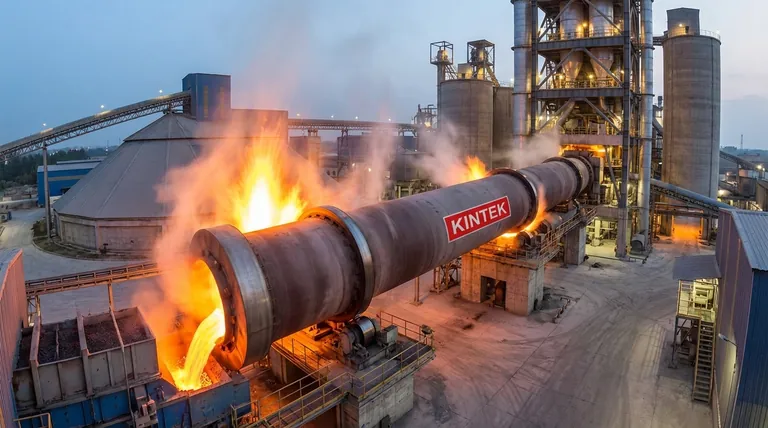
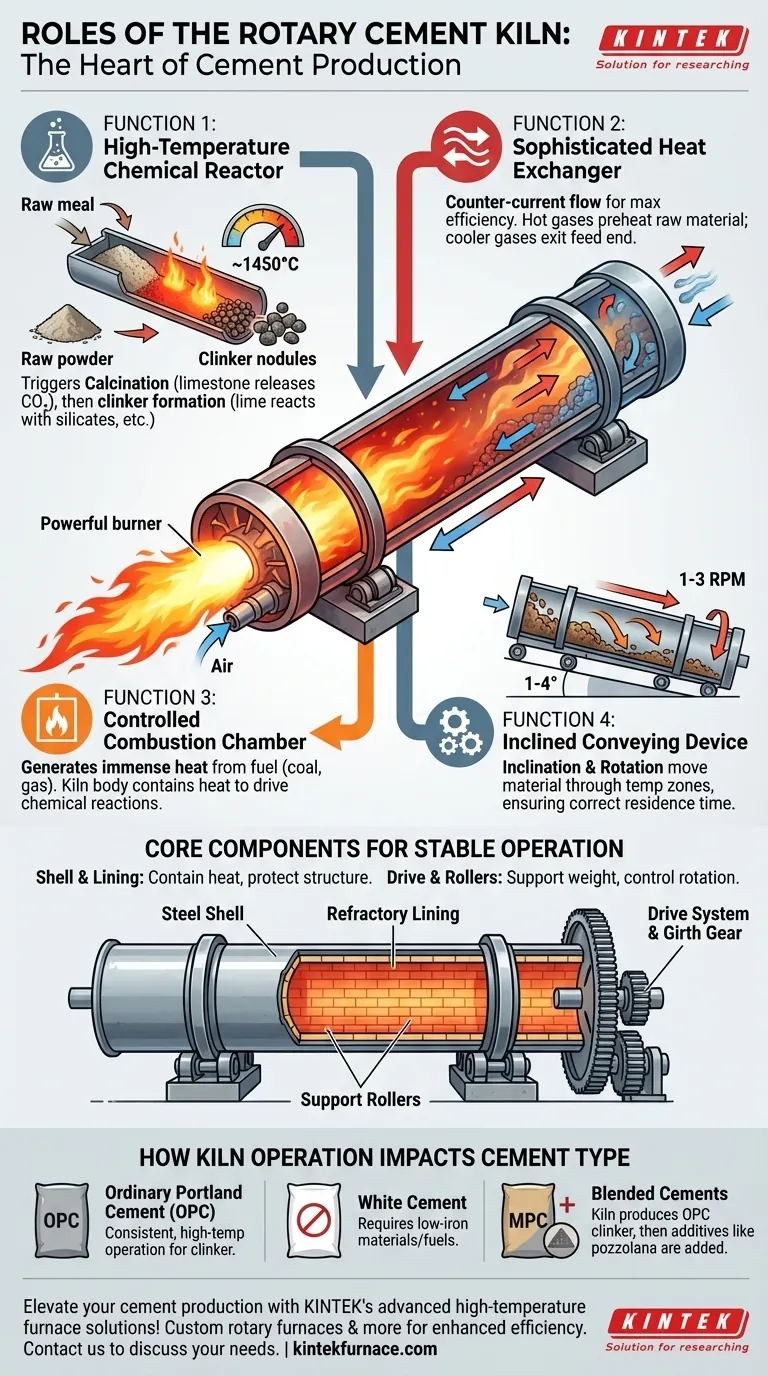
At its core, a rotary kiln is the heart of a cement plant, performing four critical roles simultaneously. It acts as a high-temperature chemical reactor, a sophisticated heat exchanger, a powerful combustion chamber, and a material conveying device, all integrated into one massive, rotating cylinder. This integration allows it to transform finely ground raw materials into cement clinker through a precisely controlled thermal process.
The rotary kiln is more than just a furnace; it's a dynamic system. Its slight inclination and constant rotation are the mechanisms that drive heat exchange, facilitate chemical reactions, and convey material, making it the indispensable engine of cement production.

The Kiln as an Integrated Process System
The genius of the rotary kiln lies in how it combines several distinct functions. Understanding each role reveals how it achieves the complex transformation of raw meal into the fundamental ingredient of cement.
Function 1: A High-Temperature Chemical Reactor
The kiln's primary purpose is to serve as a chemical reactor. Raw material enters the kiln and is heated to extreme temperatures, peaking around 1450°C (2640°F).
This intense heat triggers calcination, a process where limestone (calcium carbonate) releases carbon dioxide to become lime (calcium oxide). As the material moves further down the kiln into hotter zones, this lime reacts with silicates, aluminates, and ferrites to form new compounds known as cement clinker.
Function 2: A Sophisticated Heat Exchange Device
A rotary kiln is an incredibly efficient counter-current heat exchanger. Hot combustion gases from the burner at the lower end flow up the kiln, directly opposing the flow of the cooler raw material moving downward.
This design ensures maximum thermal efficiency. The hottest gases encounter the most processed material, while the cooler gases preheat the fresh raw material entering the kiln.
Function 3: A Controlled Combustion Chamber
At the discharge end of the kiln is a powerful burner. This firing system injects fuel (such as coal, petcoke, or natural gas) and air, creating a massive flame that generates the required thermal energy.
The kiln's body acts as the combustion chamber, containing this immense heat and directing it up the length of the cylinder to drive the chemical reactions.
Function 4: An Inclined Conveying Device
The kiln itself is a simple but effective conveyor. It is installed at a slight angle (typically 1-4 degrees) and rotates slowly (around 1-3 revolutions per minute).
This combination of inclination and rotation causes the solid material to tumble and gradually advance from the upper feed end to the lower discharge end. This movement ensures that the material spends the correct amount of time in each temperature zone for the chemical reactions to complete.
Understanding the Core Components
The kiln's ability to perform these four functions relies on its robust engineering. Several key components work in concert to ensure stable, continuous operation.
The Steel Shell and Refractory Lining
The body of the kiln is a massive welded steel cylinder. Because steel would melt at the operating temperatures, the interior is lined with layers of refractory bricks.
This lining is critical. It insulates the steel shell from the intense internal heat and radiates thermal energy back into the material bed, improving heat transfer and protecting the kiln's structural integrity.
The Drive System and Support Rollers
The immense weight of the kiln is distributed across several sets of support rollers. These rollers allow the kiln to rotate smoothly and stably.
A girth gear encircles the kiln, which is turned by a pinion gear connected to a powerful drive system. This system controls the rotational speed, which is a key parameter for managing the material's residence time inside the kiln.
How Kiln Operation Impacts Cement Type
While the fundamental process remains the same, adjustments in raw materials and kiln control are necessary to produce different types of cement. The kiln produces the clinker, which is the base for the final product.
- If your primary focus is producing Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC): The goal is consistent, high-temperature operation to ensure complete formation of the essential clinker compounds.
- If your primary focus is producing White Cement: You must use raw materials and fuels with extremely low iron and manganese content, as these elements cause the grey color of standard cement.
- If your primary focus is producing blended cements (like Portland Pozzolana): The kiln's role is to produce high-quality OPC clinker, which is then ground together with other materials like pozzolana or fly ash in a later stage.
By mastering the complex interplay of chemistry, thermodynamics, and mechanics within this single device, operators can ensure the efficient production of high-quality cement.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Reactor | Heats raw materials to ~1450°C for calcination and clinker formation. |
| Heat Exchanger | Uses counter-current flow for efficient heat transfer and material preheating. |
| Combustion Chamber | Houses burner for fuel combustion, generating high temperatures. |
| Conveying Device | Inclination and rotation move material through temperature zones. |
Elevate your cement production with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with custom rotary furnaces and more, including Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for enhanced efficiency and quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency















