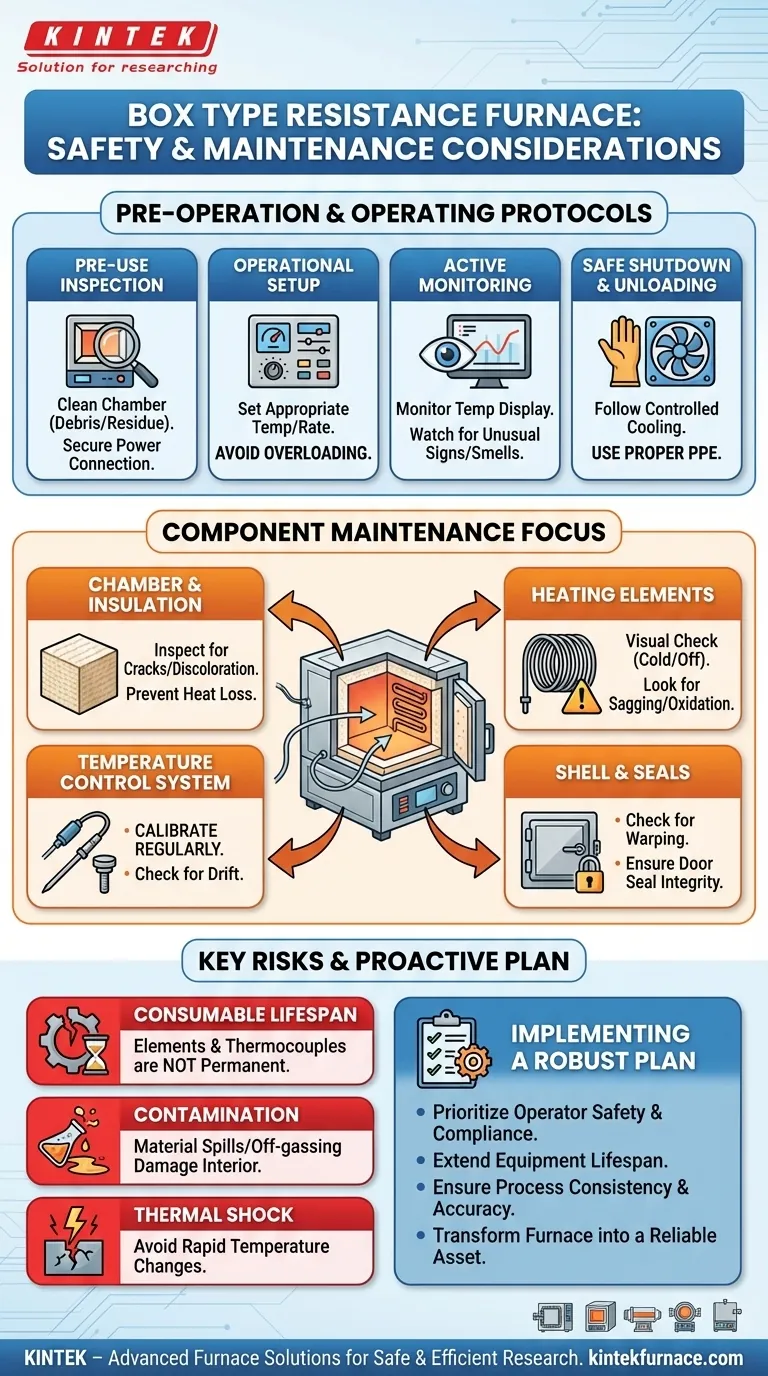
Operating a box type resistance furnace requires a disciplined approach to both safety and maintenance. The key considerations involve a three-part strategy: diligent pre-operation checks to ensure the equipment is ready, active monitoring during the heating cycle to prevent incidents, and a consistent long-term maintenance schedule focused on the furnace's core components to ensure longevity and reliability.
A box furnace's power and simplicity can mask its primary risks. The true goal of any safety and maintenance plan is to manage the inevitable degradation caused by extreme heat, protecting not only the operator but also the integrity of the equipment and the quality of your results.

Foundational Safety Procedures: Before and During Operation
Safe operation is an active process, not a passive one. It begins before the furnace is ever turned on and continues until the workpiece is cool and removed.
Pre-Use Inspection: The First Line of Defense
Before every use, conduct a brief but thorough inspection. First, check the furnace chamber for any debris, residue, or contamination from previous cycles. A clean chamber prevents unwanted chemical reactions and protects the heating elements.
Next, confirm that the power supply is correctly and securely connected. Any looseness or damage in the electrical connection is a significant fire and electrical hazard.
Setting Operational Parameters Correctly
Proper setup is critical. Always set a target temperature and heating rate that is appropriate for your material and well within the furnace's specified limits. Attempting to heat too quickly or exceed the maximum temperature can cause thermal shock to the insulation and drastically shorten the life of the heating elements.
Never overload the furnace chamber. Overloading can lead to poor temperature uniformity and places undue stress on the furnace's structural and heating components.
Active Monitoring During the Heating Cycle
Do not "set it and forget it." The digital display provides real-time temperature data; monitor it to ensure the furnace is following the desired heating profile and is not overshooting the target temperature.
Be aware of any unusual sounds, smells, or visual changes. These can be early indicators of a component failure or a problem with the material being processed.
Safe Shutdown and Unloading
Follow the manufacturer's recommended procedures for cooling. Uncontrolled, rapid cooling can damage both the furnace lining and the workpiece through thermal shock. Always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when unloading, as components will remain dangerously hot long after the power is off.
A Component-Based Maintenance Strategy
Long-term reliability depends on proactive maintenance of the furnace's key systems. Understanding each component's role is crucial for targeted upkeep.
The Furnace Chamber and Insulation
The inner walls are typically made of aluminum oxide fiber insulation. Regularly inspect this material for cracks, hardening, or discoloration. Voids in the insulation lead to heat loss, reduced energy efficiency, and potential hot spots on the furnace's outer shell.
The Heating Elements
The resistance wires or heating elements are the heart of the furnace and are consumable parts. Periodically perform a visual inspection (when the furnace is cold and off) for signs of sagging, oxidation, or brittleness. Their lifespan is finite and is directly affected by operating temperature and atmosphere.
The Temperature Control System
An accurate temperature reading is non-negotiable for both safety and process control. The system relies on temperature sensors (thermocouples) and controllers. Over time, thermocouples can drift, providing inaccurate readings. It is essential to have a schedule for checking the system's calibration against a known standard.
The Furnace Shell and Seals
Inspect the outer metal shell for any signs of warping or discoloration, which could indicate a failure in the internal insulation. For furnaces used with controlled atmospheres, the integrity of the door seals is critical. A leaking seal compromises the atmosphere, wastes gas, and can lead to inconsistent results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Objectivity requires acknowledging the inherent challenges of working with high-temperature equipment.
The Lifespan of Consumables
Heating elements and thermocouples are not permanent fixtures; they are consumables with a predictable service life. Planning for their eventual replacement as part of your regular maintenance budget is a sign of a well-run operation, not a failure.
The Danger of Contamination
Spills or off-gassing from the materials you heat can have a corrosive effect on the furnace interior. Certain materials can release agents that aggressively attack the heating elements and insulation, leading to premature failure. This is why keeping the chamber clean is a safety and maintenance priority.
Thermal Shock: A Hidden Risk
The most common cause of damage to ceramic insulation and even some workpieces is thermal shock. This occurs when the temperature changes too rapidly. Adhering to controlled heating and cooling rates is the single most important factor in preserving the furnace's structural integrity.
Implementing a Robust Safety and Maintenance Plan
Your specific approach should be tailored to your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and compliance: Enforce a mandatory pre-use checklist, ensure proper PPE is always used, and document all operational and maintenance procedures.
- If your primary focus is extending equipment lifespan: Implement a proactive maintenance schedule with a focus on visual inspection of heating elements and insulation to catch degradation early.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and accuracy: Prioritize the regular calibration of your temperature control system and maintain a scrupulously clean furnace chamber.
Ultimately, a proactive approach to safety and maintenance transforms your furnace from a simple tool into a reliable and predictable long-term asset.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Use Inspection | Check for debris, secure power connections, and clean chamber |
| Operational Setup | Set appropriate temperature/rate, avoid overloading |
| Active Monitoring | Watch for unusual sounds/smells, monitor temperature display |
| Shutdown/Unloading | Follow controlled cooling, use PPE for hot components |
| Maintenance Focus | Inspect insulation, heating elements, temperature sensors, and seals |
| Risks | Manage thermal shock, contamination, and consumable lifespan |
Ensure your laboratory's high-temperature processes are safe and efficient with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations and deliver tailored solutions for your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















