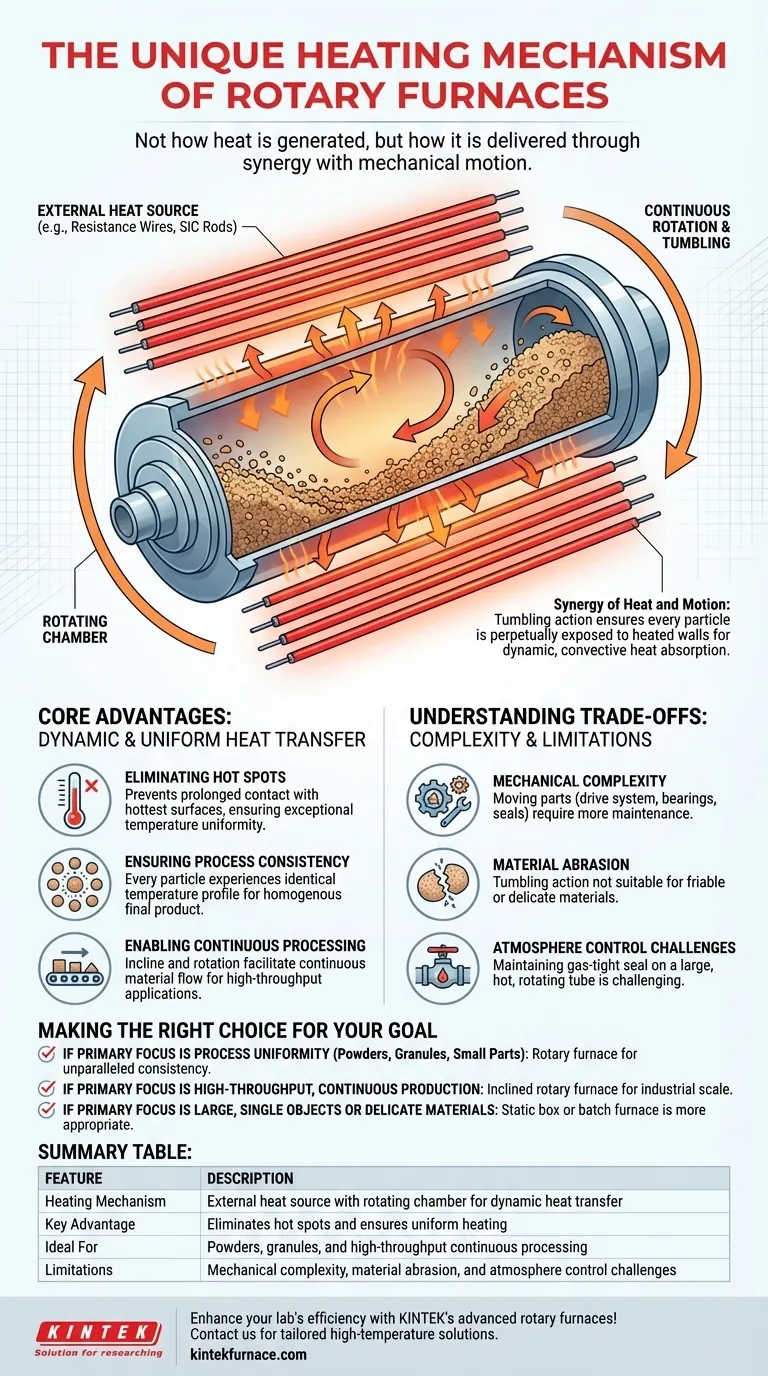
The defining characteristic of a rotary furnace's heating mechanism is not the heat source itself, but its unique synergy with mechanical motion. While the heating elements—often standard resistance wires or silicon carbon rods—are common, the furnace's innovation lies in using continuous rotation of a cylindrical chamber to dynamically and uniformly transfer that heat to the material being processed.
The uniqueness of a rotary furnace is not in how it generates heat, but in how it delivers it. The system combines a stationary, external heat source with a constantly rotating chamber, ensuring every particle of the material is heated evenly and consistently.

How the Rotary Heating System Works
To understand the system's effectiveness, it's essential to break down its two primary components and how they interact. The design is elegantly simple but produces a highly sophisticated result.
The External Heat Source
The heating elements in a rotary furnace are typically positioned outside the rotating tube or barrel.
These elements, such as resistance wires or silicon carbon (SiC) rods, generate thermal energy that radiates inward, heating the walls of the processing chamber.
The Rotating Chamber
The core of the furnace is a long, cylindrical barrel, often set at a slight incline. This chamber rotates slowly and continuously on its axis.
This rotation serves two purposes: it tumbles the material inside, and for inclined furnaces, it gradually moves the material from the entry point to the exit.
The Synergy of Heat and Motion
The true "mechanism" is the combination of these two elements. As the chamber rotates, the material inside is constantly lifted and cascaded.
This tumbling action ensures that new surfaces of the material are perpetually exposed to the heated walls of the chamber. It transforms a static heating environment into a dynamic and convective one, forcing uniform heat absorption throughout the entire batch.
The Core Advantage: Dynamic and Uniform Heat Transfer
This method of combining external heat with mechanical tumbling directly solves common problems found in static furnaces, leading to superior process control and product quality.
Eliminating Hot Spots
In a static furnace, material resting at the bottom or closest to a heating element can easily overheat, creating hot spots. The rotary furnace's tumbling action prevents any single part of the material from having prolonged contact with the hottest surfaces, ensuring exceptional temperature uniformity.
Ensuring Process Consistency
Because every particle experiences a nearly identical temperature profile, the final product is far more homogenous. This is critical for processes like calcination, pyrolysis, or coating, where consistent material properties are paramount.
Enabling Continuous Processing
The incline and rotation naturally facilitate a continuous flow of material. Raw material can be fed into the higher end and the processed product can be discharged from the lower end, making rotary furnaces ideal for high-throughput industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the rotary design introduces complexities and limitations that are important to consider.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating barrel requires a drive system, bearings, and—most critically—effective seals at both ends. These moving parts introduce mechanical wear and require more maintenance than a simple static box furnace.
Material Abrasion
The tumbling action that ensures even heating can also cause abrasion. This design is not suitable for processing friable or delicate materials that could be damaged or broken down by the constant cascading.
Atmosphere Control Challenges
While rotary furnaces can operate under controlled atmospheres or vacuums, maintaining a perfect, gas-tight seal on a large, hot, rotating tube is significantly more challenging and costly than on a sealed static chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on your material and your process objectives.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity for powders, granules, or small parts: The rotary furnace's ability to eliminate hot spots and ensure consistent heat exposure is unparalleled.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production: The inherent design of an inclined rotary furnace makes it the superior choice for industrial-scale continuous processing.
- If your primary focus is processing large, single objects or highly delicate materials: A static box or batch furnace is the more appropriate tool, as it avoids the mechanical stresses of tumbling.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is a specialized instrument engineered to solve the fundamental problem of uniform heating for bulk materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | External heat source with rotating chamber for dynamic heat transfer |
| Key Advantage | Eliminates hot spots and ensures uniform heating |
| Ideal For | Powders, granules, and high-throughput continuous processing |
| Limitations | Mechanical complexity, material abrasion, and atmosphere control challenges |
Enhance your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary furnaces can deliver superior uniformity and throughput for your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















