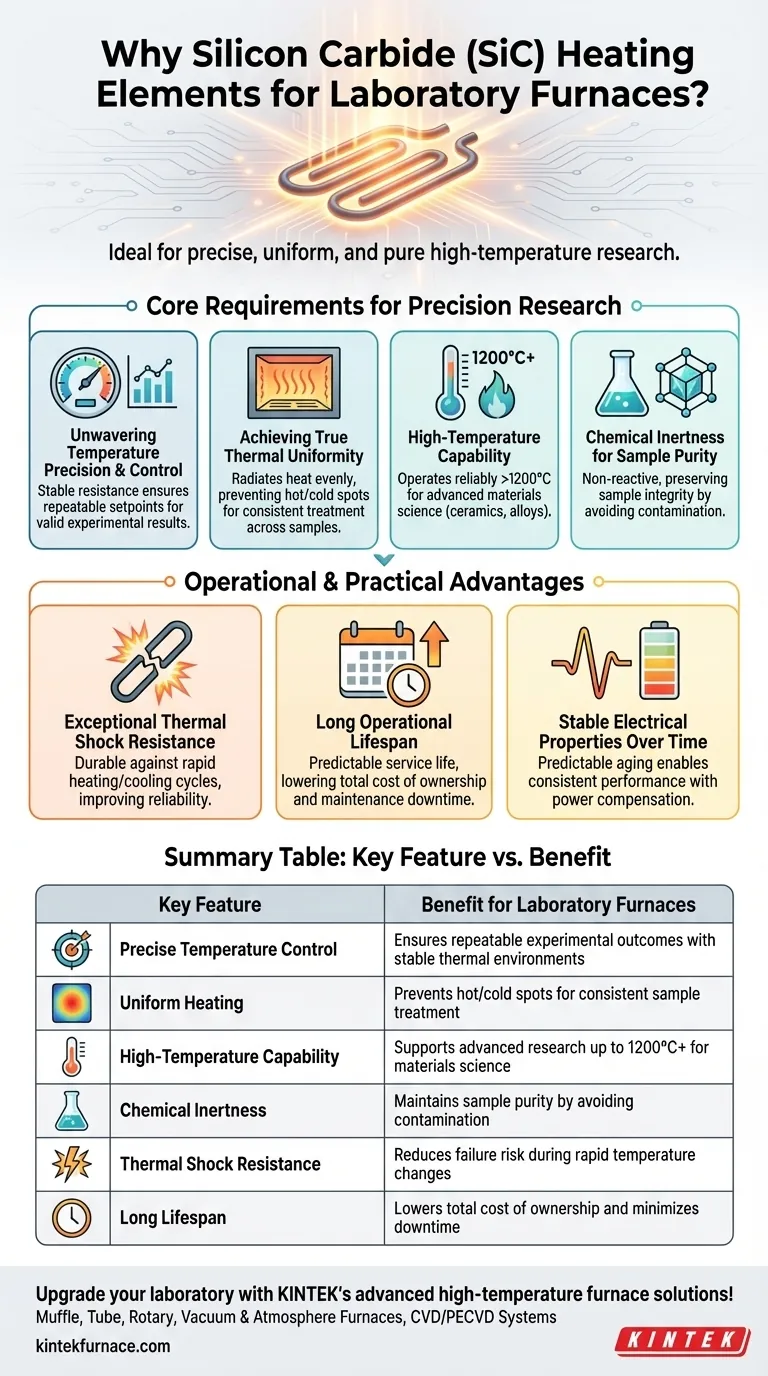
In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are ideal for laboratory furnaces because they deliver the precise temperature control, uniform heating, and chemical purity required for repeatable and valid experimental results. Their exceptional durability and high-temperature capabilities ensure reliable performance across a wide range of demanding research applications, from materials science to chemical analysis.
The core challenge in a laboratory setting isn't just generating heat, but generating controlled, predictable, and non-contaminating heat. Silicon carbide elements excel by providing a stable thermal platform that ensures the integrity of the experiment itself.
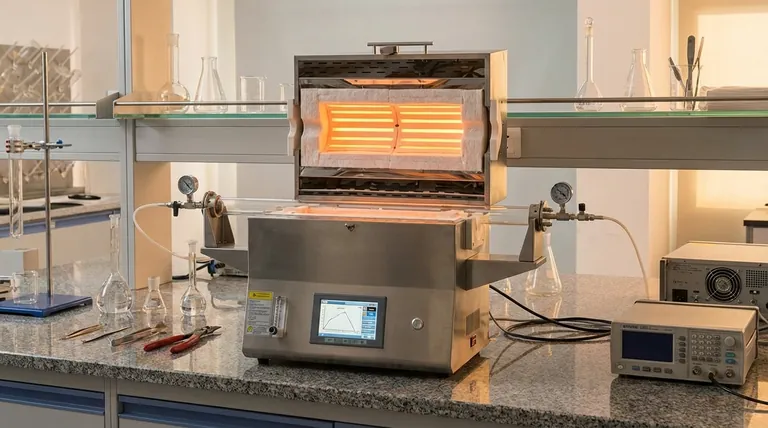

The Core Requirements of a Laboratory Furnace
A laboratory furnace is a precision instrument. Unlike many industrial applications where raw power is the goal, a lab requires finesse. The heating element is the heart of this system, and its properties directly impact the quality of the research.
Unwavering Temperature Precision and Control
The validity of an experiment often hinges on repeatability. SiC elements have stable electrical resistance characteristics, which allow modern controllers to maintain a setpoint temperature with extreme precision.
This ensures that variations in experimental outcomes are due to the tested variables, not fluctuations in the thermal environment.
Achieving True Thermal Uniformity
For any material sample, it's critical that the entire volume experiences the same temperature. SiC elements are designed to radiate heat evenly throughout the furnace chamber.
This thermal uniformity prevents hot or cold spots, guaranteeing that heat treatment, sintering, or annealing processes are consistent across the entire sample.
High-Temperature Capability for Advanced Research
Modern materials science often involves temperatures exceeding 1200°C (2192°F). SiC elements operate comfortably at these high temperatures, enabling research on advanced ceramics, alloys, and composites.
Their ability to sustain these temperatures without rapid degradation makes them suitable for long-duration tests and demanding thermal cycles.
Chemical Inertness for Sample Purity
Experiments, especially in chemistry and material development, can be highly sensitive to contamination. Silicon carbide is chemically inert in most environments.
This means the element will not react with the sample or release impurities into the furnace atmosphere, preserving the purity of the materials being tested.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
Beyond the immediate thermal properties, SiC elements offer practical benefits that are crucial for a functioning lab environment, where downtime and maintenance can derail research schedules.
Exceptional Resistance to Thermal Shock
Laboratory protocols often involve opening the furnace door or running rapid heating and cooling cycles. SiC's material structure gives it excellent resistance to thermal shock.
This durability means the elements are less likely to crack or fail when subjected to sudden temperature changes, significantly improving reliability and reducing replacement frequency.
Long Operational Lifespan
The combination of thermal shock resistance, chemical stability, and inherent durability gives SiC elements a long and predictable service life.
For a lab manager, this translates to a lower total cost of ownership, less maintenance downtime, and greater confidence in the furnace's availability for critical experiments.
Stable Electrical Properties Over Time
While all heating elements age, SiC elements do so in a predictable manner. Their electrical resistance increases slowly and consistently over their lifespan.
This predictable aging allows power control systems to compensate, ensuring consistent heat output and performance year after year.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
No component is perfect. Understanding the trade-offs associated with SiC elements is key to operating them effectively and ensuring their longevity.
Aging and Resistance Management
As SiC elements age, their resistance increases. The furnace's power supply must have sufficient voltage reserve to continue delivering the required power to the higher-resistance elements. Ignoring this can lead to slow heat-up times or an inability to reach the setpoint.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many ceramics, SiC is strong at high temperatures but can be brittle when cold. Care must be taken during installation, maintenance, or when moving the furnace to avoid mechanical shock that could fracture an element.
Sensitivity to Specific Atmospheres
While broadly inert, the lifespan of SiC elements can be negatively affected by certain reactive or reducing atmospheres. Always confirm the compatibility of the element with any specialized atmospheres you plan to use in your process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element is a foundational decision for any laboratory furnace. Your choice should align directly with your primary research goals.
- If your primary focus is experimental repeatability and data integrity: The superior temperature precision, uniformity, and chemical inertness of SiC are its most critical advantages.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials science (>1200°C): SiC provides the necessary thermal capability and stability for advanced research where other elements would fail.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational downtime and long-term cost: The exceptional durability and long, predictable lifespan of SiC elements reduce maintenance cycles and improve furnace availability.
Ultimately, choosing silicon carbide is an investment in the reliability and quality of your scientific outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit for Laboratory Furnaces |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures repeatable experimental outcomes with stable thermal environments |
| Uniform Heating | Prevents hot/cold spots for consistent sample treatment |
| High-Temperature Capability | Supports advanced research up to 1200°C+ for materials science |
| Chemical Inertness | Maintains sample purity by avoiding contamination |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Reduces failure risk during rapid temperature changes |
| Long Lifespan | Lowers total cost of ownership and minimizes downtime |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide silicon carbide heating elements and more in products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable performance, enhanced efficiency, and superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















