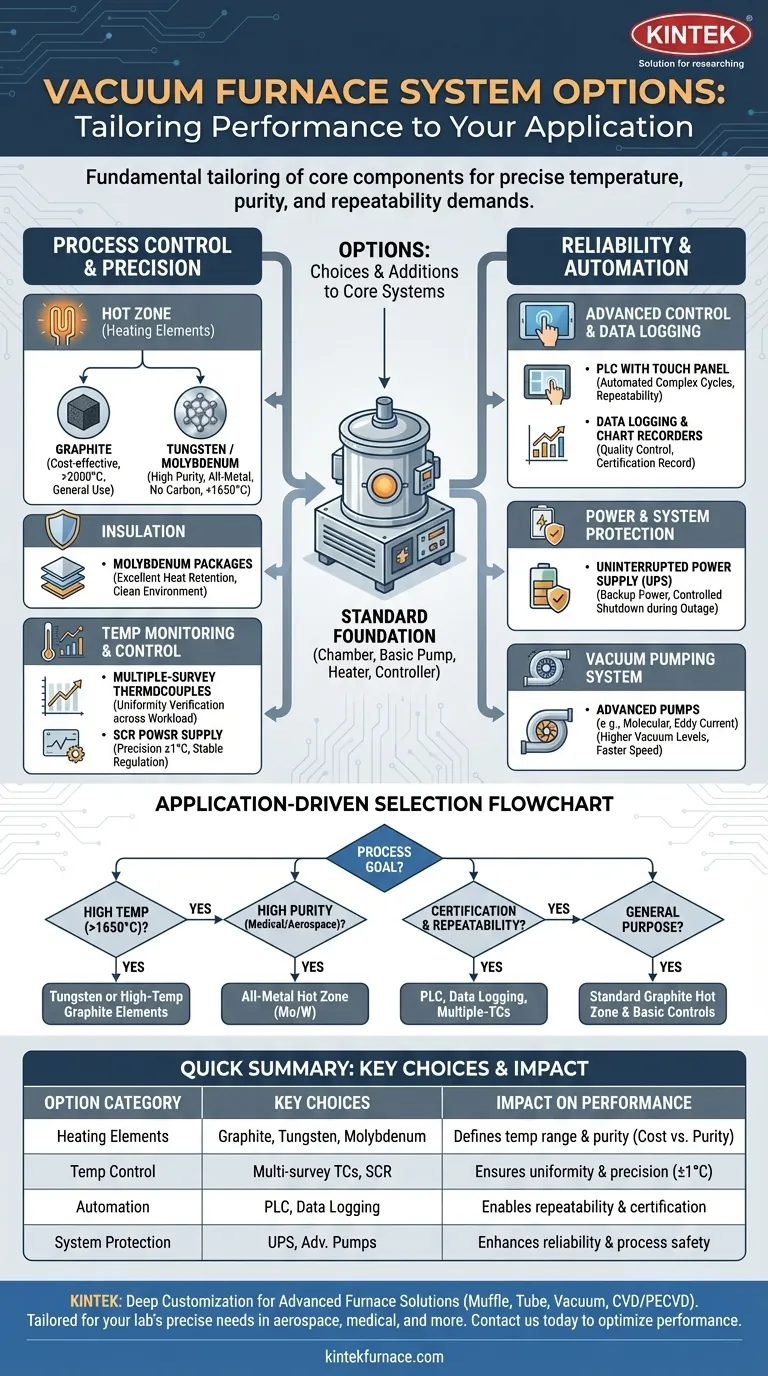
A vacuum furnace's capabilities are defined by a range of available options that enhance its core functions. These include choices for the heating elements, such as graphite or tungsten, advanced temperature monitoring with multiple-survey thermocouples, and system safeguards like an Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS). You can also specify molybdenum insulation, advanced PLC-based controls for programming, and various data recording methods.
Choosing the right options for a vacuum furnace is not about adding accessories; it's about fundamentally tailoring the system's core components—the hot zone, the controls, and the vacuum pumps—to meet the precise temperature, purity, and repeatability demands of your specific application.

Deconstructing the Vacuum Furnace: Core vs. Option
To understand the options, you must first understand the baseline system they modify. Every vacuum furnace is built around a few essential, non-negotiable systems.
The Standard Furnace Foundation
A standard system includes an airtight furnace chamber, a basic vacuum pumping system to remove atmosphere, an electric heating element, and a temperature controller. These core components are what make it a vacuum furnace.
Where "Options" Come Into Play
Options are choices you make within these core systems or additions you make to them. For example, every furnace has a heating element, but the material of that element (graphite, molybdenum, tungsten) is a critical option that dictates performance.
Key Options for Process Control and Precision
These options directly impact the quality, consistency, and temperature capabilities of your heat-treating process.
Heating Elements and Hot Zone
The choice of heating element and insulation (the "hot zone") is the most important decision, as it defines the furnace's operating temperature and chemical environment.
- Graphite Elements: A common, cost-effective choice suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications. They offer excellent high-temperature performance, often exceeding 2000°C.
- Tungsten or Molybdenum Elements: These all-metal hot zones are chosen for processes requiring high purity and no carbon contamination. Molybdenum is typically used for temperatures up to 1650°C, while tungsten is used for even higher temperatures.
Insulation Packages
Proper insulation ensures temperature uniformity and energy efficiency. An option like molybdenum insulation within a stainless steel containment structure provides excellent heat retention and a clean environment, complementing an all-metal hot zone.
Temperature Monitoring and Control
Standard systems often include a single thermocouple to measure temperature.
- Multiple-Survey Thermocouples: This option places several thermocouples throughout the chamber. It is essential for verifying temperature uniformity across the entire workload, a common requirement for aerospace or medical device certification.
- Advanced Power Regulation: An SCR Power Supply provides highly stable and precise power regulation to the heating elements, enabling tight temperature control, often to within +/- 1 degree.
Options for System Reliability and Automation
These features enhance ease of use, protect your investment, and ensure process data is captured accurately.
Advanced Control and Data Logging
While a basic controller can run a simple cycle, advanced systems offer complete automation.
- PLC Control with Touch Panel: A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) allows you to program, save, and automatically execute complex cycles with multiple ramps, soaks, and gas backfills.
- Data Logging & Chart Recorders: This feature provides a complete digital or physical record of the process parameters (temperature, vacuum level, time). It is critical for quality control, troubleshooting, and process certification.
Power and System Protection
External events can ruin a multi-hour furnace run.
- Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS): A UPS provides backup power to the furnace controls and critical systems during a power outage, allowing for a controlled shutdown or the ability to ride through a brief interruption, saving the workload.
The Vacuum Pumping System
The standard vacuum system includes a mechanical pump. However, the type and combination of pumps is a crucial option that determines the ultimate vacuum level. Upgrades can include molecular pumps or eddy current pumps to achieve higher vacuum levels faster.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting options always involves balancing cost against capability. There is no single "best" configuration.
Graphite vs. All-Metal Hot Zones
Graphite is robust and less expensive, making it ideal for general heat treating. However, it can be a source of carbon, which is unacceptable for certain sensitive alloys or medical implants. All-metal zones are clean but more expensive and can be more fragile.
Basic Controls vs. Full Automation
A simple controller is easy to use and maintain. A fully automated PLC system offers perfect repeatability and data logging for certification but comes with a higher initial cost and greater complexity.
Temperature Capability vs. Cost
Achieving higher temperatures (above 1650°C) requires more expensive materials for heating elements and insulation, like tungsten. Carefully assess the maximum temperature your process truly requires to avoid over-specifying the furnace and incurring unnecessary cost.
Selecting the Right Options for Your Application
Your choice of options should be driven entirely by your process goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1650°C): You must specify tungsten or high-temperature graphite heating elements and appropriate high-grade insulation.
- If your primary focus is high purity for medical or aerospace parts: An all-metal hot zone (molybdenum or tungsten) is non-negotiable to prevent carbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is process certification and repeatability: A PLC-based control system with full data logging and multiple-survey thermocouples is essential for proving your process meets specifications.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose tool steel heat treating: A standard furnace with a graphite hot zone and basic programmable controls is often the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
By understanding how these options align with your goals, you can configure a vacuum furnace that is a precise and powerful tool for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Option Category | Key Choices | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Graphite, Tungsten, Molybdenum | Defines temperature range and purity; graphite for cost-effectiveness, metal for high purity |
| Temperature Control | Multiple-survey thermocouples, SCR power supply | Ensures uniformity and precision (±1°C) |
| Insulation | Molybdenum packages | Improves heat retention and energy efficiency |
| Automation | PLC controls, data logging | Enables repeatability and certification compliance |
| System Protection | UPS, advanced vacuum pumps | Enhances reliability and process safety |
Ready to configure a vacuum furnace that meets your exact needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace is tailored for precise temperature control, purity, and repeatability in applications like aerospace, medical devices, or general heat treating. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















