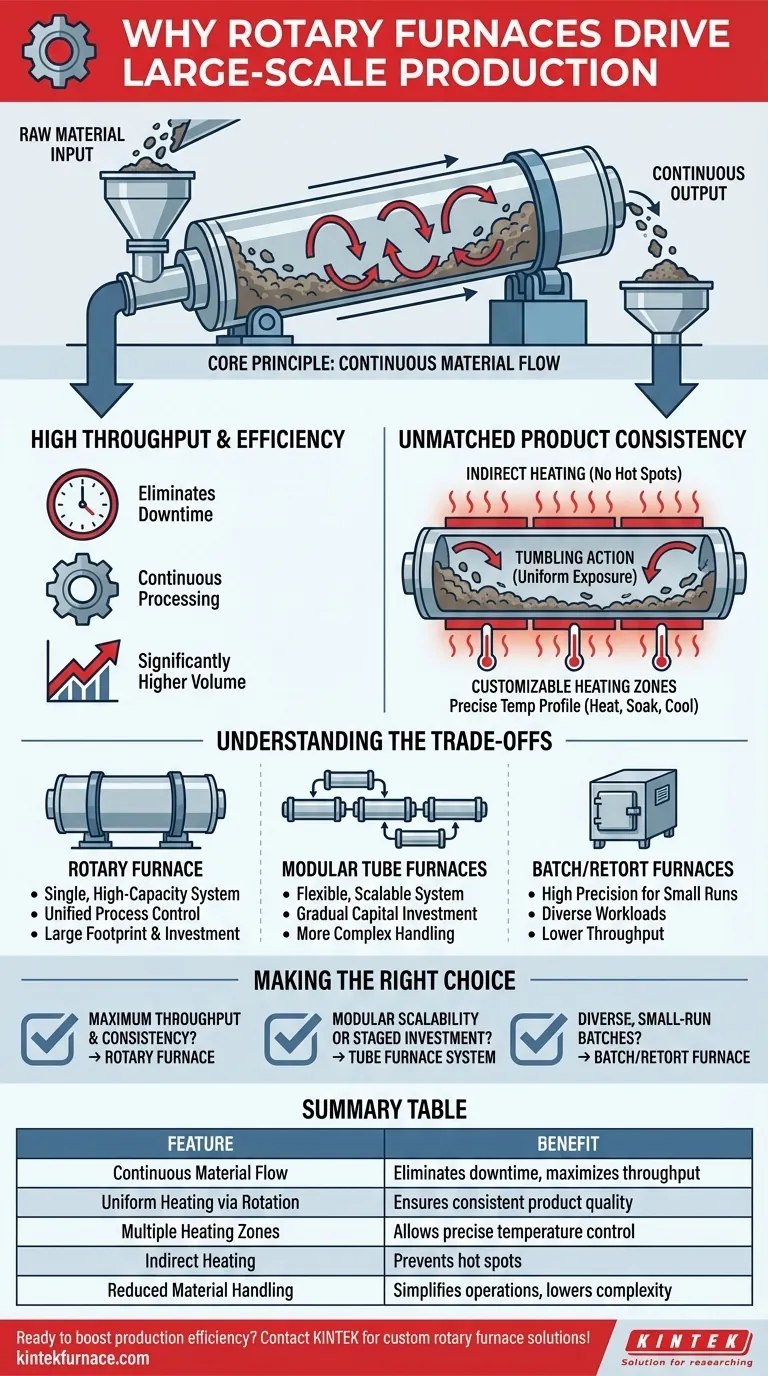
For any industrial operation where high volume is non-negotiable, the rotary furnace provides an unmatched solution for thermal processing. Its design is fundamentally centered on continuous material flow, which enables high throughput while its unique rotating barrel ensures every particle receives uniform heat treatment. This combination of continuous operation and consistent heating is what makes it ideal for demanding, large-scale production environments.
A rotary furnace is not simply a large oven; it is a dynamic processing system. Its core advantage lies in its ability to transform a static, batch-based process into a continuous, high-volume flow, delivering superior product consistency at an industrial scale.
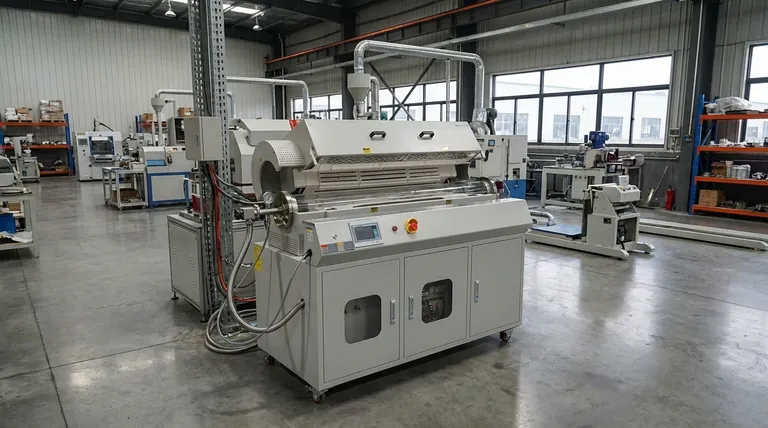

The Core Principle: Continuous Material Flow
The defining feature of a rotary furnace is its ability to process material without interruption. This operational principle is the foundation of its efficiency in high-volume settings.
How a Rotary Furnace Works
A rotary furnace consists of a long, cylindrical tube or barrel, slightly inclined and rotating slowly on its axis. Raw material is fed into the higher end, and the combination of gravity and rotation causes it to tumble and move continuously toward the lower, discharge end.
The Impact on Throughput
Because material is constantly being fed in and discharged, the furnace operates in a continuous processing mode rather than a discrete batch mode. This eliminates the downtime associated with loading and unloading, leading directly to significantly higher throughput.
Minimizing Material Handling
This continuous system design inherently reduces the need for manual or complex robotic material handling between batches. The streamlined flow from input to output simplifies the overall production line and reduces operational complexity.
Achieving Unmatched Product Consistency
In large-scale production, consistency is just as important as volume. The rotary furnace is engineered to deliver exceptional product uniformity, which is critical for meeting stringent quality specifications.
The Role of Indirect Heating
Most rotary furnaces use indirect heating, where external heating elements heat the outside of the rotating barrel. The heat is then transferred conductively to the material inside, preventing direct flame impingement or contact with heating elements, which can cause hot spots and non-uniform processing.
Uniformity Through Rotation
The slow, constant rotation is the key to uniformity. It gently tumbles the material, ensuring that every particle is continuously exposed to the heated surface of the barrel. This prevents some parts of the material from being over-processed while others are under-processed, a common problem in large static furnaces.
Customizable Heating Zones
Industrial rotary furnaces are often designed with multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the barrel. This allows for the creation of a precise temperature profile, enabling complex processes that may require heating, soaking, and cooling stages within a single, continuous operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Rotary Furnaces vs. Scaled Tube Furnaces
While a large rotary furnace is a single, integrated system, it is also possible to achieve scale by linking multiple smaller tube furnaces. A rotary furnace offers simpler, more unified process control, but the modular tube furnace approach can offer flexibility, redundancy, and a more gradual capital investment.
Material Limitations
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can be a drawback for certain materials. Very delicate or friable materials may break down, while sticky powders or materials prone to agglomeration can build up on the furnace walls, impeding flow and heat transfer.
Initial Investment and Footprint
A large-scale rotary furnace represents a significant capital investment and requires a substantial physical footprint within a plant. Its singular, high-capacity nature makes it less adaptable for small, varied production runs compared to smaller batch or retort furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your primary production goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and consistency: A rotary furnace is the definitive choice for its continuous operation and superior heat uniformity.
- If your primary focus is modular scalability or a staged investment: A system of multiple connected tube furnaces may offer a more flexible path to achieving large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse, small-run batches with high precision: A versatile retort or batch furnace provides superior control for varied, non-continuous workloads.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace means matching the equipment's core design principle to your specific operational and material requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Material Flow | Eliminates downtime, maximizes throughput |
| Uniform Heating via Rotation | Ensures consistent product quality |
| Multiple Heating Zones | Allows precise temperature control for complex processes |
| Indirect Heating | Prevents hot spots and non-uniform processing |
| Reduced Material Handling | Simplifies operations and lowers complexity |
Ready to boost your production efficiency with a custom rotary furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for large-scale industrial environments. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















