Beyond lithium processing, indirect rotary kilns are exceptionally versatile for the thermal treatment of a wide range of materials where product purity and atmospheric control are critical. Their unique design makes them suitable for processes involving high-value materials such as rare earth elements, catalysts, and various metal oxides, as well as for specific environmental applications like pyrolysis.
The decision to use an indirect rotary kiln is driven less by the specific material and more by the process requirements. They are the ideal solution when you must prevent contact between your material and combustion gases, require a specific inert or reactive atmosphere, or need exceptionally precise temperature control.
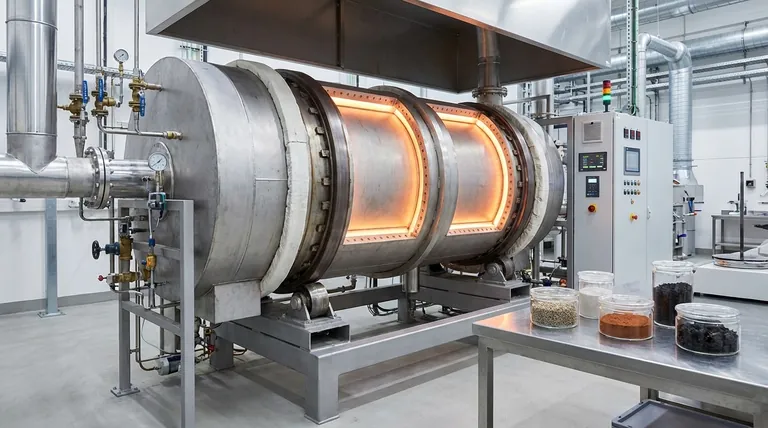

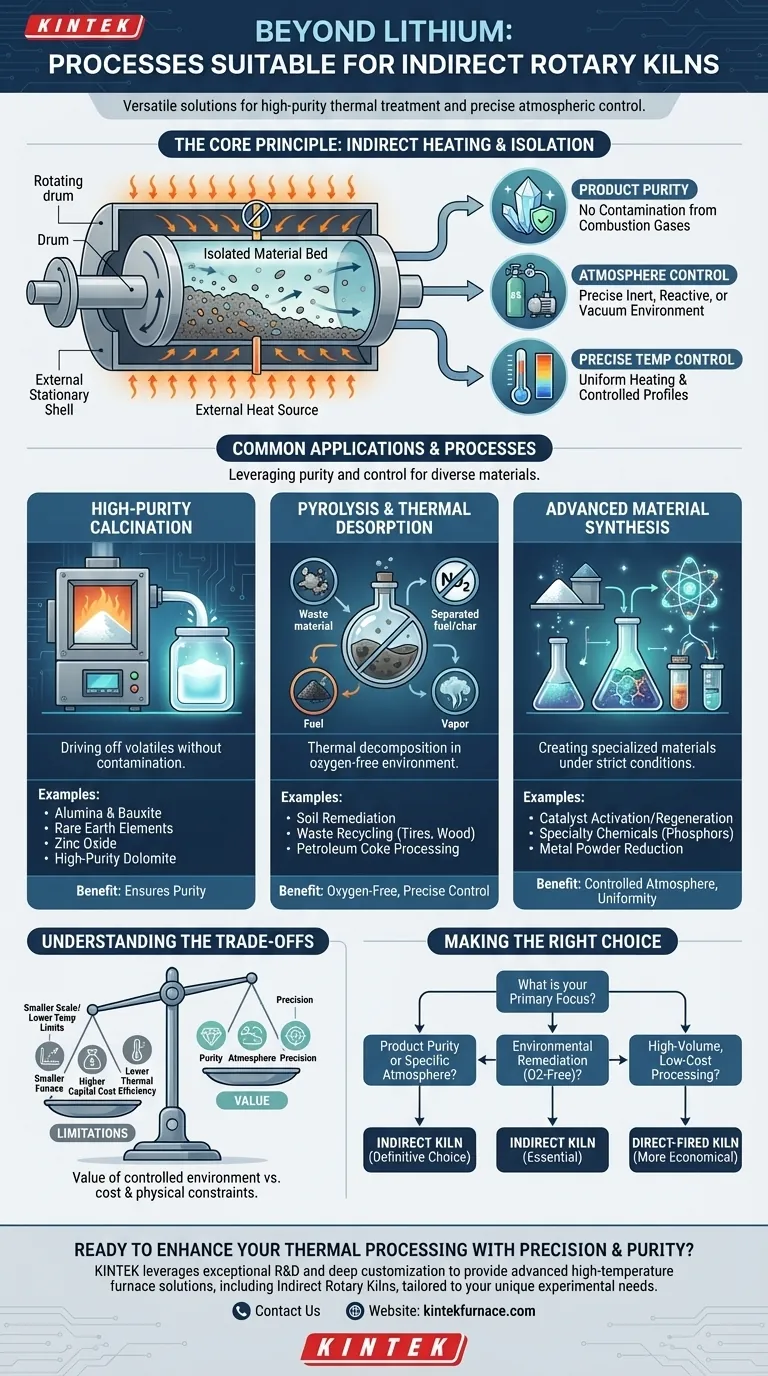
The Core Principle: When to Choose an Indirect Kiln
The fundamental difference between a direct and an indirect kiln is how heat is applied. In an indirect kiln, the rotating drum is heated from the outside, transferring energy through the shell wall to the material inside. This design creates a completely isolated internal environment.
To Avoid Product Contamination
The most common reason to select an indirect kiln is to maintain product purity. Because the material never comes into contact with the flame or flue gases from the heat source, there is no risk of contamination from combustion byproducts like sulfur or ash.
This is critical for high-value materials like catalysts, phosphors, titanates, and certain chemical compounds where even trace impurities can ruin the final product.
To Control the Process Atmosphere
The isolated chamber of an indirect kiln allows you to precisely control the internal atmosphere. You can operate under a vacuum, introduce an inert gas like nitrogen to prevent oxidation, or use a reactive gas for specific chemical processes.
This capability is essential for pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen), certain types of mineral roasting, and the activation of sensitive catalysts.
To Achieve Precise Temperature Control
Heating the shell externally provides highly uniform and controlled heat transfer to the material bed. This prevents localized hot spots and allows for very precise temperature profiles along the length of the kiln.
This level of control is necessary for materials with narrow processing windows or for heat-setting applications where consistent properties are paramount.
Common Applications and Processes
Based on these principles, indirect kilns excel in several key areas beyond lithium processing.
High-Purity Calcination
Calcination is the process of heating a solid to a high temperature to drive off volatile components, such as water or carbon dioxide. Using an indirect kiln ensures the resulting calcined product, like soda ash or magnesite, is free from combustion contaminants.
This method is frequently used for:
- Alumina and Bauxite
- Phosphate and Rare Earth Elements
- Dolomite and Limestone (for high-purity applications)
- Zinc Oxide
Pyrolysis and Thermal Desorption
These processes require an oxygen-free environment, making indirect kilns the only viable continuous option. Pyrolysis is used to thermally decompose organic materials, while thermal desorption is used to vaporize contaminants from a solid matrix.
Key applications include:
- Soil Remediation: Removing contaminants like petroleum hydrocarbons from soil.
- Waste Recycling: Converting waste wood, scrap tires, or sewage sludge into fuel or char.
- Petroleum Coke Processing: Removing residual volatiles to create a purer carbon product.
Advanced Material Synthesis
The production of many advanced materials requires clean processing environments and specific atmospheric conditions that only an indirect kiln can provide.
This includes the synthesis and activation of:
- Catalysts: Activating or regenerating catalysts without poisoning them.
- Specialty Chemicals: Producing high-purity titanates, phosphors, and ferrites.
- Metal Powders: Reducing metal oxides to pure metal powders in a controlled atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, indirect kilns are not the universal solution. Their design comes with specific limitations you must consider.
Limitations on Scale and Temperature
The need to heat the kiln shell externally creates immense mechanical stress on the metal at high temperatures. This practical constraint means indirect kilns generally have a smaller diameter and a lower maximum operating temperature than their direct-fired counterparts.
Higher Capital Cost
The external furnace, specialized seals, and often the need for high-temperature alloy shells make indirect kilns more expensive to build than direct-fired kilns of a similar capacity.
Thermal Efficiency
Transferring heat through a thick metal shell is inherently less efficient than passing hot gas directly through and over the material bed. While design features can improve efficiency, indirect kilns may have higher energy consumption for a given throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct kiln technology requires matching your process needs to the fundamental strengths of the equipment.
- If your primary focus is product purity or requires a specific atmosphere: An indirect kiln is the definitive choice for materials like catalysts, specialty chemicals, or for processes like pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost processing: A direct-fired kiln is likely more economical for robust materials like cement, limestone, or lightweight aggregate where direct contact with flue gas is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation: An indirect kiln is essential for oxygen-free processes like thermal desorption of soil or the pyrolysis of waste materials.
Ultimately, the choice hinges on whether the value of a controlled, contamination-free environment outweighs the higher cost and physical limitations of the indirect design.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Calcination | Alumina, Rare Earth Elements, Zinc Oxide | Avoids contamination, ensures purity |
| Pyrolysis and Thermal Desorption | Soil remediation, waste recycling, petroleum coke | Oxygen-free environment, precise control |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Catalysts, specialty chemicals, metal powders | Controlled atmosphere, uniform heating |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with precision and purity? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including indirect rotary kilns. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're working with catalysts, rare earth elements, or environmental applications, we deliver tailored solutions for contamination-free, controlled-atmosphere processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- Why are inert atmosphere furnaces important for graphite and carbon products? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure High-Performance Results
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















