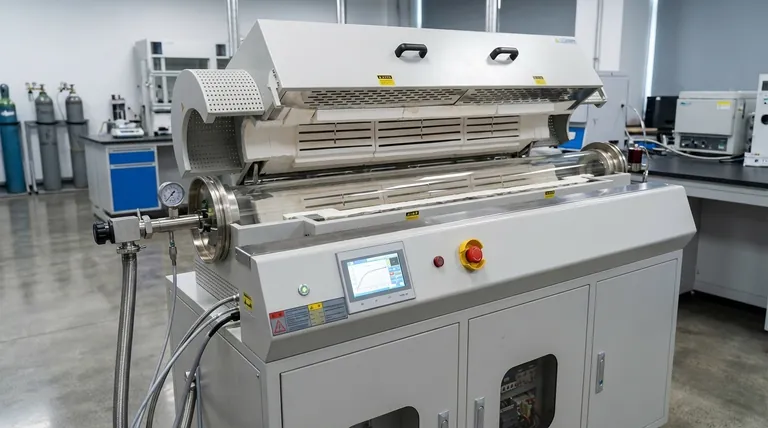
At their core, rotary furnaces are user-friendly because their design philosophy centers on automation and process efficiency. This significantly reduces the need for manual labor and constant operator intervention, streamlines workflows, and simplifies complex thermal processes through intuitive control systems.
The operational simplicity of a rotary furnace isn't just about an easy-to-use interface; it's a result of a highly engineered system designed to deliver precise, repeatable results with minimal human input, directly impacting labor costs, process consistency, and overall plant efficiency.

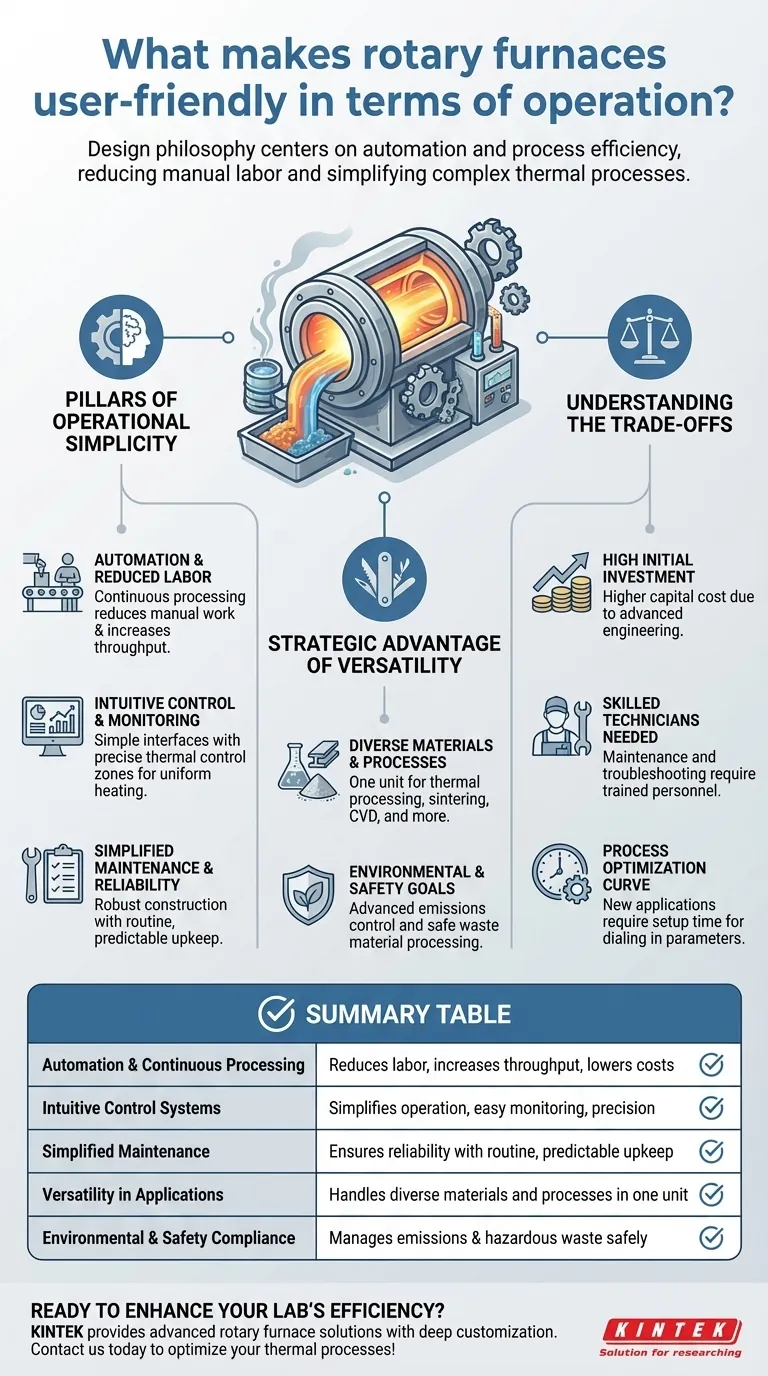
The Pillars of Operational Simplicity
A rotary furnace's user-friendliness stems from several interconnected design principles. These features work together to reduce complexity and lower the barrier to achieving high-quality, consistent output.
Automation and Reduced Labor
The primary feature is its continuous processing capability. Material is fed in, processed through the rotating tube, and discharged automatically, unlike batch systems that require constant loading and unloading.
This design inherently reduces the need for manual work. With fewer personnel required for operation, facilities can achieve significant cost savings in labor while increasing throughput.
Intuitive Control and Monitoring
Modern rotary furnaces feature intuitive interfaces that simplify the management of complex thermal variables. Operators can set and monitor parameters without needing deep engineering expertise for routine tasks.
The system uses multiple thermal control zones to apply heat with exceptional precision. This ensures uniform temperature distribution across the material, a critical factor that is automated rather than manually managed.
Simplified Maintenance and Reliability
These furnaces are engineered for long-term reliability. The operational design focuses on minimizing downtime through robust construction and components.
Maintenance typically involves routine inspections and predictable upkeep, rather than frequent, complex repairs. This foresight in design ensures the system remains a reliable asset, not an operational burden.
The Strategic Advantage of Versatility
Beyond simple operation, true user-friendliness comes from a system's ability to adapt. The versatility of a rotary furnace is a key operational advantage, especially in dynamic research or manufacturing environments.
Accommodating Diverse Materials and Processes
A single rotary furnace can handle a vast range of applications, from thermal processing and sintering to material synthesis and chemical vapor deposition. This flexibility allows one piece of equipment to serve multiple functions.
This versatility is crucial for researchers and manufacturers who need to adapt to different experimental or production needs without investing in multiple specialized furnaces.
Driving Environmental and Safety Goals
The furnace's efficiency extends to environmental performance. Advanced emissions control systems reduce harmful outputs, simplifying regulatory compliance.
They are also highly effective at processing various waste materials, including hazardous waste, safely. This capability turns a potential liability into a manageable process while also enabling the recovery of valuable materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While operationally simple, a rotary furnace is a sophisticated piece of industrial equipment. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its complexities.
High Initial Investment
The advanced automation, precise control systems, and robust engineering that make these furnaces user-friendly also contribute to a higher initial capital cost compared to simpler batch furnaces.
The Need for Skilled Technicians
While daily operation is simplified, maintenance and troubleshooting require skilled technicians. The control systems, sensors, and mechanical components are complex and cannot be serviced by untrained personnel.
Process Optimization Curve
Its versatility is a major benefit, but switching between vastly different materials or processes is not instantaneous. Each new application requires an optimization phase to dial in the correct temperatures, rotation speeds, and residence times to ensure desired results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace requires aligning its capabilities with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: The furnace's automation and low labor requirements deliver unmatched operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness at scale.
- If your primary focus is research and development or multi-product manufacturing: The system's versatility and ability to streamline different processes in a single unit provide critical adaptability.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and waste valorization: The furnace's capability to safely process hazardous materials and its advanced emissions controls are essential for meeting environmental targets.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace's user-friendliness is a function of its ability to make complex, high-temperature processes simple, repeatable, and efficient.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automation & Continuous Processing | Reduces labor, increases throughput, and lowers costs |
| Intuitive Control Systems | Simplifies operation with easy monitoring and precision |
| Simplified Maintenance | Ensures reliability with routine, predictable upkeep |
| Versatility in Applications | Handles diverse materials and processes in one unit |
| Environmental & Safety Compliance | Manages emissions and hazardous waste safely |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a user-friendly rotary furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















