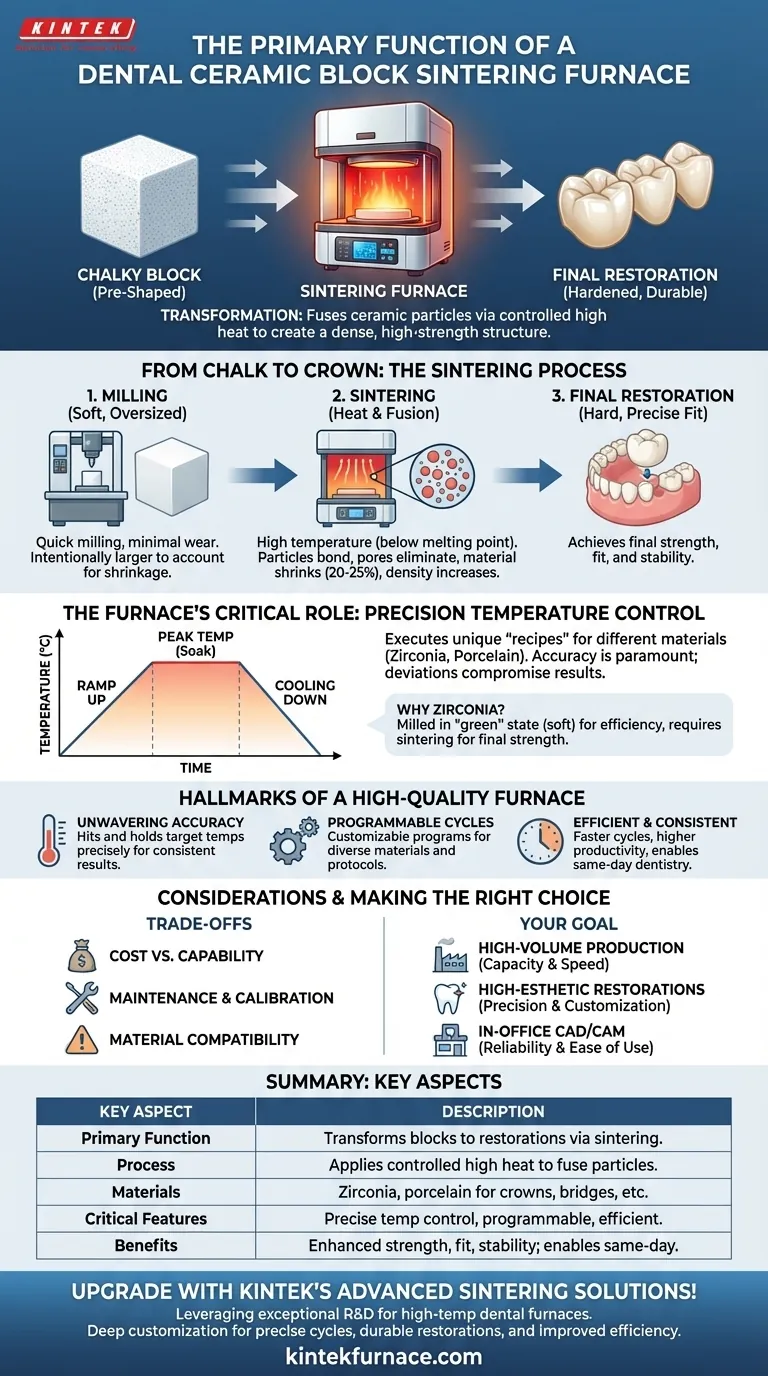
The primary function of a dental ceramic sintering furnace is to transform a pre-shaped, chalky block of ceramic material into a final, hardened, and durable dental restoration. It achieves this by applying precisely controlled high temperatures in a process known as sintering, which fuses the ceramic particles together to create a dense, high-strength structure suitable for crowns, bridges, and implants.
A sintering furnace is not merely an oven; it is a precision instrument at the heart of the digital dentistry workflow. Its true purpose is to reliably and predictably impart the final strength, fit, and stability required for modern, high-performance ceramic restorations.
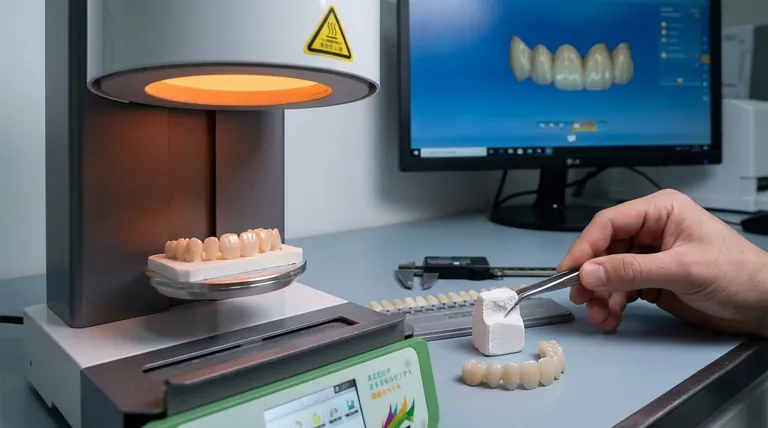

From Chalk to Crown: The Sintering Process Explained
Understanding the function of the furnace requires understanding the "why" behind the process. Ceramic blocks used in CAD/CAM dentistry are not ready for a patient's mouth immediately after being milled. They require a critical thermal transformation.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a process where a powdered or porous material is heated to a high temperature—below its melting point—causing the individual particles to bond and fuse.
This process eliminates the pores between the particles, causing the material to shrink and dramatically increase in density and strength. It's how a soft, oversized ceramic milling block becomes a restoration strong enough to withstand biting forces.
The Role of Temperature and Time
The furnace's primary job is to manage temperature with extreme accuracy. Different ceramic materials, like zirconia or porcelain, have unique "recipes" or firing cycles.
These cycles dictate the rate of heating, the peak temperature, how long the restoration "soaks" at that temperature, and the rate of cooling. Deviations can lead to a weak, warped, or discolored restoration, compromising the final result.
Why Zirconia Requires Sintering
Most modern ceramic restorations are made from zirconia. For milling, zirconia is provided in a "green" or pre-sintered state, which is soft and chalk-like.
This softness allows it to be milled quickly and with minimal wear on the milling burs. The restoration is intentionally milled larger than its final size to account for the predictable shrinkage (often 20-25%) that occurs inside the sintering furnace.
The Hallmarks of a High-Quality Sintering Furnace
Not all furnaces are created equal. Their performance directly impacts the quality and consistency of the final dental work. Key capabilities separate a basic unit from a high-performance one.
Unwavering Temperature Accuracy
The single most critical feature is the ability to hit and hold target temperatures precisely. Consistent and predictable results are only possible when the furnace executes the exact heating program required by the ceramic manufacturer.
Programmable and Versatile Cycles
A high-quality furnace allows for multiple, customizable programs. This versatility is essential for dental labs that work with a wide range of ceramic materials, each requiring its own specific heating protocol for optimal strength and esthetics.
Efficient and Consistent Results
Modern furnaces are designed for both speed and consistency. Faster sintering cycles improve lab productivity and enable same-day dentistry. This efficiency saves time and reduces costs by minimizing the need for adjustments or remakes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While essential, integrating a sintering furnace involves practical considerations that every dental professional should understand.
Cost vs. Capability
Entry-level furnaces may perform the basic function, but higher-end models offer faster cycles, larger capacities, and more precise control. The initial investment must be weighed against the lab's or clinic's need for throughput and material versatility.
Maintenance and Calibration
A sintering furnace is not a "set and forget" appliance. It requires regular calibration to ensure its temperature readings remain accurate. Heating elements also have a limited lifespan and must be replaced periodically to maintain performance.
Material-Specific Limitations
A furnace must be compatible with the materials you intend to use. Using the wrong sintering program for a specific brand of zirconia can easily result in a failed restoration, wasting both time and materials. Always follow the manufacturer's validated parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace depends entirely on the specific objectives of your dental practice or laboratory.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Prioritize furnaces with large tray capacities and fast sintering cycles to maximize daily throughput.
- If your primary focus is specialized, high-esthetic restorations: Look for a furnace with exceptional temperature precision and highly customizable programs to handle diverse and advanced ceramic materials.
- If your primary focus is integrating an in-office CAD/CAM system: Choose a reliable, user-friendly furnace that is validated by the manufacturer of your chosen ceramic blocks to ensure predictable results.
Ultimately, the right sintering furnace is an investment in clinical precision, operational efficiency, and predictable patient outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Transforms pre-shaped ceramic blocks into hardened dental restorations via sintering. |
| Process | Applies controlled high temperatures to fuse particles, increasing density and strength. |
| Materials Handled | Zirconia, porcelain, and other ceramics for crowns, bridges, and implants. |
| Critical Features | Precise temperature control, programmable cycles, efficiency, and consistency. |
| Benefits | Enhanced strength, fit, and stability of restorations; supports same-day dentistry. |
Upgrade your dental lab or practice with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces tailored for dental ceramics, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise sintering cycles for zirconia and other materials, delivering durable, high-strength restorations with improved efficiency and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow and patient outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision



















