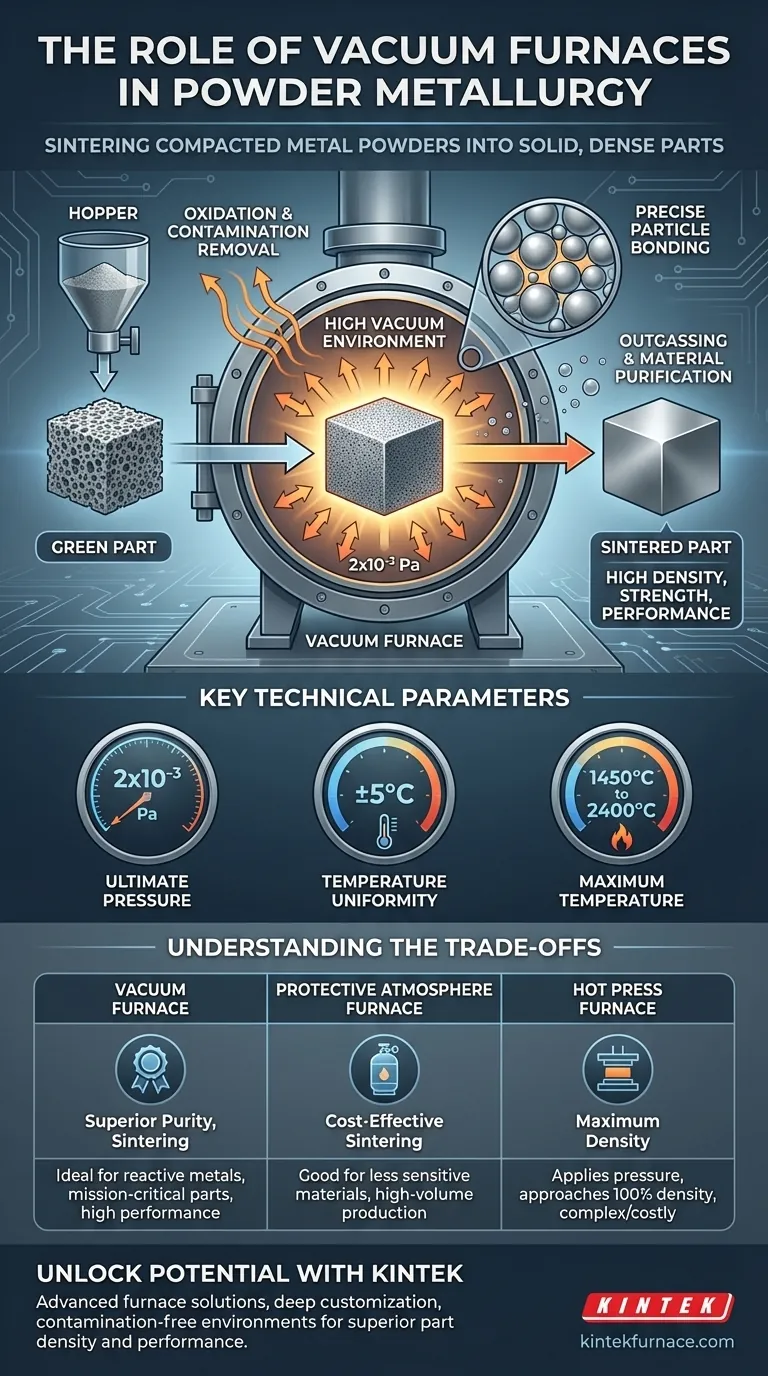
In powder metallurgy, the vacuum furnace serves one primary, critical function: it sinters compacted metal powders into a solid, dense part. By creating a highly controlled, contamination-free environment, the furnace enables the individual powder particles to bond together, dramatically increasing the material's density, strength, and overall performance.
The core purpose of using a vacuum furnace is not just to apply heat, but to create an exceptionally pure environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, ensuring the metallurgical bonds between powder particles are as strong and clean as possible.

Why a Vacuum is Essential for Sintering
Sintering involves heating a compacted powder (a "green part") to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them into a solid piece. The atmosphere in which this occurs is paramount.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most significant benefit of a vacuum is the removal of atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
When heated, most metals will readily react with oxygen to form oxides on their surfaces. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the clean, metal-to-metal contact required for effective diffusion and bonding.
A vacuum furnace evacuates the chamber to a near-perfect vacuum, removing these reactive gases and ensuring the powder particles remain pure throughout the heating cycle.
Promoting Precise Particle Bonding
With clean, unoxidized surfaces, the metal powder particles can bond directly and efficiently.
This controlled environment allows for the formation of a uniform microstructure, which is directly responsible for the final part's mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and ductility.
Outgassing and Material Purification
The vacuum actively pulls volatile substances and trapped gases out of the powder compact as it heats up.
This outgassing process serves as a final purification step, removing contaminants that may have been introduced during powder production or handling, leading to a higher-quality final component.
Key Technical Parameters
The effectiveness of a vacuum sintering furnace is defined by its ability to precisely control the environment. Several key parameters are critical.
Ultimate Pressure (Vacuum Level)
This measures how completely the air has been removed. An ultimate pressure of 2x10⁻³ Pa is a very high vacuum, indicating an extremely pure environment with minimal residual gas to interfere with the process.
Temperature Uniformity
A specification like ±5°C means the temperature is consistent across the entire heated zone. This uniformity is vital for ensuring the part sinters evenly, preventing warpage, internal stresses, and inconsistent density.
Maximum Temperature
Furnaces operate at temperatures from 1450°C to 2400°C. This wide range allows them to process a vast array of materials, from common steels to high-performance superalloys and refractory metals that require extreme heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vacuum vs. Other Furnace Types
While vacuum furnaces are powerful, they are not the only option. The choice depends on the material and the desired outcome.
Vacuum vs. Protective Atmosphere Furnaces
A protective atmosphere furnace, such as a box furnace, doesn't create a vacuum. Instead, it flushes the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to displace the oxygen.
This method is often less expensive and faster than pulling a hard vacuum. However, it cannot achieve the same level of purity, making vacuum furnaces superior for reactive metals (like titanium) or applications demanding the highest possible performance.
Sintering vs. Hot Pressing
A hot press furnace applies both high temperature and external mechanical pressure simultaneously.
This combination achieves higher densities than sintering alone, often approaching 100% of the theoretical maximum. It is used for applications where maximum density and mechanical properties are non-negotiable, though it is typically a more complex and costly process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process is a balance of material requirements, cost, and final part specifications.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance: A vacuum furnace is the superior choice, especially for reactive metals or mission-critical components where any contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: A protective atmosphere furnace can be a suitable alternative for less sensitive materials where good, but not perfect, properties are sufficient.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum possible density: A hot press furnace should be considered, as the application of external pressure provides a level of densification that sintering alone cannot match.
Understanding these fundamental principles allows you to select the precise thermal process that aligns with your material, budget, and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Powder Metallurgy |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sinters compacted metal powders into solid, dense parts |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, ensures clean bonding, purifies materials |
| Critical Parameters | Ultimate pressure (e.g., 2x10⁻³ Pa), temperature uniformity (±5°C), max temperature (1450°C-2400°C) |
| Comparison | Superior purity vs. protective atmosphere; less dense vs. hot pressing |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Powder Metallurgy Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're working with reactive metals or need high-purity sintering, our vacuum furnaces deliver contamination-free environments for superior part density and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and enhance your material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery
- What processing conditions does a vacuum furnace provide for TiCp/Fe microspheres? Sintering at 900 °C
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary in copper slag impoverishment? Maximize Your Matte Separation Efficiency



















