At its core, implementing an inert atmosphere involves one of two primary strategies: purging or displacement. The goal is to systematically remove reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor from a contained space and replace them with a non-reactive gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon. Techniques range from simple gas bubbling in a flask to sophisticated, sealed vacuum systems used in industrial manufacturing.
The choice of method is not about finding the "best" one, but about making a strategic trade-off. You must balance the required level of atmospheric purity against the operational cost, scale, and critical safety considerations of your specific application.

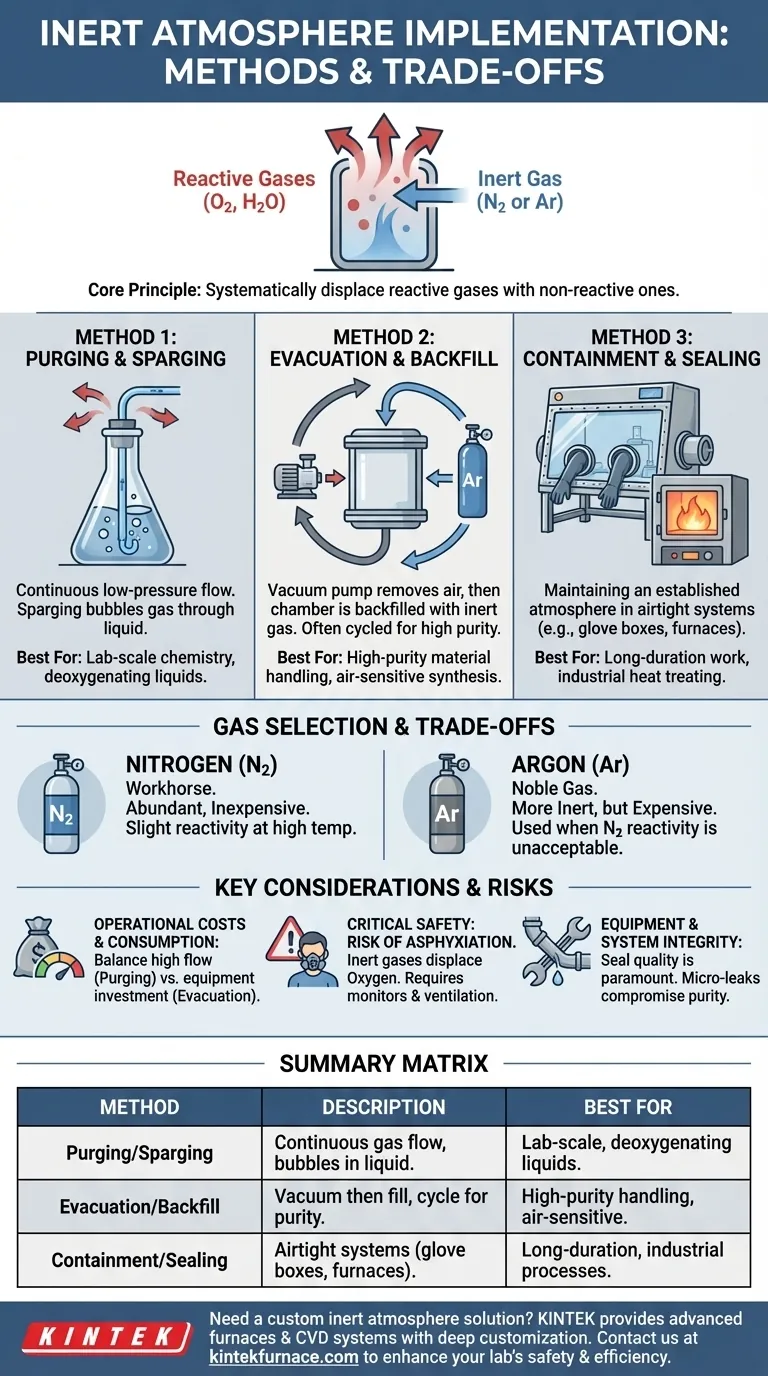
The Core Principle: Displacing Reactive Gases
An inert atmosphere is essential for any process where the components would be damaged by reacting with ambient air. The entire strategy hinges on reducing the concentration of these reactive gases to an acceptable minimum.
Why Oxygen and Water are the Enemy
For most applications, oxygen is the primary adversary. It is highly reactive and readily causes oxidation (like rust on iron or degradation of sensitive chemicals), which can compromise the integrity, purity, and performance of materials.
Water vapor is another common culprit, capable of participating in unwanted hydration reactions or acting as a catalyst for other forms of degradation.
Choosing Your Inert Gas
Nitrogen (N₂) is the workhorse of inerting applications. It is relatively non-reactive for most purposes and is abundant and inexpensive to produce.
Argon (Ar) is used when even the slight reactivity of nitrogen at high temperatures (forming nitrides) is unacceptable. It is a noble gas and therefore more inert than nitrogen, but it is also significantly more expensive.
Key Implementation Methods
The specific technique used depends heavily on the scale of the operation and the level of purity required.
Method 1: Purging and Sparging
This method involves creating a continuous, low-pressure flow of inert gas into a vessel. This steady flow displaces the ambient air, gradually lowering the oxygen concentration.
Sparging is a specific form of purging used for liquids. The inert gas is bubbled directly through the solution, which efficiently removes dissolved oxygen. This is common in electrochemistry and lab-scale chemical synthesis.
Method 2: Evacuation and Backfill
This is a more rigorous method for achieving high purity. The process involves using a vacuum pump to remove nearly all of the air from a sealed chamber.
Once a sufficient vacuum is achieved, the chamber is backfilled with high-purity inert gas. For extremely sensitive applications, this "pump-and-purge" cycle may be repeated several times to reduce reactive gas concentrations to parts-per-million (ppm) levels.
Method 3: Containment and Sealing
This is not a method of creating an inert atmosphere, but of maintaining one. Systems like glove boxes or sealed industrial furnaces are designed to be airtight.
Once an inert atmosphere is established inside (using purging or evacuation), the sealed integrity of the container prevents ambient air from leaking back in. This is critical for long-duration work or continuous industrial processes like heat treating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Implementing an inert atmosphere introduces new operational complexities and hazards that must be managed carefully.
Operational Costs and Gas Consumption
Continuous purging can be costly due to the high volume of gas consumed. Evacuation-and-backfill methods use less gas per cycle but require investment in vacuum pumps and robust, vacuum-rated chambers. The price difference between nitrogen and argon is also a major budgetary factor.
Critical Safety: The Risk of Asphyxiation
This is the most significant hazard. Inert gases displace oxygen. In a poorly ventilated area, a leak can quickly create an oxygen-deficient environment, leading to asphyxiation without warning, as the body does not sense the lack of oxygen. Personal oxygen monitors and proper ventilation are non-negotiable safety requirements.
Equipment and System Integrity
The effectiveness of any inerting process depends on the quality of the seals in the system. Even a microscopic leak can continuously introduce oxygen, compromising the entire process. This necessitates specialized equipment, leak-tight fittings, and regular system validation.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Choose your method based on your primary goal and the constraints of your process.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale chemistry or deoxygenating liquids: Simple purging or sparging with nitrogen directly into the flask is often sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material handling or air-sensitive synthesis: An evacuation-and-backfill system, often within a sealed glove box, is the industry standard for maximum purity.
- If your primary focus is a large-scale industrial process like heat treating: A sealed furnace using a continuous, low-flow purge of nitrogen strikes the best balance between cost, scale, and effectiveness.
Understanding these fundamental methods empowers you to create and maintain the precise atmospheric control your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Method | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Purging and Sparging | Continuous gas flow to displace air; sparging bubbles gas through liquids | Lab-scale chemistry, deoxygenating liquids |
| Evacuation and Backfill | Vacuum removal of air followed by inert gas fill for high purity | High-purity material handling, air-sensitive synthesis |
| Containment and Sealing | Airtight systems like glove boxes to maintain inert atmospheres | Long-duration work, industrial processes like heat treating |
Need a custom inert atmosphere solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What technological features enhance the efficiency of vacuum furnaces? Boost Performance with Advanced Control & Energy Savings
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















