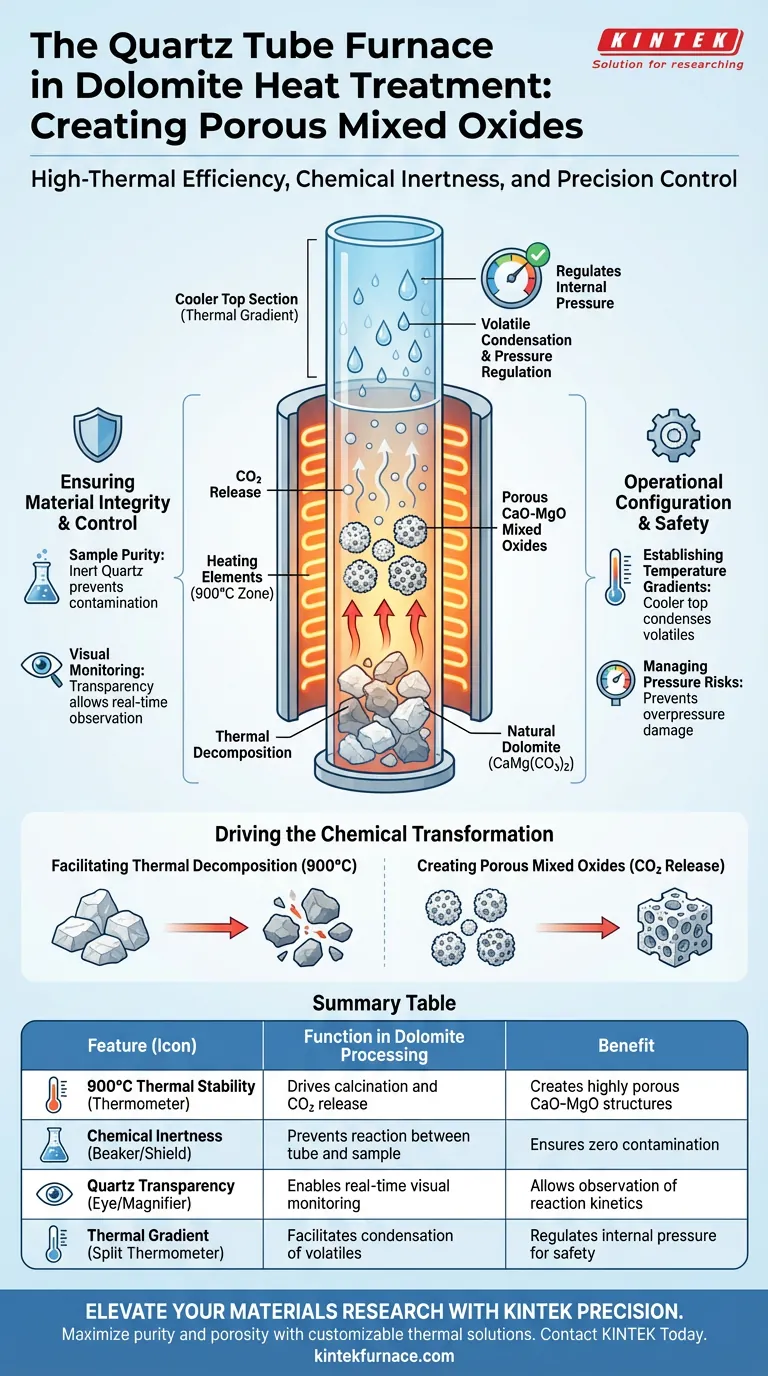
The Quartz Tube Furnace serves as the primary vessel for calcination, specifically engineered to convert natural dolomite into mixed oxides (calcium oxide-magnesium oxide) through high-temperature thermal decomposition. Operating at 900°C in an air atmosphere, it drives the release of carbon dioxide while ensuring the final material remains free from external contaminants.
The core value of using a Quartz Tube Furnace lies in its ability to balance high-thermal efficiency with chemical inertness, producing a highly porous, pure CaO-MgO structure essential for effective adsorption.
Driving the Chemical Transformation
Facilitating Thermal Decomposition
The primary function of the furnace is to provide a stable, high-temperature environment of 900°C.
Under these conditions, natural dolomite undergoes thermal decomposition. This process breaks down the mineral's structure to facilitate the necessary chemical changes.
Creating Porous Mixed Oxides
As the dolomite decomposes, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2).
The escape of this gas is critical. It leaves behind a porous structure composed of Calcium Oxide (CaO) and Magnesium Oxide (MgO), converting the raw mineral into a functional adsorbent material.
Ensuring Material Integrity and Control
Guaranteeing Sample Purity
One of the most critical requirements for preparing mixed oxides is preventing contamination.
The chemical stability of the quartz material ensures that the furnace tube itself does not react with the dolomite. This guarantees that no external impurities leach into the adsorbent material during the high-temperature process.
Enabling Visual Monitoring
Unlike opaque ceramic or metal furnaces, the quartz tube offers transparency.
This allows researchers to visually monitor the sample in real-time. Being able to observe physical changes during the heating process provides critical insights into the reaction kinetics.
Operational Configuration and Safety
Establishing Temperature Gradients
In specific vertical setups, the furnace is designed to create distinct thermal zones.
The bottom of the quartz tube remains in the high-temperature zone to drive the reaction. However, the upper end is positioned to protrude outside the heating element, creating a cooler top section.
Regulating Internal Pressure
This temperature gradient serves a vital safety function.
The cooler upper section allows volatile byproducts to condense rather than building up as gas. This effectively regulates internal pressure, preventing overpressure damage to the tube and maintaining a stable reaction environment.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Managing Pressure Risks
While the quartz tube is effective, it is a closed system that requires careful pressure management.
Without the proper vertical configuration or temperature gradient, the release of CO2 could lead to dangerous overpressure. The system relies on the condensation of volatiles to mitigate this risk.
Handling Fragility
Quartz provides excellent thermal and chemical properties, but it remains a brittle material.
Unlike metal reactors, quartz tubes are susceptible to physical damage if mishandled or subjected to rapid, uneven thermal shock. Operators must prioritize careful setup to prevent tube failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a Quartz Tube Furnace for dolomite processing, consider your specific experimental priorities:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Rely on the chemical inertness of the quartz to prevent contamination, ensuring the final CaO-MgO oxide is suitable for sensitive adsorption applications.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Utilize a vertical tube configuration to establish a temperature gradient, allowing volatiles to condense and preventing dangerous pressure buildup.
- If your primary focus is Experimental Insight: Take advantage of the quartz tube's transparency to visually document the physical transformation of the dolomite in real-time.
The Quartz Tube Furnace is not just a heating element; it is a precision instrument that protects the chemical integrity of your sample while driving the essential phase changes required for high-quality mixed oxides.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Dolomite Processing | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 900°C Thermal Stability | Drives calcination and CO2 release | Creates highly porous CaO-MgO structures |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reaction between tube and sample | Ensures zero contamination of mixed oxides |
| Quartz Transparency | Enables real-time visual monitoring | Allows observation of reaction kinetics |
| Thermal Gradient | Facilitates condensation of volatiles | Regulates internal pressure for safety |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the purity and porosity of your mixed oxide preparations with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Whether you are processing dolomite or developing advanced catalysts, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique atmospheric and thermal requirements.
Ready to optimize your calcination process?
Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with our Experts
Visual Guide
References
- Iyiade Gbolahan Alalade, V. Collins-Martı́nez. Moderate-Temperature Carbon Capture Using Thermally Pre-Treated Dolomite: A Novel Approach. DOI: 10.3390/c11020037
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















