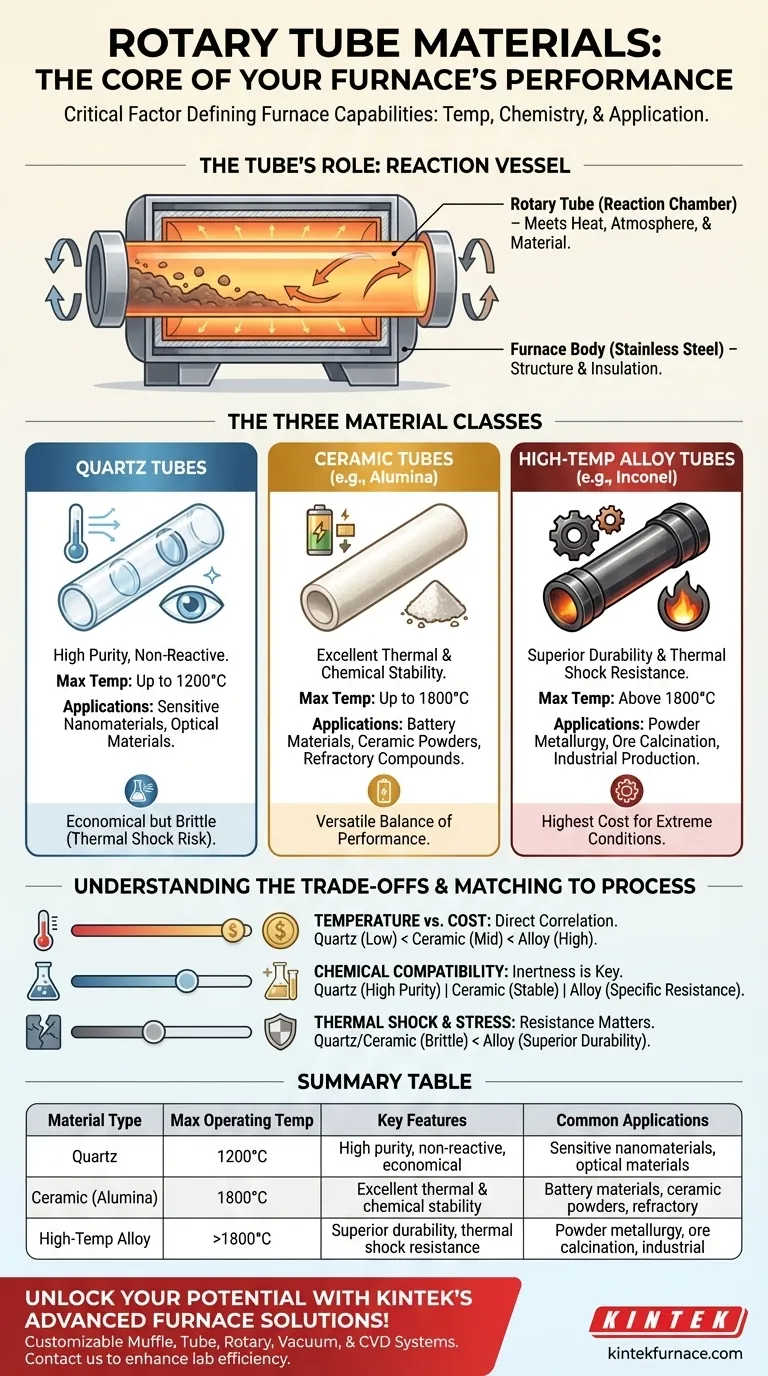
At its core, a rotary tube's material composition is determined by the extreme conditions it must endure. The component is most commonly made from one of three material classes: quartz, ceramic, or a high-temperature alloy. The specific choice is dictated by the required operating temperature and the chemical nature of the materials being processed.
The selection of the rotary tube's material is the single most critical factor defining the furnace's capabilities. This choice directly governs the maximum processing temperature, chemical compatibility, and ultimately, which applications the furnace is suitable for.

The Role of the Tube in Furnace Design
The rotary tube is not merely a container; it is the heart of the furnace's reaction chamber. Understanding its function is key to appreciating why its material is so critical.
The Central Reaction Vessel
A rotary tube furnace is designed for continuous, uniform thermal treatment of powders and other granular materials. The tube itself rotates, tumbling the material within to ensure every particle is exposed to the controlled temperature and atmosphere.
This component is where the heat, process atmosphere, and raw materials all meet. Therefore, the tube must be able to withstand these conditions without degrading or contaminating the product.
Distinguishing the Tube from the Furnace Body
It is important to differentiate the rotary tube from the main furnace body. The outer casing is often constructed from double-walled stainless steel, which provides structural integrity, durability, and a housing for insulation.
The rotary tube, however, is a specialized, often interchangeable component that sits inside the furnace and is directly exposed to the process. Its material science is far more demanding than that of the outer shell.
A Breakdown of Rotary Tube Materials
Each material option offers a unique profile of thermal and chemical resistance, making it suitable for different applications.
Quartz Tubes
Quartz is a form of high-purity glass. It is an excellent choice when process purity is paramount and operating temperatures are moderate. It provides a clean, non-reactive environment for sensitive materials.
Ceramic Tubes
Ceramics, such as high-purity alumina, are a step up in temperature capability. They offer excellent thermal resistance and chemical stability at high temperatures, making them suitable for processing many ceramic powders, battery materials, and refractory compounds.
High-Temperature Alloy Tubes
For the most demanding applications involving extreme heat and mechanical stress, high-temperature alloys (like Inconel) are used. These metal tubes provide superior durability and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for heavy industrial processes like powder metallurgy and calcination of ores.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is a matter of balancing performance requirements with physical and economic constraints.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between a material's maximum operating temperature and its cost. Quartz is the most economical for lower-temperature work, while high-temperature alloys represent a significant investment for specialized, extreme-heat applications.
Chemical Compatibility
The tube material must be inert to the materials being processed. For example, processing highly reactive or corrosive substances requires a tube made of a very stable ceramic or a specific alloy to prevent unwanted chemical reactions and contamination.
Thermal Shock and Mechanical Stress
The constant rotation and intense heating and cooling cycles place significant stress on the tube. Materials like quartz and certain ceramics can be brittle and susceptible to cracking from rapid temperature changes (thermal shock), requiring carefully controlled process parameters. Metal alloys generally offer superior resistance to both thermal and mechanical shock.
Matching the Material to Your Process
Your specific application dictates the ideal tube material. Use the following guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is high purity at moderate temperatures: Quartz is the most effective and economical choice for applications like processing sensitive optical or nanomaterials.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-temperature processing: An alumina ceramic tube provides a versatile balance of thermal resistance and chemical stability for a wide range of materials, from battery cathodes to refractory powders.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production at extreme temperatures: A high-temperature alloy is necessary to ensure durability and reliability when processing materials like metal powders or ores under demanding conditions.
Ultimately, selecting the correct tube material is the foundational step toward achieving consistent, reliable, and successful thermal processing results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Max Operating Temp | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | High purity, non-reactive, economical | Sensitive nanomaterials, optical materials |
| Ceramic (e.g., Alumina) | Up to 1800°C | Excellent thermal and chemical stability | Battery materials, ceramic powders, refractory compounds |
| High-Temperature Alloy (e.g., Inconel) | Above 1800°C | Superior durability, thermal shock resistance | Powder metallurgy, calcination of ores, industrial production |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Don't let material limitations hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries



















