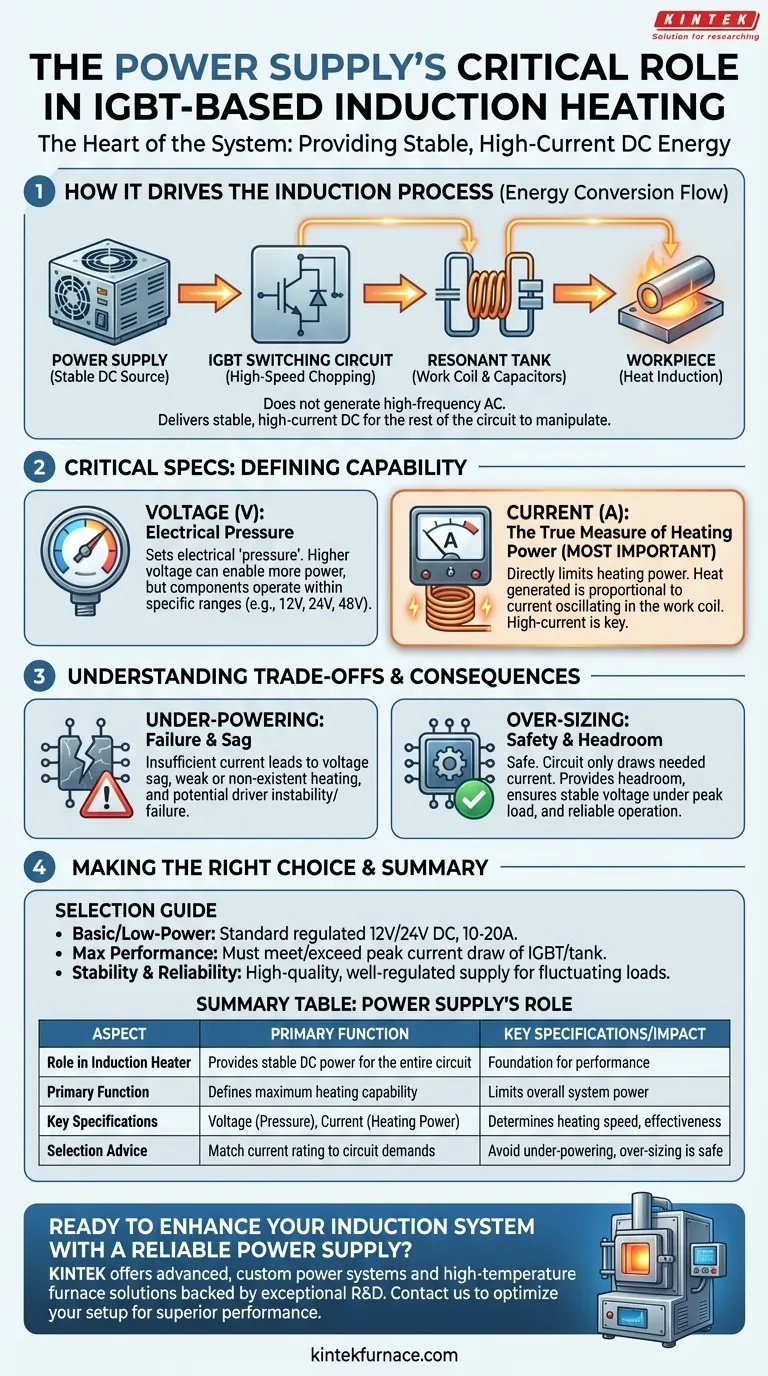
At its core, the power supply is the heart of an IGBT-based induction heater, providing the raw electrical energy required for the entire heating process. It does not generate the high-frequency alternating current itself, but rather delivers a stable, high-current DC voltage that the rest of the circuit uses to create the heating effect.
The power supply doesn't just turn the heater on; it defines the system's maximum heating capability. Its voltage and, more critically, its current rating directly limit the amount of power the IGBTs can switch into the work coil, ultimately determining how quickly and effectively you can heat a workpiece.
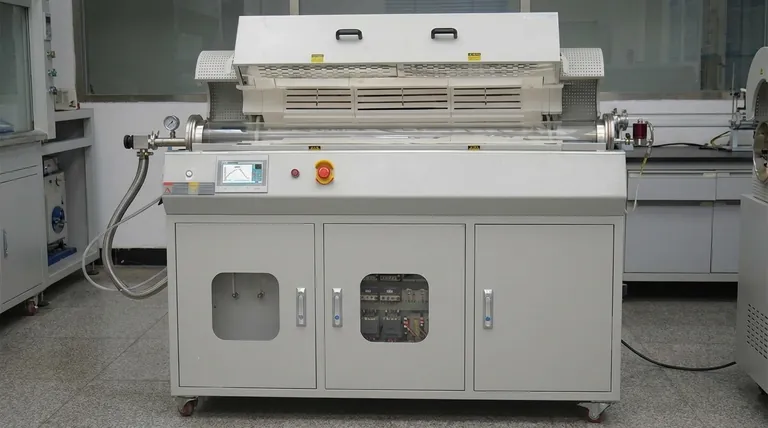

How the Power Supply Drives the Induction Process
The power supply is the first link in a chain of energy conversion. Its role is to provide a steady and powerful source of DC energy that the other components can manipulate.
Powering the Switching Circuit (IGBTs)
The Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) in the circuit function as extremely fast electronic switches. They take the smooth DC input from the power supply and "chop" it into high-frequency pulses.
The power supply provides the bulk voltage and current that flows through these IGBTs. Without a robust power source, the IGBTs would have no significant energy to switch.
Energizing the Resonant Tank
These high-frequency pulses from the IGBTs are then fed into the resonant tank circuit, which consists of the work coil and a bank of capacitors.
The resonant tank smooths these pulses into a powerful, high-frequency alternating current within the coil. This current generates the intense, fluctuating magnetic field responsible for inducing heat in a metal workpiece. The energy for this entire process originates from the main power supply.
Why Voltage and Current Ratings Are Critical
The specifications of your power supply are not arbitrary; they are the primary limiting factors for your heater's performance.
Voltage (V): Setting the Electrical Pressure
The voltage of the power supply (e.g., 12V, 24V, 48V) sets the electrical "pressure" for the entire system. While a higher voltage can enable more power, the driver circuit and IGBTs are typically designed to operate within a specific voltage range.
Current (A): The True Measure of Heating Power
Current capacity is the single most important specification of the power supply for an induction heater. Induction heating is a high-current application. The amount of heat generated is directly related to the amount of current oscillating in the work coil.
A power supply with an insufficient current rating will be unable to meet the demands of the circuit. This results in poor heating performance and can cause the power supply's voltage to drop or even cause the supply to shut down or fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a power supply involves balancing cost, size, and performance. Understanding the consequences of your choice is critical.
The Consequence of Under-Powering
Using a power supply with a lower current rating than the circuit demands is the most common point of failure. The circuit will attempt to draw more current than the supply can provide, leading to a sharp voltage drop (voltage sag).
This condition starves the entire circuit of energy, resulting in weak or non-existent heating and potentially unstable operation of the IGBT driver circuit.
The Safety of "Over-Sizing"
You cannot damage an induction heater by using a power supply with too much current capacity. The circuit will only draw the current it needs to operate.
A power supply with a current rating significantly higher than the circuit's maximum draw simply provides headroom. This ensures the supply is not strained and can deliver stable voltage even under peak load, leading to a more reliable system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Heater
Your goal for the induction heater project dictates the type of power supply you should select.
- If your primary focus is building a basic, low-power heater: A standard, regulated 12V or 24V DC power supply with a current rating of 10-20A is a suitable and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum heating performance: You must select a power supply whose maximum continuous current output meets or exceeds the peak current draw of your specific IGBT and resonant tank design.
- If your primary focus is system stability and reliability: Prioritize a high-quality, well-regulated power supply from a reputable brand to ensure it delivers clean, stable voltage under the heavy and fluctuating loads typical of induction heating.
Ultimately, treating the power supply as a foundational performance component, not an afterthought, is the key to building a successful and powerful induction heater.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Induction Heater |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides stable DC power for the entire circuit |
| Key Specifications | Voltage sets electrical pressure; current limits heating power |
| Impact on Performance | Determines heating speed, effectiveness, and system reliability |
| Common Ratings | 12V-48V DC, with current capacity critical for high-power needs |
| Selection Advice | Match current rating to circuit demands to avoid under-powering |
Ready to enhance your induction heating system with a reliable power supply? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom power systems for diverse laboratory needs. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup for superior performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















