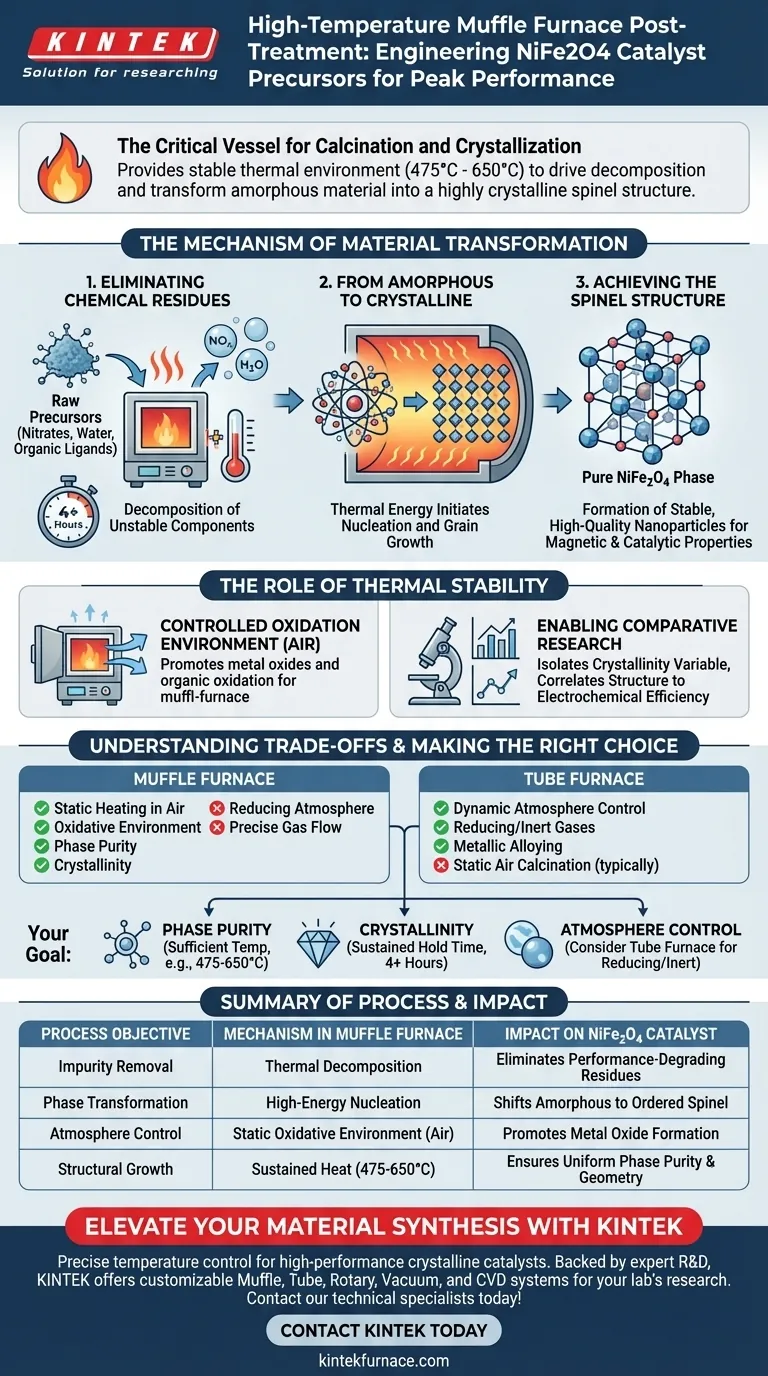
The high-temperature muffle furnace serves as the critical vessel for calcination and crystallization. In the post-treatment of NiFe2O4 catalyst precursors, this equipment provides a stable thermal environment (typically around 475°C to 650°C) required to drive complete chemical decomposition. Its primary function is to eliminate residual impurities, such as nitrates or water, and force the material to transition from an amorphous, disordered state into a highly crystalline spinel structure.
The muffle furnace facilitates a dual process: it purges the material of volatile residues through heat and supplies the energy needed for crystal nucleation, ensuring the formation of a pure, stable NiFe2O4 phase.

The Mechanism of Material Transformation
Eliminating Chemical Residues
The initial precursors obtained from synthesis methods like spray pyrolysis often contain residual nitrates, water, or organic ligands.
A muffle furnace maintains a high temperature for an extended duration (e.g., 4 hours), ensuring these unstable components are fully decomposed and removed.
Failure to remove these residues would leave impurities that degrade the final electrochemical performance of the catalyst.
From Amorphous to Crystalline
Raw precursors often exist in an amorphous state, lacking a defined internal structure.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace initiates nucleation, where atoms arrange themselves into an ordered pattern.
As heating continues, these nuclei grow, transforming the bulk material into a solid crystalline form.
Achieving the Spinel Structure
For NiFe2O4, the specific goal of this heat treatment is to achieve a cubic spinel crystal structure.
This specific atomic arrangement is characteristic of high-quality nanoparticles and is essential for the material's magnetic and catalytic properties.
The muffle furnace ensures the phase transformation is uniform throughout the sample.
The Role of Thermal Stability
Controlled Oxidation Environment
Unlike tube furnaces which are often used for reducing atmospheres (removing oxygen), muffle furnaces are typically used for calcination in air.
This environment promotes the oxidation of organic polymer networks and facilitates the formation of metal oxides.
It allows for the necessary diffusion reactions to occur, effectively doping nickel species into the lattice or distributing them on particle surfaces.
Enabling Comparative Research
The primary reference highlights that this treatment allows for comparative studies on how crystallinity affects performance.
By strictly controlling the temperature (e.g., at 475°C), researchers can isolate the variable of crystallinity.
This consistency allows for a clear correlation between the structural order of the catalyst and its resulting electrochemical efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere Limitations
While muffle furnaces excel at static heating in air, they lack the dynamic atmosphere control of a tube furnace.
If your synthesis requires a reducing atmosphere (to remove oxygen) or the introduction of inert gases to prevent oxidation, a muffle furnace is generally unsuitable.
Tube furnaces are preferred when precise gas flow is needed to induce metallic alloying or prevent oxide formation.
Temperature Sensitivity
The specific temperature setting is a critical variable that dictates the final material properties.
Temperatures that are too low may result in incomplete decomposition of nitrates, leaving impurities.
Conversely, temperatures that are significantly higher than necessary can lead to excessive sintering, reducing the surface area of the nanoparticles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your post-treatment, align your thermal protocol with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the temperature is sufficient (e.g., 475°C - 650°C) to fully decompose all nitrates and volatile precursors.
- If your primary focus is Crystallinity: Prioritize a sustained hold time (e.g., 4+ hours) to allow for complete nucleation and grain growth of the spinel structure.
- If your primary focus is Atmosphere Control: Verify if an oxidative environment is acceptable; if a reducing atmosphere is required, switch to a tube furnace.
Mastering the calcination process is not just about heating; it is about precisely engineering the atomic structure of your catalyst for peak performance.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Mechanism in Muffle Furnace | Impact on NiFe2O4 Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Impurity Removal | Thermal decomposition of nitrates & water | Eliminates residues that degrade electrochemical performance |
| Phase Transformation | High-energy crystal nucleation | Shifts material from amorphous state to ordered spinel structure |
| Atmosphere Control | Static oxidative environment (Air) | Promotes metal oxide formation and organic polymer oxidation |
| Structural Growth | Sustained heat (475°C - 650°C) | Ensures uniform phase purity and specific cubic spinel geometry |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is the difference between an amorphous precursor and a high-performance crystalline catalyst. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your lab's high-temperature research.
Whether you are engineering NiFe2O4 spinel structures or developing next-generation nanoparticles, our furnaces provide the stability and uniformity your work deserves. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific thermal processing needs with our technical specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Jan Witte, Thomas Turek. Efficient Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis on Amorphous Spray‐Pyrolyzed NiFe<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>. DOI: 10.1002/celc.202500226
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What specific thermal conditions must a high-temperature muffle furnace provide for BiOI to BiVO4 conversion?
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in SiCf/Al-Mg pretreatment? Optimize Fiber Bonding with Thermal De-sizing
- How do high-temperature muffle furnaces and ceramic crucibles ensure accuracy? Achieve Precise Alloy Oxidation Data
- How does Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) compare to traditional muffle furnace sintering? Achieve Fine-Grained Ceramics
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace? Master Eggshell Adsorbent Activation
- How does an electric furnace contribute to energy efficiency? Maximize Your Lab's Heating Performance
- How is a high-temperature muffle furnace used in PGC annealing? Optimize Your Phosphor-in-Glass Synthesis
- Why is a laboratory muffle furnace core to CCT nanocatalyst prep? Optimize Your Calcination Results



















