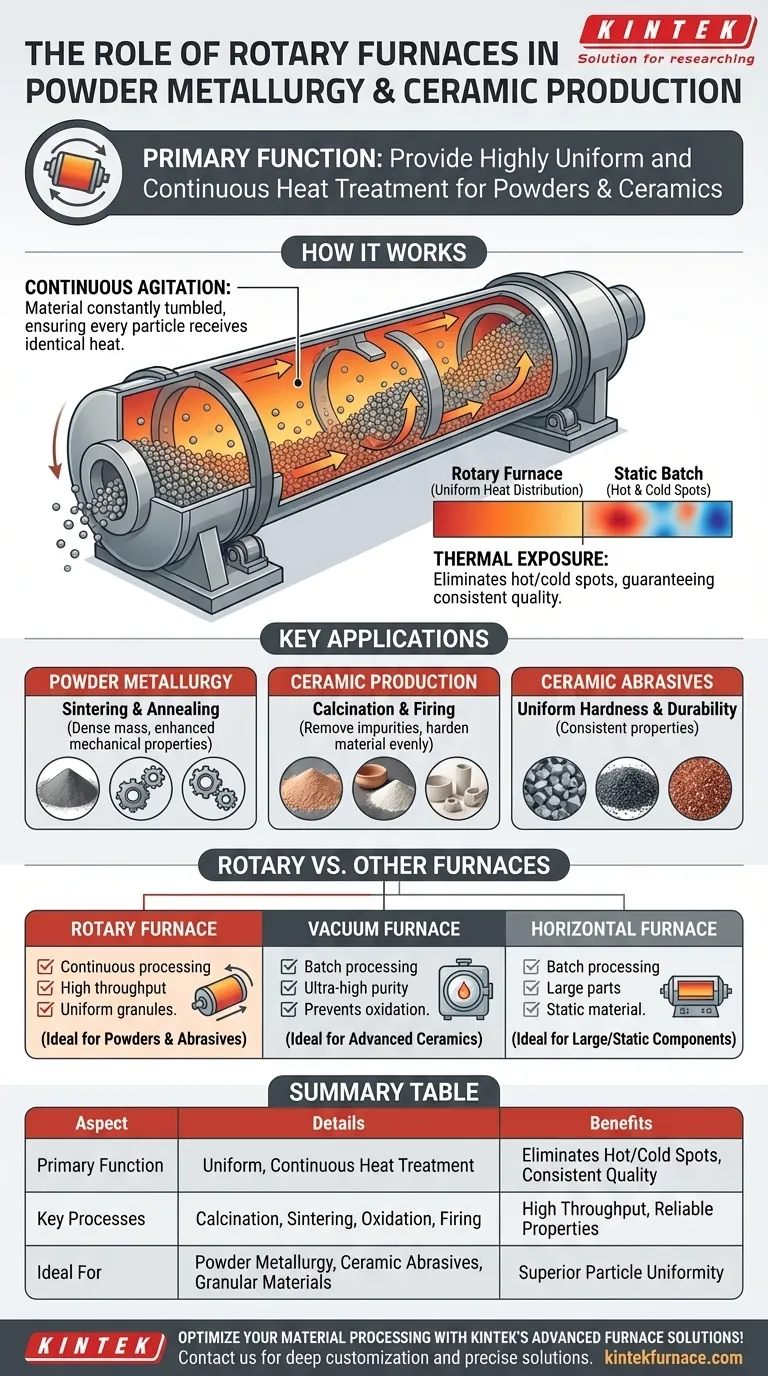
In powder metallurgy and ceramic production, rotary furnaces serve the critical function of providing highly uniform and continuous heat treatment. This capability is essential for processes like calcination, sintering, and oxidation, where consistent thermal exposure across all material is necessary to produce high-quality powders and abrasives with predictable, reliable properties.
The core value of a rotary furnace lies in its continuous motion. By constantly tumbling the material, it ensures every particle receives identical heat treatment, eliminating inconsistencies and guaranteeing uniform product quality in high-throughput environments.

How Rotary Furnaces Achieve Unmatched Uniformity
The design of a rotary furnace is purpose-built to solve the challenge of inconsistent heating common in static batch processes. Its effectiveness comes from a simple but powerful mechanical principle.
The Principle of Continuous Agitation
A rotary furnace consists of a slowly rotating cylindrical drum. As it turns, internal fixtures, often called flipping plates or lifters, continuously scoop material from the bottom and allow it to cascade through the heated atmosphere inside.
This constant lifting and tumbling ensures that no single part of the material batch is over- or under-heated. Every particle is exposed to the heat source—the drum wall itself—in a repetitive and predictable cycle.
Ensuring Consistent Thermal Exposure
This continuous movement prevents the formation of hot and cold spots within the material bed. The result is an exceptionally uniform thermal profile throughout the entire batch, which is critical for achieving consistent final properties like density, purity, and hardness.
Controlled Processing Environments
Modern rotary furnaces allow for precise control over the internal atmosphere. This enables processes like sintering or firing to occur without the risk of unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, that could compromise the material's purity and structural integrity.
Key Applications in Material Processing
The unique heating method of rotary furnaces makes them indispensable for several key industrial processes where particle or powder consistency is paramount.
Powder Metallurgy
In powder metallurgy, rotary furnaces are used for processes like sintering and annealing metal powders. Uniform heating helps consolidate the powders into a dense mass with enhanced mechanical properties without fully melting them, a crucial step in forming high-performance alloys and metal products.
Ceramic Production: Calcination and Firing
Calcination is a thermal treatment process used to remove impurities and volatile substances from raw materials. The uniform heating of a rotary furnace ensures this purification is complete and even, which is foundational for creating high-purity ceramics. It is also used for firing, where the consistent temperature hardens the material evenly.
Manufacturing Ceramic Abrasives
Producing high-quality ceramic abrasives demands exceptionally consistent material properties. The uniform heat treatment from a rotary furnace ensures that every abrasive grain achieves the same level of hardness and durability, leading to a more reliable and effective final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Other Furnaces
While powerful, a rotary furnace is not the universal solution for all thermal processing. The optimal choice depends entirely on the material, the process, and the desired outcome.
Rotary vs. Vacuum Furnaces
A rotary furnace is ideal for continuous, high-throughput processing where uniformity in granular material is the primary goal.
A vacuum furnace, by contrast, is a batch-process tool. It excels at producing dense, ultra-high-purity materials by preventing any atmospheric contamination. It is essential for sintering advanced ceramics like silicon carbide (SiC) or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) to near-theoretical density for extreme applications.
Rotary vs. Horizontal Furnaces
Rotary furnaces are superior for processing powders, granules, and other free-flowing materials that benefit from agitation.
Horizontal or other stationary batch furnaces are often more practical and cost-effective for processing large, solid components or when dealing with materials that cannot be tumbled. They can be engineered for high-volume throughput but do not offer the inherent particle-level uniformity of a rotary system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The trade-offs between continuous processing, batch purity, and material form factor are the central considerations.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production of consistent powders or abrasives: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice for its unparalleled heating uniformity and continuous operation.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure, high-density advanced ceramics: A vacuum furnace is required to achieve the necessary atmospheric control and material integrity.
- If your primary focus is processing large, static parts or specific batch volumes: A stationary batch furnace often provides a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's core strengths with your specific material requirements is the key to achieving optimal results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides uniform, continuous heat treatment for powders and ceramics |
| Key Processes | Calcination, sintering, oxidation, firing |
| Benefits | Eliminates hot/cold spots, ensures consistent particle exposure, high throughput |
| Ideal For | Powder metallurgy, ceramic abrasives, granular materials |
| Comparison | Superior for powders vs. static furnaces; batch vacuum for high purity |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your powder metallurgy and ceramic production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















