In the building materials industry, rotary tube furnaces are the critical technology used for the high-temperature chemical transformation of raw materials into stable, intermediate products. Their primary roles are producing cement clinkers—the core component of Portland cement—and burning gypsum to create plaster. They accomplish this by continuously processing large volumes of material with highly uniform and controlled heat.
The core challenge in producing building materials is achieving consistent chemical and physical properties across immense quantities of product. Rotary tube furnaces solve this by combining continuous material flow with precise, uniform heating, ensuring every particle undergoes the necessary transformation at an industrial scale.

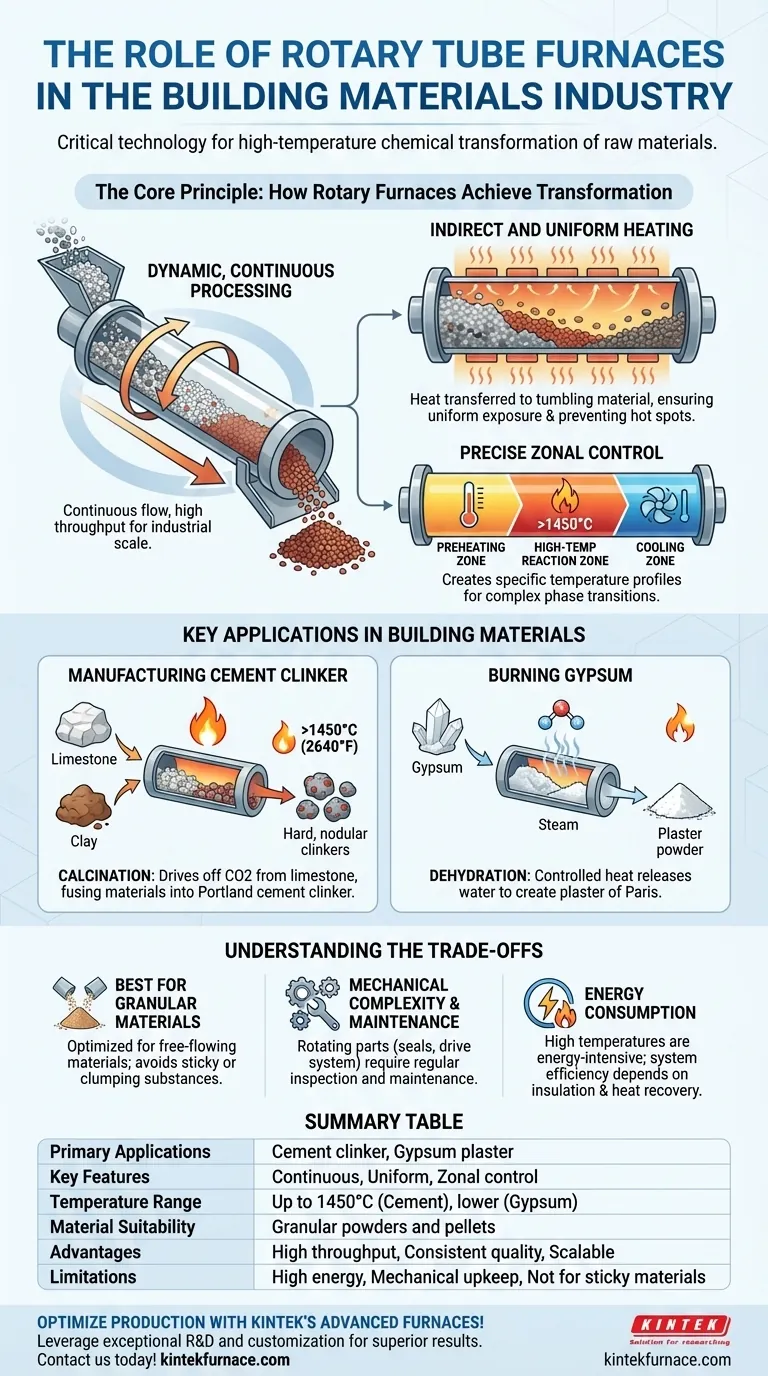
The Core Principle: How Rotary Furnaces Achieve Transformation
To understand the role of these furnaces, you must first understand their fundamental design. They are not simply ovens; they are dynamic processing systems engineered for specific outcomes.
Dynamic, Continuous Processing
A rotary tube furnace consists of a long, cylindrical tube that is slightly inclined and rotates slowly along its axis. Raw material is continuously fed into the higher end and, due to the rotation and incline, gradually tumbles its way to the lower end where it is discharged.
This continuous movement is the key to their high throughput, making them ideal for the massive scale required by the building materials industry.
Indirect and Uniform Heating
The furnace operates on an indirect firing principle. The rotating tube is housed within a larger, static heating chamber. Heating elements or burners heat the outside of the tube, and that heat is transferred to the material tumbling inside.
The constant rotation ensures every particle is lifted and showered through the hot atmosphere of the tube, guaranteeing exceptionally uniform heat exposure. This prevents hot spots and ensures the chemical reactions proceed evenly throughout the entire batch.
Precise Zonal Control
Industrial rotary furnaces are often designed with multiple thermal control zones along the length of the tube. This allows engineers to create a precise temperature profile for the material as it travels.
A typical profile might involve a preheating zone, a high-temperature reaction (or "calcination") zone, and a cooling zone. This level of control is essential for complex chemical phase transitions that define the final properties of the material.
Key Applications in Building Materials
The unique capabilities of rotary furnaces make them indispensable for two foundational processes in the industry.
Manufacturing Cement Clinker
Cement clinker is the primary component of modern Portland cement. It is formed by heating a homogenous mixture of limestone and clay to temperatures exceeding 1450°C (2640°F).
In this process, the rotary furnace performs calcination, driving off carbon dioxide from the limestone and fusing the remaining materials into new compounds. The uniform, extreme heat ensures this complex chemical reaction is complete, producing the hard, nodular clinkers that are later ground into cement powder.
Burning Gypsum
When gypsum rock is heated, it undergoes dehydration, releasing water molecules to become calcium sulfate hemihydrate—commonly known as plaster of Paris.
A rotary furnace provides the controlled, consistent heat required for this process, typically at much lower temperatures than cement production. The precise temperature control prevents "dead-burning" the gypsum, which would render it unusable as a plaster.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary tube furnaces are a specialized solution with specific limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Best Suited for Granular Materials
The design is optimized for processing powders, pellets, and other free-flowing granular materials. Materials that are sticky, have a low melting point, or could agglomerate into large clumps can cause significant operational problems.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating nature of the furnace introduces mechanical complexity. The seals at either end of the tube and the drive system that turns the cylinder are points of wear that require regular inspection and maintenance to prevent heat loss and ensure reliability.
Energy Consumption
Heating a large, rotating metal tube to very high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. While heat transfer to the material is highly efficient, overall system efficiency depends on insulation, seal integrity, and heat recovery systems, which add to the capital cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material, production volume, and desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of materials like cement clinker or iron ore pellets: A rotary tube furnace is the industry-standard solution, offering unmatched throughput and product consistency.
- If your primary focus is lower-temperature dehydration of powders like gypsum: The continuous processing and uniform heating of a rotary furnace provide superior efficiency and quality control over static batch methods at scale.
- If your primary focus is R&D, small-batch processing, or handling materials sensitive to mechanical agitation: A static box or tube furnace may be a more appropriate choice, as it eliminates the mechanical complexity and potential for dust generation.
Ultimately, the strength of the rotary tube furnace lies in its ability to impose precise thermal control on a continuously moving stream of material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Applications | Cement clinker production, Gypsum burning for plaster |
| Key Features | Continuous processing, Uniform heating, Zonal temperature control |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1450°C for cement, lower for gypsum |
| Material Suitability | Best for granular materials like powders and pellets |
| Advantages | High throughput, Consistent product quality, Industrial scalability |
| Limitations | High energy consumption, Mechanical complexity, Not for sticky materials |
Optimize your building materials production with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions tailored for cement, gypsum, and more. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















