recognized industry standards and certifications, such as CE (for Europe) or others relevant to your region. These certifications indicate that the equipment has been tested to meet established safety and operational guidelines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Use your primary operational driver to guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: Prioritize a high-power (kW) system with a robust, closed-loop water cooling system and a durable crucible designed for your specific alloy.
- If your primary focus is handling diverse, smaller batches: Look for a versatile power supply with a wider frequency range and a furnace body that allows for quick and easy crucible change-outs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: Scrutinize the energy efficiency rating (kW/kg) and ask for data on power consumption during a typical melt cycle.
- If you are a new or growing operation: Emphasize a scalable system that can grow with you and choose a supplier with a proven reputation for excellent technical support.
By methodically aligning these technical choices with your strategic goals, you ensure your furnace becomes a productive and reliable asset, not an operational bottleneck.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Production Goal | Melting capacity, speed, power (kW), frequency (kHz) |
| Material Alignment | Crucible type (graphite/ceramic), coil design, metal compatibility |
| Trade-offs | Upfront cost vs. efficiency, scalability vs. specialization, supplier support |
| Safety & Reliability | Protection systems, operator safety features, certifications (e.g., CE) |
Ready to optimize your melting process? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including induction melting systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable, efficient furnaces can enhance your production and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















