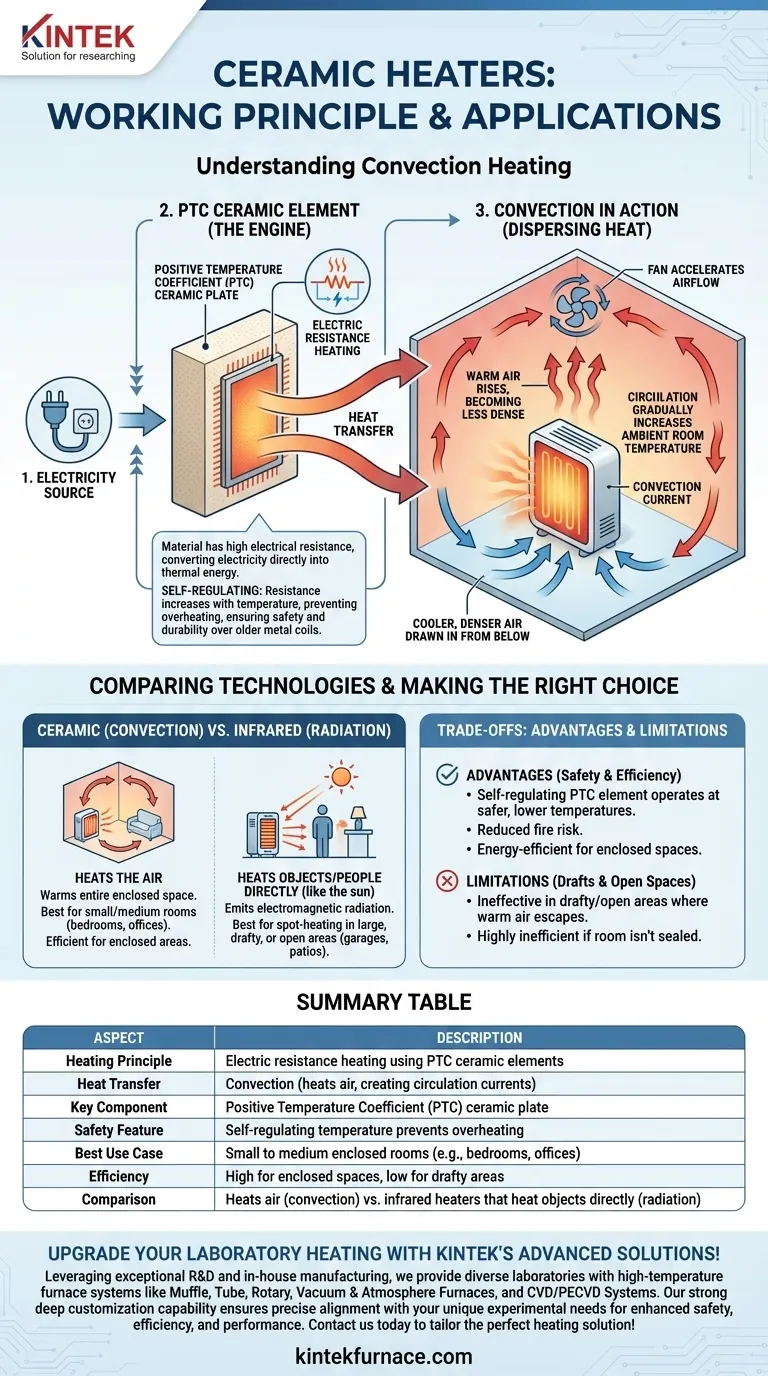
At its core, a ceramic heater operates on the principle of electric resistance heating. When you plug it in, electricity flows through a specialized heating element made of a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic. This material has high electrical resistance, which causes it to heat up significantly as electricity passes through it, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy.
The essential difference in a ceramic heater is not how it generates heat—which is standard electric resistance—but what generates the heat. It uses a durable ceramic plate instead of a metal coil, and it warms a room primarily by heating the air around it through convection.

The Core Mechanism: From Electricity to Airflow
The working principle of a ceramic heater is a simple, elegant process that involves converting electricity into heat and then transferring that heat to your room.
The Role of the Ceramic Element
The "engine" of the heater is its ceramic element. This is typically a plate or block made from an advanced ceramic material, often barium titanate.
Unlike a simple metal wire, this PTC ceramic is a semiconductor. This means its resistance increases sharply as its temperature rises, making it self-regulating and preventing it from overheating.
This design is inherently safer and more durable than older heaters that use thin, red-hot metal coils which can be a fire hazard and burn out over time.
Dispersing the Heat: Convection in Action
Once the ceramic element is hot, the heat must be moved into the room. This is achieved through convection.
The air immediately surrounding the hot ceramic plate is warmed, causing it to become less dense and rise. Cooler, denser air from the room is then drawn in from below to take its place, get heated, and rise in turn.
This process creates a continuous circulation of air—a convection current—that gradually increases the overall ambient temperature of the room. Many ceramic heaters include a fan to accelerate this process significantly.
How Ceramic Heaters Compare to Other Technologies
Understanding the alternatives clarifies why you might choose a ceramic heater. The primary distinction is how heat is delivered into the space.
Ceramic (Convection) vs. Infrared (Radiation)
This is the most critical comparison. A ceramic heater heats the air, which then warms the room and its occupants.
An infrared heater works like the sun. It emits electromagnetic radiation that travels through the air without heating it, directly warming any objects or people it strikes. It provides a feeling of "instant heat" on your skin.
Ceramic heaters are for raising the temperature of an entire enclosed space. Infrared heaters are for spot-heating a specific zone within a larger or draftier area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No heating technology is perfect for every situation. Ceramic heaters have distinct advantages and limitations rooted in their design.
Advantage: Safety and Efficiency
The self-regulating nature of PTC ceramic means the elements operate at a lower, safer temperature than glowing metal coils. This greatly reduces the risk of fire and makes the exterior of the unit less hot to the touch.
Because they heat up quickly and transfer heat effectively to the air, they are very energy-efficient for their intended purpose: heating a defined, enclosed space.
Limitation: Ineffective in Drafty or Open Spaces
The greatest strength of a ceramic heater—heating the air—is also its primary weakness.
In a room with drafts, open doors, or high ceilings, the warm air it produces will continuously escape or stratify, forcing the heater to run constantly without ever achieving the desired temperature. This makes it highly inefficient in such environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct technology, you must match the heater's operating principle to the space you need to heat.
- If your primary focus is heating a small to medium-sized, enclosed room like a bedroom or office: A ceramic heater is an excellent choice, providing safe, even, and efficient warmth.
- If your primary focus is feeling warm immediately in a specific spot within a large, open, or drafty area like a garage, workshop, or patio: An infrared (radiant) heater is superior because it heats you directly, not the air that is escaping.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a constant, gentle background heat in a well-insulated room: A ceramic heater provides a reliable and consistent convection current to achieve this.
Ultimately, choosing the right heater comes down to understanding the fundamental difference between heating the air versus heating objects.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Electric resistance heating using PTC ceramic elements |
| Heat Transfer | Convection (heats air, creating circulation currents) |
| Key Component | Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic plate |
| Safety Feature | Self-regulating temperature prevents overheating |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium enclosed rooms (e.g., bedrooms, offices) |
| Efficiency | High for enclosed spaces, low for drafty areas |
| Comparison | Heats air (convection) vs. infrared heaters that heat objects directly (radiation) |
Upgrade your laboratory heating with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for enhanced safety, efficiency, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor the perfect heating solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















