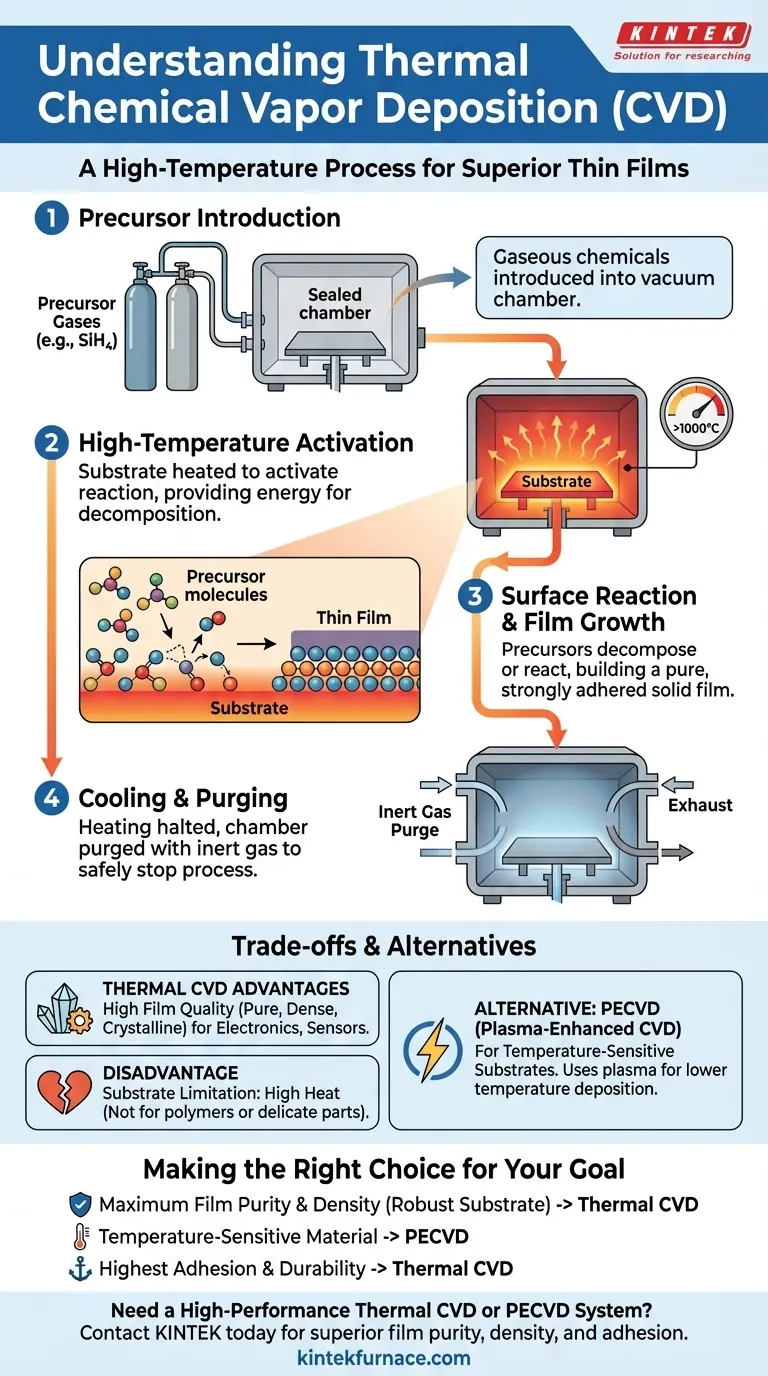
At its core, thermal chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a process that uses high heat to trigger a chemical reaction among gaseous precursors, causing them to deposit a solid, high-purity thin film onto a target surface. The process unfolds in four distinct stages: introducing controlled gases into a chamber, heating the substrate to activate a reaction, allowing the solid film to grow on the surface, and finally cooling the system while removing excess gases.
The central purpose of thermal CVD is to create exceptionally pure and durable thin films. It achieves this by using high temperature as the sole energy source to break down chemical vapors, which then reconstruct themselves atom-by-atom as a solid layer on a substrate within a highly controlled vacuum environment.

Deconstructing the Thermal CVD Process
To truly understand thermal CVD, we must look at it as a sequence of carefully controlled physical and chemical events. Each step has a specific purpose in building the final film.
Step 1: Precursor Introduction
The process begins by introducing one or more gaseous chemicals, known as precursors, into a sealed reaction chamber under vacuum.
These precursors are carefully selected to contain the specific atoms required for the final film. For example, to deposit a silicon film, a gas like silane (SiH₄) might be used.
Step 2: High-Temperature Activation
The object to be coated, called the substrate, is heated to an extremely high temperature, often several hundred or even over a thousand degrees Celsius.
This thermal energy is the defining feature of thermal CVD. It acts as the catalyst, providing the necessary activation energy to initiate the chemical reactions on the hot substrate surface.
Step 3: Surface Reaction and Film Growth
When the hot precursor gases make contact with the even hotter substrate, they either decompose (break apart) or react with one another.
The desired atoms are then released and bond directly to the substrate's surface. This process builds a new, solid layer atom-by-atom, resulting in a thin film that is exceptionally dense, pure, and strongly adhered to the surface.
Step 4: Cooling and Purging
Once the film reaches the desired thickness, the heating systems are shut down.
The chamber is then purged with an inert gas to remove any unreacted precursor gases and chemical byproducts. This step immediately halts the deposition process and ensures the chamber is safe to open.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal CVD
While powerful, thermal CVD is not a universal solution. Its reliance on high heat creates a clear set of advantages and disadvantages that determine where it can be applied.
Advantage: High Film Quality
The high temperatures used in thermal CVD typically result in films with superior quality. They are often highly crystalline, extremely pure, and very dense, making them ideal for high-performance applications in automotive sensors, electronics, and biosensors.
Disadvantage: Substrate Limitation
The primary drawback is the intense heat itself. This process cannot be used on materials with low melting points or those that could be damaged by high temperatures, such as most polymers (plastics) or delicate electronic components.
The Alternative: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
For temperature-sensitive substrates, a different method called Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is used. Instead of relying solely on heat, PECVD uses an electric field to create a plasma, which energizes the precursor gases and allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use thermal CVD hinges on balancing the need for film quality against the temperature tolerance of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and density on a robust substrate: Thermal CVD is the superior choice for creating high-performance coatings on materials that can withstand the heat.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: You must use a low-temperature alternative like PECVD to prevent damage to the substrate.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible adhesion and durability: Thermal CVD's high-temperature process promotes strong chemical bonds between the film and substrate, creating an exceptionally resilient coating.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental role of temperature is the key to selecting the correct deposition technique for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Precursor Introduction | Introduce controlled gases into a vacuum chamber. |
| 2 | High-Temperature Activation | Heat substrate to trigger chemical reactions. |
| 3 | Surface Reaction & Growth | Atoms bond to substrate, building the film layer-by-layer. |
| 4 | Cooling & Purging | Halt deposition and remove excess gases. |
Need a High-Performance Thermal CVD or PECVD System for Your Lab?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for applications in electronics, automotive sensors, and biosensors.
Contact us today to discuss how our thermal expertise can help you achieve superior film purity, density, and adhesion.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















