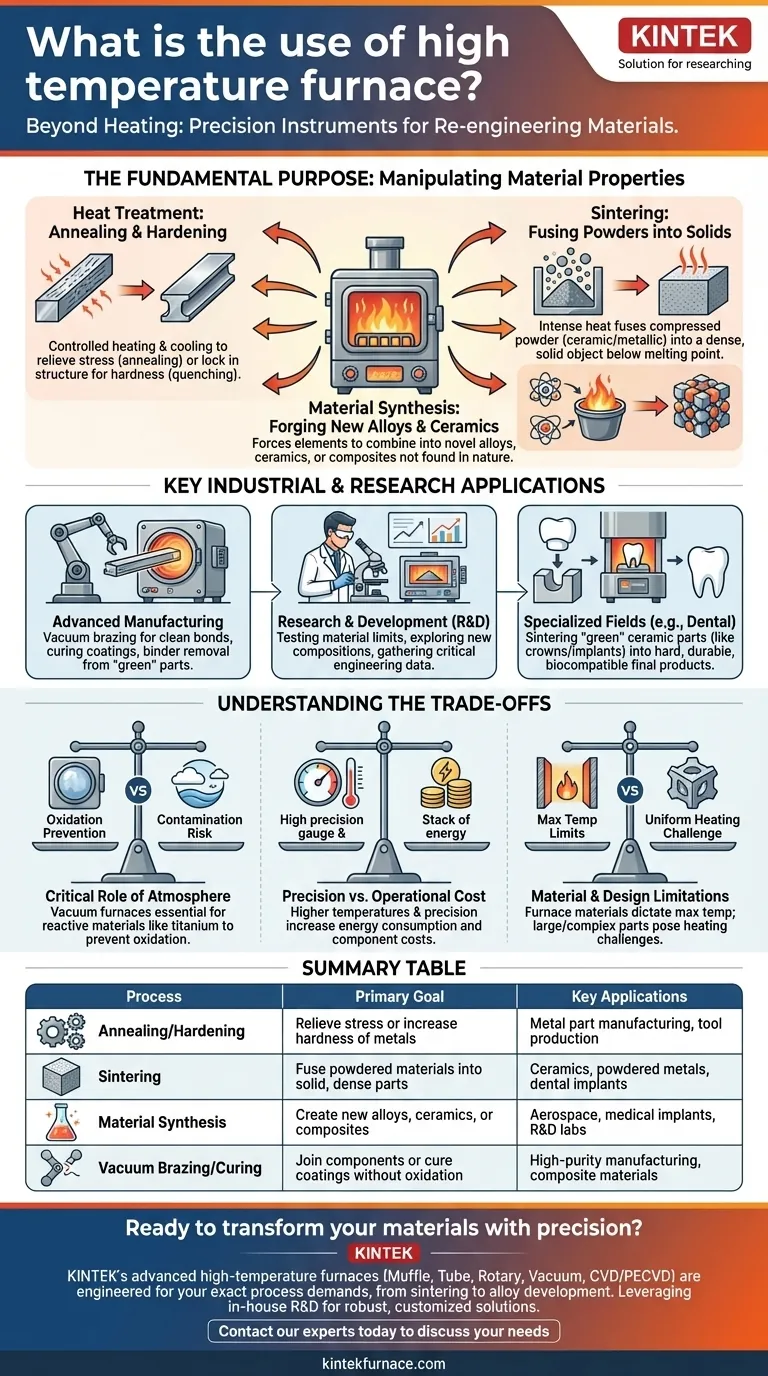
At their core, high-temperature furnaces are not just for heating things. They are precision instruments used to fundamentally alter the physical and chemical properties of materials. Their applications range from industrial manufacturing of metal and ceramic parts to advanced research in university and commercial labs, employing processes like annealing, sintering, and material synthesis.
The true purpose of a high-temperature furnace is to apply controlled thermal energy to re-engineer a material's internal structure. This allows us to create materials with specific, enhanced properties—such as increased strength, hardness, or purity—that are not achievable at normal temperatures.
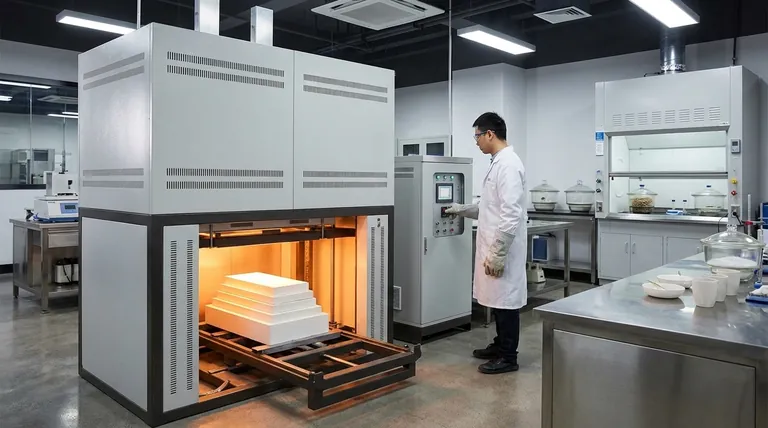

The Fundamental Purpose: Manipulating Material Properties
A high-temperature furnace provides the extreme environment needed to force atoms and molecules into new arrangements. This controlled transformation is the foundation of modern materials science.
Heat Treatment: Annealing and Hardening
Heat treatment involves heating a material (typically metal) to a specific temperature and then cooling it at a controlled rate. Annealing, for example, involves slow cooling to relieve internal stresses and make a material softer and more workable.
Conversely, rapid cooling, or quenching, can lock in a crystalline structure that makes the material significantly harder and more brittle.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering is a remarkable process where a compressed powder—often ceramic or metallic—is heated to a high temperature just below its melting point. The intense heat causes the individual particles to bond and fuse together, forming a solid, dense object.
This technique is critical for creating components from materials with extremely high melting points, such as technical ceramics used in electronics or aerospace.
Material Synthesis: Forging New Alloys and Ceramics
Many advanced materials simply do not exist in nature. High-temperature furnaces provide the energy required to force different elements to combine into new alloys, ceramics, or composites.
This process is the cornerstone of research and development, enabling the creation of novel materials with tailored characteristics for extreme applications, from jet engines to medical implants.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The principles of high-temperature processing are applied across a wide range of fields, each leveraging thermal energy for a specific outcome.
Advanced Manufacturing
In production environments, these furnaces are workhorses. They are used for vacuum brazing, where components are joined in an oxygen-free environment to create strong, clean bonds.
They are also used for curing specialized coatings and composites or for binder removal, a preliminary step where a temporary binding agent is burned out of a "green" part before final sintering.
Research & Development (R&D)
University and corporate labs rely on high-temperature furnaces to test the limits of materials. Researchers expose samples to extreme heat to measure their performance and degradation, providing critical data for engineering applications.
These furnaces are also the primary tool for exploring entirely new material compositions and manufacturing processes on a small, experimental scale.
Specialized Fields (e.g., Dental and Medical)
A common and precise application is in dental labs. When a ceramic crown or implant is made, it is often milled from a soft, chalky block.
That "green" part is then placed in a high-temperature furnace and sintered. This process shrinks the part and transforms it into the incredibly hard, durable, and biocompatible final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, operating a high-temperature furnace involves critical considerations and is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature. Many materials, like titanium alloys or high-purity metals, will rapidly oxidize or become contaminated if heated in the presence of air.
For these applications, a vacuum furnace is essential. It removes the atmosphere to prevent these unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the material's integrity.
Precision vs. Operational Cost
Higher temperatures and greater precision come at a cost. These furnaces consume significant energy, and the components required to withstand extreme heat (like heating elements and insulation) are expensive and have finite lifespans.
The choice of furnace is therefore a trade-off between the required process accuracy and the budget for operation and maintenance.
Material and Design Limitations
The furnace itself imposes limitations. The maximum achievable temperature is dictated by the materials used in its construction.
Furthermore, the size and geometry of the parts being processed must be considered, as ensuring uniform heating throughout a large or complex object is a significant engineering challenge.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Choosing the right high-temperature process depends entirely on what you intend to achieve with your material.
- If your primary focus is improving existing metal parts: You need a furnace capable of precise heat treatments like annealing or quenching to control hardness and ductility.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes from ceramics or powdered metals: Your goal requires a furnace designed for sintering, which fuses powdered materials into a solid, dense mass.
- If your primary focus is developing new, high-purity materials: A vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is essential to prevent contamination and enable the synthesis of reactive or sensitive alloys.
Ultimately, a high-temperature furnace is a strategic tool for intentionally re-engineering materials from the inside out.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing/Hardening | Relieve stress or increase hardness of metals | Metal part manufacturing, tool production |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials into solid, dense parts | Ceramics, powdered metals, dental implants |
| Material Synthesis | Create new alloys, ceramics, or composites | Aerospace, medical implants, R&D labs |
| Vacuum Brazing/Curing | Join components or cure coatings without oxidation | High-purity manufacturing, composite materials |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—are engineered to meet the exact demands of your processes, from sintering ceramics to developing new alloys.
Leveraging exceptional in-house R&D and manufacturing, we provide robust solutions and deep customization to precisely fit your unique experimental or production requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior material properties and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















