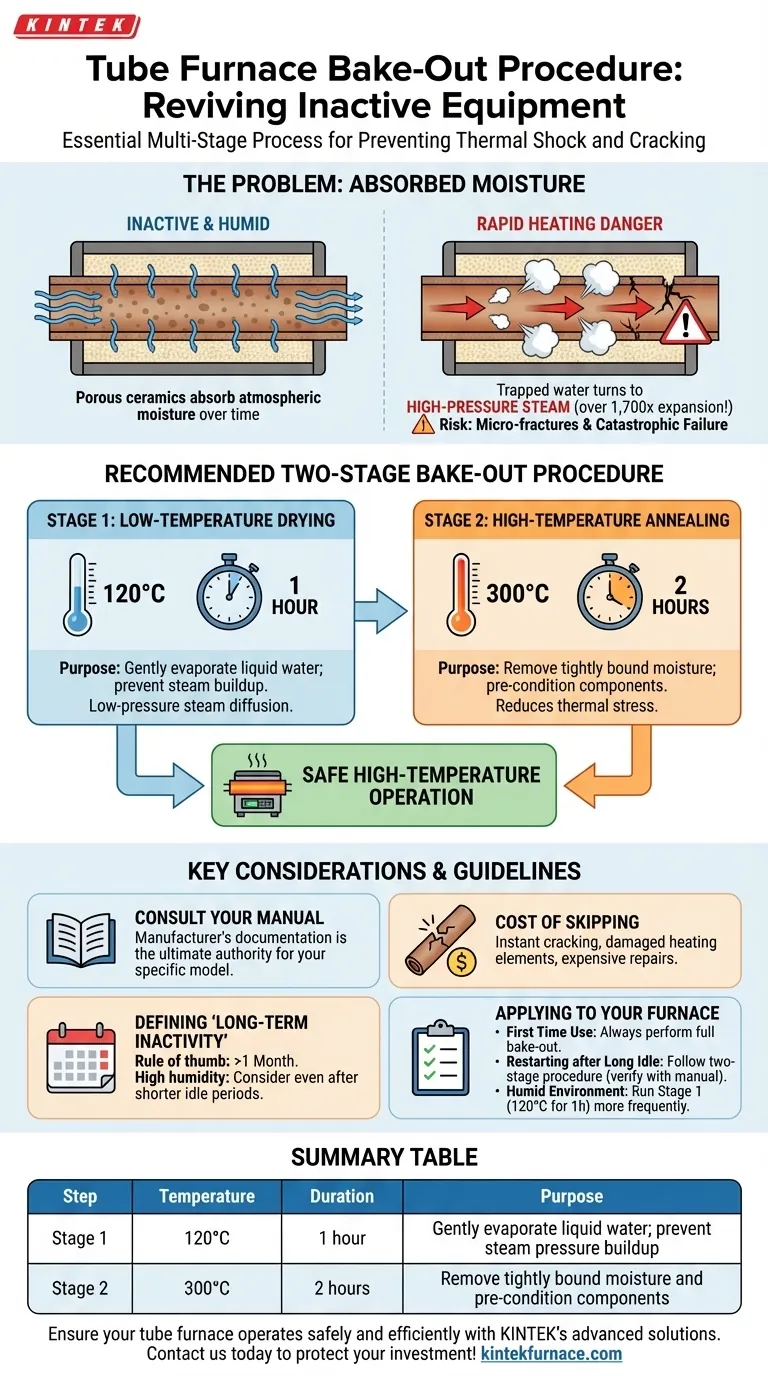
For a tube furnace that has been inactive for a long period, the standard procedure is to perform a multi-stage bake-out before resuming high-temperature operation. This involves heating the furnace to 120°C for one hour, followed by a second stage at approximately 300°C for two hours. This process is critical for preventing thermal shock and cracking of the furnace components.
The core principle behind this procedure is the slow and gentle removal of absorbed atmospheric moisture from the furnace's porous ceramic insulation and tube. Heating the furnace too rapidly will turn this trapped water into high-pressure steam, which can cause micro-fractures and lead to catastrophic failure of the equipment.

Why a Bake-Out is Non-Negotiable
A tube furnace that appears perfectly fine on the outside can hold a hidden risk after a period of disuse. Understanding the mechanism of failure is key to appreciating why this pre-heating step is essential.
The Hidden Danger: Absorbed Moisture
Ceramic materials, including the furnace tube and the surrounding insulation, are porous by nature. Over time, especially in humid environments, these materials act like a sponge, slowly absorbing water molecules from the air.
This moisture becomes trapped deep within the material's microscopic pores. It is not visible and cannot be wiped away.
The Mechanism of Failure: Water to Steam
When the furnace is heated rapidly, this trapped liquid water quickly turns into steam. The phase change from water to steam involves a massive expansion in volume (over 1,700 times).
If this expansion occurs too quickly within the confined pores of the ceramic, it generates immense internal pressure. This pressure can easily exceed the material's tensile strength, creating micro-fractures that propagate and result in a cracked furnace tube or damaged insulation.
Protecting Your Investment
Performing a bake-out is not just a procedural formality; it is a fundamental act of preventative maintenance. A cracked furnace tube can lead to a ruined experiment, contamination of the heating elements, and costly repairs. Taking a few hours to condition the furnace properly protects your valuable equipment for the long term.
The Standard Two-Stage Bake-Out Procedure
The recommended procedure is designed to remove moisture in a controlled manner, preventing the build-up of destructive internal pressure.
Stage 1: Low-Temperature Drying (~120°C for 1 Hour)
The purpose of this initial stage is to gently evaporate the liquid water. Holding the temperature just above the boiling point of water (100°C) allows the moisture to turn into low-pressure steam and slowly diffuse out of the ceramic materials without causing damage.
Stage 2: High-Temperature Annealing (~300°C for 2 Hours)
After the bulk of the moisture is gone, this second stage ensures any remaining, more tightly bound water is driven off. It also serves to gently heat and pre-condition the furnace components, reducing the thermal stress they will experience when ramped up to much higher operating temperatures.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the two-stage bake-out is a reliable general guideline, a few points must be considered for safe and effective operation.
Always Consult Your Manual
The procedure described (120°C then 300°C) is a widely accepted industry best practice. However, the manufacturer's official documentation is the ultimate authority. Always check the manual for your specific furnace model, as it may specify different temperatures or durations.
The Cost of Skipping the Procedure
Skipping the bake-out is a significant gamble. The primary risk is a cracked furnace tube, which can happen instantly and audibly upon rapid heating. This compromises the integrity of your process atmosphere and can damage the heating elements, leading to expensive and time-consuming repairs.
Defining "Long-Term Inactivity"
There is no universal definition, but a good rule of thumb is to perform a bake-out if the furnace has been idle for more than a month. If the furnace is stored in a high-humidity environment, you should consider performing this procedure even after shorter idle periods of a few weeks.
Applying This to Your Furnace
Use the following guidelines to decide on the best course of action for your equipment.
- If you are using a furnace for the very first time: Always perform the full, manufacturer-specified bake-out procedure without exception.
- If you are restarting a furnace after a long idle period: Follow the two-stage bake-out as a reliable general practice, but always verify it against your specific model's manual first.
- If your lab is in a very humid environment: Consider running the low-temperature drying stage (120°C for 1 hour) more frequently as a precautionary measure, even after shorter periods of inactivity.
Following this deliberate conditioning procedure is the most effective way to ensure the long-term reliability and safety of your high-temperature equipment.
Summary Table:
| Step | Temperature | Duration | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 120°C | 1 hour | Gently evaporate liquid water to prevent steam pressure buildup |
| Stage 2 | 300°C | 2 hours | Remove tightly bound moisture and pre-condition components |
Ensure your tube furnace operates safely and efficiently with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to protect your investment and enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















