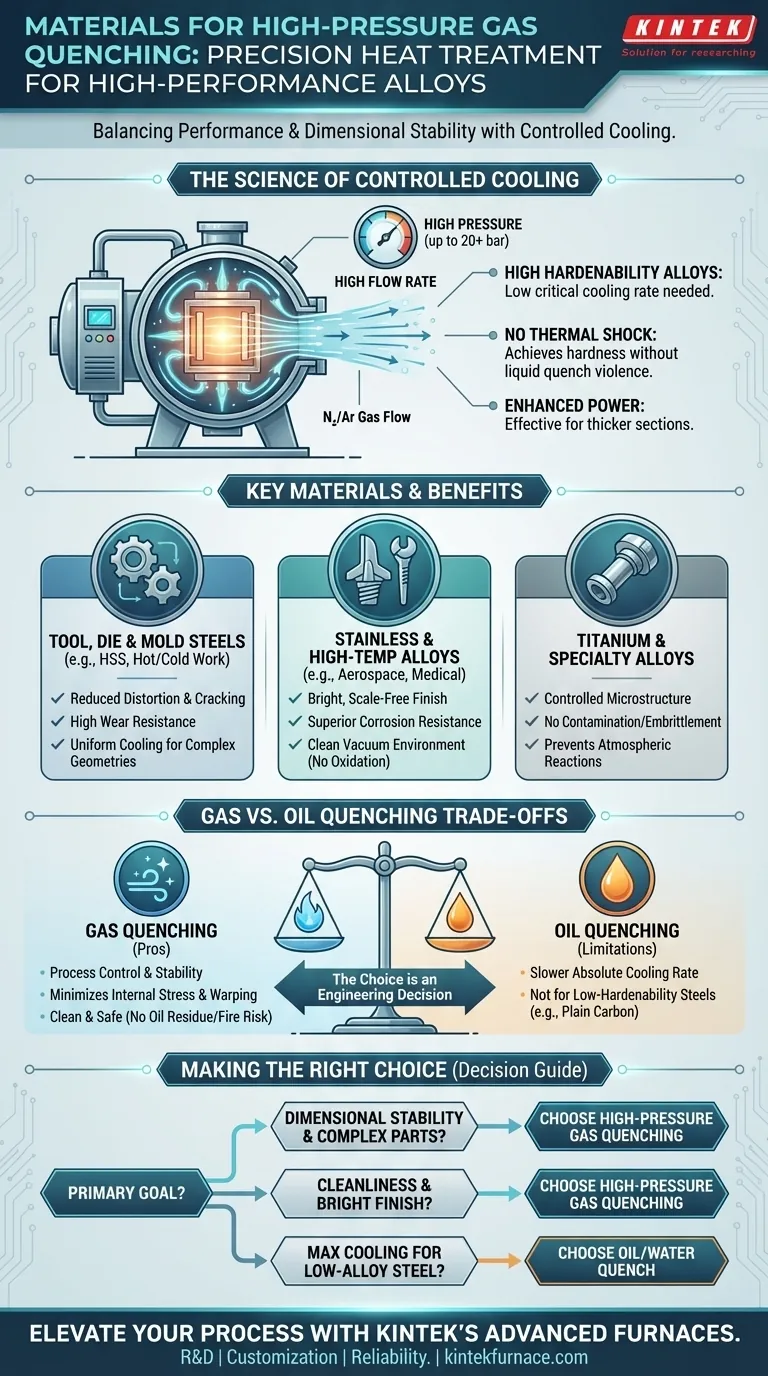
In short, this process is for high-performance alloys that demand precision. A high-pressure, high-flow rate gas quenching vacuum furnace is primarily used for the heat treatment of materials such as cold and hot work tool steels, high-speed steels, high-temperature alloys, stainless steels, and titanium alloys. It is also suitable for processing certain elastic alloys and magnetic materials that require specific properties achievable through controlled cooling.
The core principle is simple: this advanced quenching method is chosen for materials with sufficient hardenability. These alloys can achieve their required hardness without the extreme thermal shock of an oil or water quench, making gas quenching the ideal balance between performance and dimensional stability.

Why Gas Quenching is the Superior Choice for These Materials
The decision to use high-pressure gas quenching (HPGQ) is not arbitrary; it is driven by the fundamental metallurgical properties of the materials being treated. It's a method that prioritizes control and precision over sheer cooling speed.
The Principle of Hardenability
Hardenability is a measure of a material's ability to form a hardened structure (martensite) when cooled from a high temperature. It is not the same as maximum hardness.
Alloys like high-speed steel and high-chromium die steels are engineered with elements that increase their hardenability. This means they have a low critical cooling rate; they don't need to be cooled extremely fast to become hard.
Achieving Hardness Without the Shock
The goal of quenching is to cool the metal fast enough to prevent the formation of soft phases, forcing the microstructure to transform into hard martensite.
For high-hardenability steels, the rapid, high-flow stream of an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is more than fast enough to exceed this critical cooling rate. This achieves full hardness without the violent shock of a liquid quench.
The Role of High Pressure and High Flow
Early gas quenching was limited to only the highest-hardenability alloys. Modern furnaces use high pressures (up to 20 bar or more) and high-flow rates to dramatically increase the gas's cooling power.
This enhancement allows the process to effectively harden thicker sections and a wider range of alloy steels, bridging the gap between conventional gas quenching and the faster speeds of oil quenching.
A Closer Look at Key Material Categories
Different materials benefit from high-pressure gas quenching for specific reasons, but the common thread is the need for precise control over the final properties and dimensions.
Tool, Die, and Mold Steels
These materials, including high-speed steel and hot/cold work die steels, are the classic application. They must be extremely hard and wear-resistant.
Crucially, components like molds and dies have intricate, complex geometries. Gas quenching provides uniform cooling, which dramatically reduces distortion, warping, and the risk of cracking compared to an oil quench.
Stainless Steels and High-Temperature Alloys
Used in demanding aerospace, medical, and energy applications, these alloys require specific mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
The clean, inert atmosphere of a vacuum furnace prevents surface oxidation and contamination. Gas quenching maintains this cleanliness, resulting in a bright, scale-free finish that often eliminates the need for post-processing.
Titanium and Other Specialty Alloys
Titanium alloys are sensitive and reactive at high temperatures. The vacuum environment is essential to prevent embrittlement from atmospheric gases.
Gas quenching provides the controlled cooling necessary to achieve the desired microstructure and mechanical properties without introducing the contamination or distortion risks associated with liquid quenching.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gas vs. Oil Quenching
While powerful, high-pressure gas quenching is not a universal solution. The choice between gas and oil is a critical engineering decision based on clear trade-offs.
The Advantage of Gas: Process Control and Stability
The primary benefit of gas quenching is the minimization of internal stresses. By cooling the part more uniformly, it prevents the distortion and warping that often plague liquid-quenched components, reducing scrap rates and post-machining costs.
The Advantage of Gas: Cleanliness and Safety
Gas quenching is an environmentally clean and safe process. It eliminates oil residue, the need for costly and messy washing stations, and the significant fire hazard associated with hot oil baths.
The Limitation of Gas: Absolute Cooling Rate
Even at high pressures, gas is less dense than liquid and has a lower heat capacity. Therefore, its maximum cooling rate is still slower than that of oil.
This makes gas quenching unsuitable for materials with low hardenability, such as plain carbon steels or some low-alloy steels. These materials require the extreme cooling speed of oil or water to achieve full hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your material's composition and the component's end-use dictate the correct heat treatment path. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is hardening high-alloy steels, tool steels, or parts with complex geometries: High-pressure gas quenching is the superior choice to ensure dimensional stability and minimize the risk of cracking.
- If your primary focus is hardening low-alloy or plain carbon steels: An oil or water quench is almost always necessary to achieve the rapid cooling required for full martensitic transformation.
- If your primary focus is process cleanliness, safety, and a bright, scale-free finish: Gas quenching provides significant operational advantages and delivers a cleaner final product.
Ultimately, selecting the right quenching method is about matching the material's inherent properties with your final performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tool, Die, and Mold Steels | High-speed steel, Hot/cold work die steels | High hardness, Reduced distortion, Wear resistance |
| Stainless Steels and High-Temperature Alloys | Aerospace alloys, Medical-grade stainless | Corrosion resistance, Scale-free finish, Cleanliness |
| Titanium and Specialty Alloys | Titanium alloys, Elastic alloys | Controlled microstructure, No contamination, Dimensional stability |
Elevate your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your material processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















