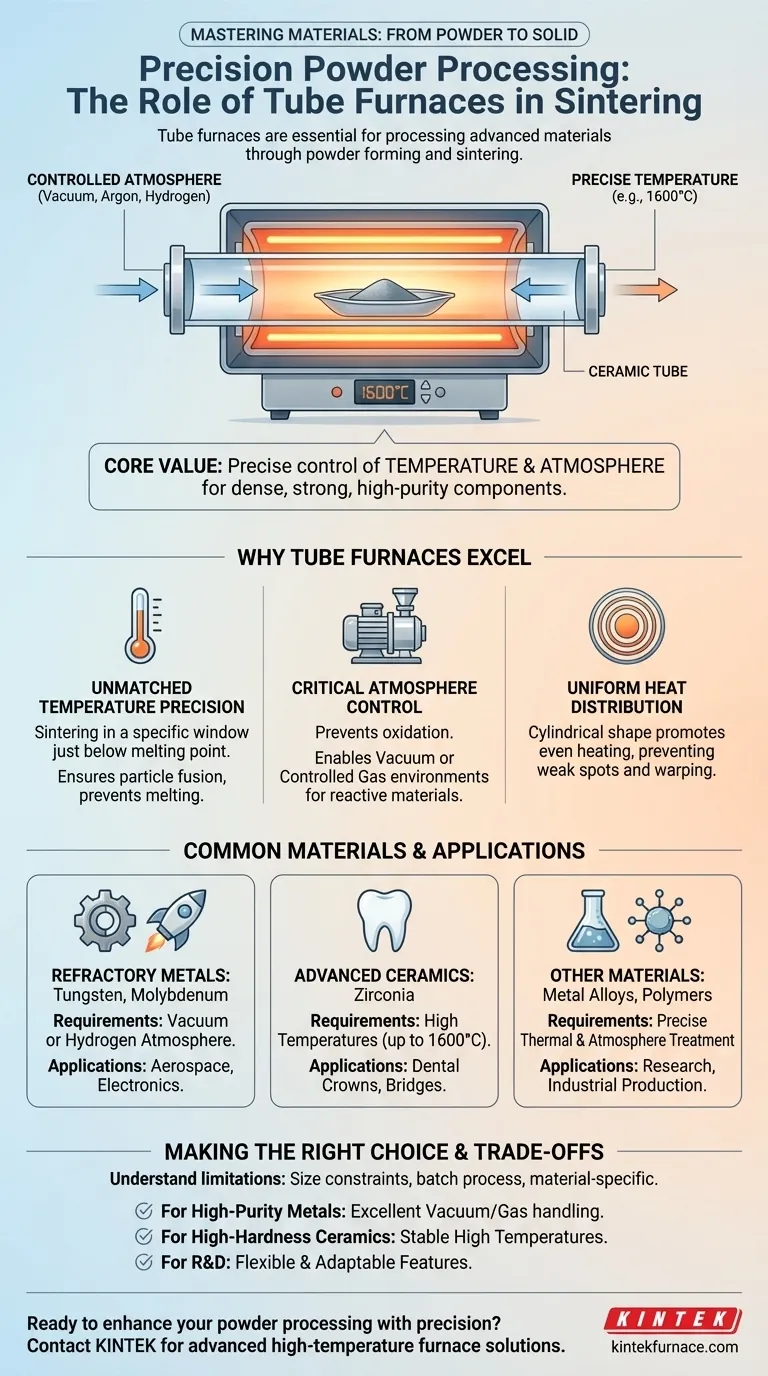
In short, tube furnaces are essential for processing a wide range of advanced materials through powder forming and sintering. They are commonly used for high-performance refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, advanced ceramics such as zirconia, and various other metal alloys and polymers where precise process control is critical.
The core value of a tube furnace for sintering lies in its ability to precisely control the two most important variables: temperature and atmosphere. This control is the key to transforming loose powder into a dense, strong, and high-purity final component.

Why Tube Furnaces Excel at Powder Processing
Sintering is a thermal process for compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat, without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Tube furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for this task due to their unique design.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
Sintering occurs within a very specific temperature window just below a material's melting point.
Precise temperature control ensures that powder particles fuse together to increase density and strength, rather than melting and losing their shape. Furnaces capable of reaching and holding temperatures as high as 1600°C are necessary for materials like dental zirconia to achieve their final hardness.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Many advanced materials, especially metals, will rapidly oxidize at high temperatures if exposed to air.
The enclosed, tubular design of these furnaces makes it easy to create a vacuum or introduce a specific controlled atmosphere (such as argon or hydrogen). This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, which is crucial when sintering reactive metals like tungsten and molybdenum.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The cylindrical shape of the heating chamber naturally promotes even heat distribution around the sample.
This uniformity is vital for ensuring the entire part sinters consistently, preventing weak spots, internal stresses, or warping that could result from uneven heating.
Common Materials and Their Applications
The combination of high heat and atmospheric control makes tube furnaces versatile for processing materials that are central to modern technology.
Refractory Metals: Tungsten & Molybdenum
These metals are defined by their extremely high melting points and are used in demanding, high-temperature applications.
During sintering, a vacuum or hydrogen atmosphere is essential to prevent them from becoming brittle due to oxidation. This process yields dense, strong components for industries like aerospace and electronics.
Advanced Ceramics: Zirconia
Zirconia is a prime example of a high-performance ceramic processed in tube furnaces, particularly for dental applications.
After a dental crown or bridge is milled from a block of zirconia, it is in a soft, porous state. The sintering process, often at temperatures up to 1600°C, dramatically increases its density, strength, and hardness to its final, durable form.
Other Metals, Alloys, and Polymers
The principles extend to a broad range of other materials. This includes hard alloys and specialty polymers that require precise thermal treatment to achieve their desired properties.
Whether for research or industrial production, the furnace's ability to create a repeatable, controlled environment ensures consistent results across different material types.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Size and Geometry Limitations
The primary constraint is the diameter of the tube. These furnaces are ideal for processing powders into rods, small components, or test samples that fit within the processing tube. They are not designed for very large or complex geometries.
Not a High-Speed Process
Sintering is inherently a time-consuming process. It involves carefully controlled temperature ramps for heating and cooling to avoid thermal shock and ensure uniform densification. It is a batch process, not a continuous, high-throughput method.
Material-Specific Requirements
You cannot use a one-size-fits-all approach. The required temperature profile and atmosphere are entirely dependent on the material being processed. Using the wrong parameters will result in a failed or low-quality part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material dictates your furnace requirements. The right choice depends on your specific application and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity refractory metals (like tungsten): A furnace with excellent vacuum capabilities or precise gas handling for a hydrogen atmosphere is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-hardness ceramics (like zirconia): Prioritize a furnace model capable of achieving stable, very high temperatures (1600°C or more) to ensure complete densification.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Opt for a versatile furnace that offers flexible temperature programming and can be adapted for use with multiple process gases.
Ultimately, mastering powder processing in a tube furnace comes from understanding the crucial interplay between your material, the temperature, and the atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Key Processing Requirements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Vacuum or hydrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation | Aerospace, electronics components |
| Advanced Ceramics | Zirconia | High temperatures up to 1600°C for densification | Dental crowns, bridges |
| Other Materials | Metal alloys, polymers | Precise temperature and atmosphere control | Research, industrial production |
Ready to enhance your powder processing with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with refractory metals, ceramics, or other materials, our furnaces ensure precise temperature and atmosphere control for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















