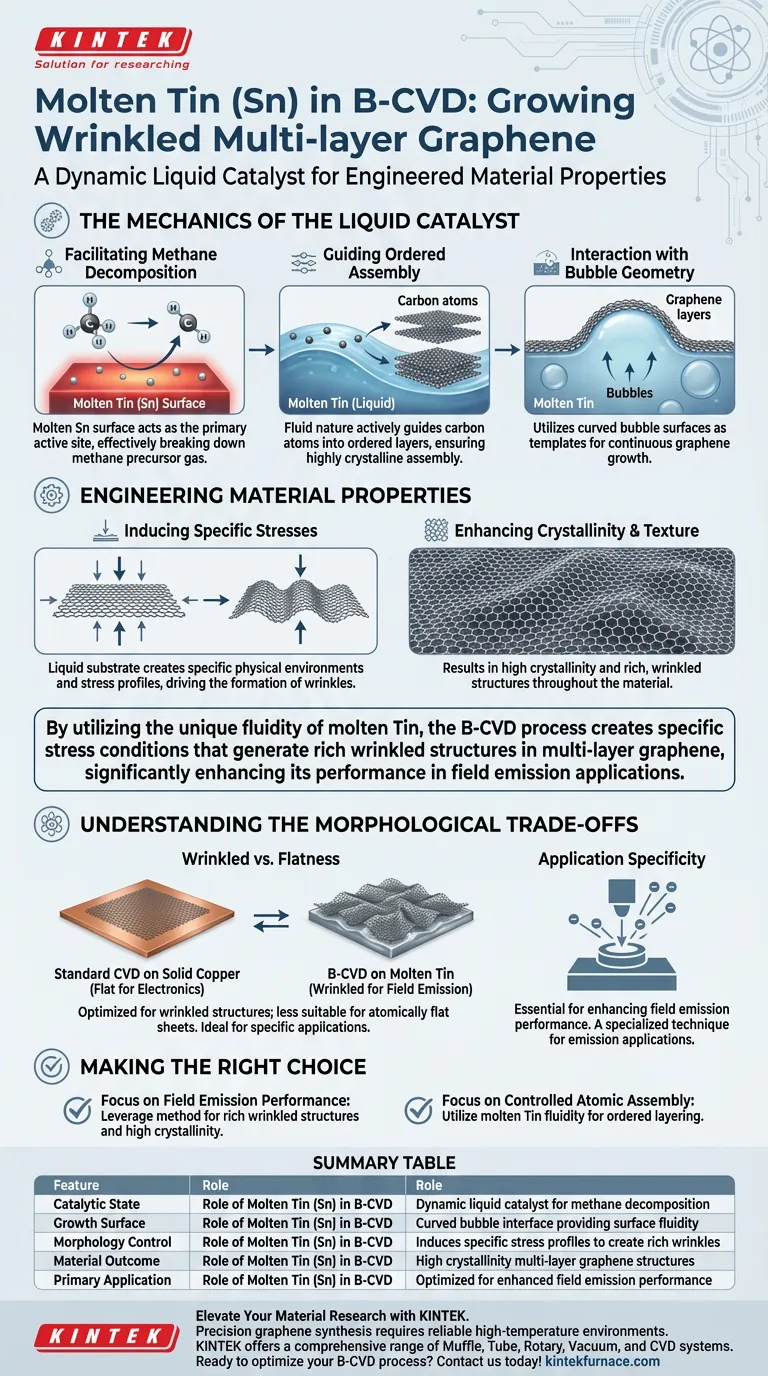
Molten Tin (Sn) serves as a dynamic liquid catalyst in the Bubble-assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (B-CVD) process. It provides the essential reaction surface for decomposing methane and uses its fluid nature to guide carbon atoms into highly crystalline, wrinkled multi-layer graphene structures on the surface of forming bubbles.
By utilizing the unique fluidity of molten Tin, the B-CVD process creates specific stress conditions that generate rich wrinkled structures in multi-layer graphene, significantly enhancing its performance in field emission applications.

The Mechanics of the Liquid Catalyst
Facilitating Methane Decomposition
The molten Tin surface acts as the primary active site for the chemical reaction.
It facilitates the effective decomposition of the methane precursor gas, breaking it down to release the carbon atoms necessary for growth.
Guiding Ordered Assembly
Unlike solid catalysts, the liquid state of Tin provides surface fluidity.
This fluid nature allows the Tin to actively guide the carbon atoms. It ensures they assemble in an ordered manner as they form layers on the surface of the bubbles generated within the melt.
Interaction with Bubble Geometry
The growth process is intimately tied to the formation of bubbles within the molten metal.
The Tin catalyst utilizes the curved liquid surface of these bubbles as a template. This allows the graphene to grow continuously along the bubble interface.
Engineering Material Properties
Inducing Specific Stresses
The liquid substrate does not merely hold the material; it creates a specific physical environment.
The interaction between the graphene and the liquid Tin induces distinct stress profiles during growth. These stresses are not defects but engineered features that drive the final morphology.
Enhancing Crystallinity and Texture
The B-CVD process on molten Tin results in multi-layer graphene with high crystallinity.
Furthermore, the induced stresses lead to the formation of rich, wrinkled structures throughout the material. This texture is not accidental; it is a direct result of using a liquid metal interface.
Understanding the Morphological Trade-offs
Wrinkles vs. Flatness
It is important to recognize that this process is optimized for creating wrinkled graphene.
While standard CVD on solid copper often aims for flatness for electronic transport, the molten Tin method intentionally introduces roughness. This makes it ideal for specific applications but potentially less suitable for those requiring atomically flat sheets.
Application Specificity
The specific morphology created by the Tin catalyst is purpose-built.
The combination of high crystallinity and wrinkled structures is specifically cited as essential for enhancing field emission performance. The process is therefore best viewed as a specialized technique for emission applications rather than general-purpose graphene synthesis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating the B-CVD process using molten Tin, consider your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is field emission performance: Leverage this method to generate the rich wrinkled structures and high crystallinity required for superior electron emission.
- If your primary focus is controlled atomic assembly: Utilize the fluidity of the molten Tin to guide carbon atoms into ordered layers more effectively than static solid substrates might allow.
Ultimately, the use of molten Tin transforms the CVD process from simple deposition into a dynamic tool for engineering complex, high-performance graphene surface textures.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Molten Tin (Sn) in B-CVD |
|---|---|
| Catalytic State | Dynamic liquid catalyst for methane decomposition |
| Growth Surface | Curved bubble interface providing surface fluidity |
| Morphology Control | Induces specific stress profiles to create rich wrinkles |
| Material Outcome | High crystallinity multi-layer graphene structures |
| Primary Application | Optimized for enhanced field emission performance |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision graphene synthesis requires reliable high-temperature environments. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are exploring liquid metal catalysts or standard vapor deposition, our advanced thermal solutions ensure consistent results for target customers in high-tech research and industry.
Ready to optimize your B-CVD process? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Wenmei Lv, Yongliang Tang. A Study on the Field Emission Characteristics of High-Quality Wrinkled Multilayer Graphene Cathodes. DOI: 10.3390/nano14070613
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of high-bias gas ion cleaning? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion
- What happens during the chemical reactions in CVD? Master Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is the function of the 800 °C argon heat treatment in CNT prep? Mastering Roll-to-Roll Substrate Engineering
- How is the CVD process environment created? Master Precise Control for Superior Thin Films
- Why is industrial-grade copper foam utilized as a growth substrate for ReO3–Cu2Te? Enhance CVD Catalyst Performance
- What are the limitations of CVD? Balancing Cost, Safety, and Temperature for Optimal Results
- What process control is achieved through automatic butterfly and needle valves in CVD? Master Precise Chamber Stability
- How do vapor-phase precursors contribute to the CVD process? Unlock Precise Thin Film Deposition










