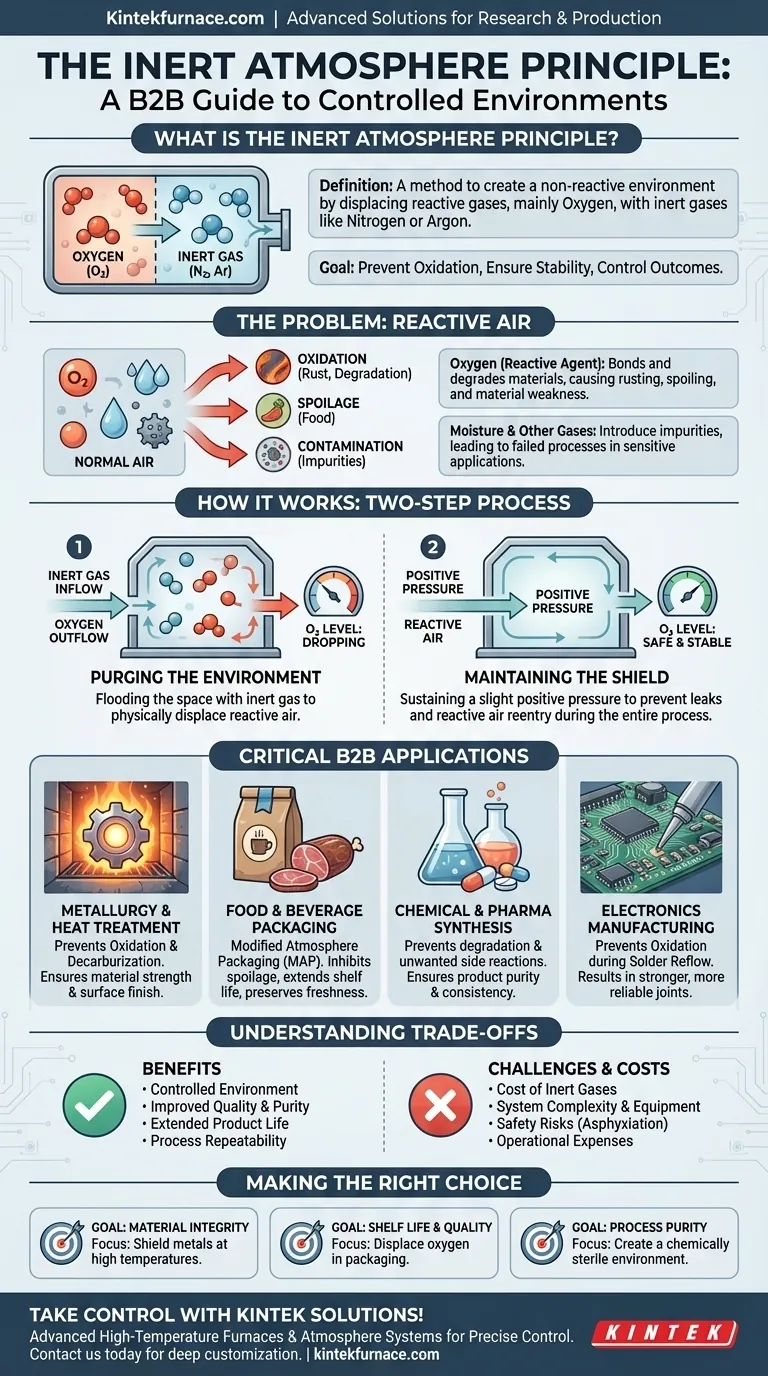
In essence, the inert atmosphere principle is a method for creating a controlled, non-reactive environment. This is achieved by systematically replacing reactive gases in a given space, primarily oxygen, with a non-reactive or "inert" gas like nitrogen or argon. The goal is to prevent unwanted chemical changes such as oxidation, ensuring the integrity and stability of materials and processes.
The core challenge in many technical fields is that the air around us is chemically reactive. The inert atmosphere principle provides the solution by creating a protective "shield" of non-reactive gas, allowing you to control the chemical environment to dictate the final outcome.

The Core Problem: Why Air Can Be an Enemy
To understand the value of an inert atmosphere, you must first recognize the threats posed by normal air. The ambient atmosphere is a mixture of gases that can actively and often destructively interfere with sensitive work.
The Role of Oxygen as a Reactive Agent
Oxygen is the primary adversary. It is highly reactive and seeks to bond with other elements in a process called oxidation.
This reaction is responsible for common forms of degradation, such as the rusting of metal, the spoilage of food, and the discoloration of chemicals. In high-temperature processes like welding or heat treatment, uncontrolled oxygen can ruin the structural properties of a material.
Contamination from Moisture and Other Gases
Air also contains water vapor and other trace gases. These can introduce moisture into a process, leading to contamination or unwanted side reactions.
For highly sensitive applications in electronics or chemical synthesis, even minute amounts of these contaminants can cause a process to fail or yield impure results.
How the Inert Atmosphere Principle Works
Implementing an inert atmosphere is a precise, two-step process that involves displacing ambient air and then maintaining the protective environment.
Step 1: Purging the Environment
The first step is to purge the chamber or enclosure. This is done by flooding the space with a continuous flow of an inert gas, such as nitrogen.
This influx of inert gas physically displaces the oxygen-rich air, pushing it out through vents. The purge continues until oxygen sensors confirm that the concentration has dropped to a safe, pre-determined level.
Step 2: Maintaining the Inert Shield
Once purged, the inert atmosphere must be maintained throughout the entire process, including any heating or cooling cycles.
This is often achieved by maintaining a slight positive pressure with the inert gas. This ensures that if any minor leaks exist in the enclosure, the inert gas will flow outward, preventing reactive air from seeping back in.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, applying the inert atmosphere principle is not without its challenges and costs. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging these factors.
Cost of Inert Gases
Nitrogen and, to a greater extent, argon are industrial commodities with associated costs. For large-scale or continuous operations, the consumption of these gases can represent a significant operational expense.
System Complexity and Safety
Creating and maintaining an inert atmosphere requires specialized equipment. This includes sealed furnaces or glove boxes, gas delivery systems, and oxygen monitoring sensors, adding to capital costs and system complexity.
Furthermore, inert gases are asphyxiants. Robust safety protocols are mandatory to protect personnel from the risk of oxygen-deficient environments.
Critical Applications Across Industries
The principle is not a niche academic concept; it is a foundational technique used to guarantee quality and safety in numerous fields.
Heat Treatment and Metallurgy
In furnaces, an inert atmosphere prevents oxidation and decarburization of metals at high temperatures. This ensures that components like steel or titanium alloys retain their designed strength and surface finish.
Food and Beverage Packaging
Known as "modified atmosphere packaging," this application uses nitrogen to displace oxygen in food packages. This inhibits the growth of aerobic microbes and slows oxidative spoilage, dramatically extending the shelf life and preserving the freshness of products like coffee, snack foods, and cured meats.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Synthesis
Many chemical reagents and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are sensitive to air and moisture. Performing synthesis in an inert environment prevents degradation and unwanted side reactions, ensuring product purity and process repeatability.
Electronics Manufacturing
During solder reflow, an inert atmosphere prevents the oxidation of circuit boards, component leads, and the solder itself. This results in stronger, more reliable solder joints and reduces manufacturing defects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying this principle effectively depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is material integrity at high temperatures: Your key is using an inert atmosphere to shield metals from oxidation, preserving their fundamental structural properties.
- If your primary focus is product shelf life and quality: The crucial action is displacing oxygen from packaging to stop the chemical and biological processes that cause spoilage.
- If your primary focus is process purity and repeatability: The goal is to create a chemically sterile environment that eliminates variable reactions with air, ensuring consistent and predictable results.
Ultimately, mastering the inert atmosphere principle is about taking control of the invisible factors that determine success.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Principle | Replaces reactive gases (e.g., oxygen) with inert gases (e.g., nitrogen, argon) to create a non-reactive environment. |
| Steps | 1. Purging: Displace air with inert gas. 2. Maintaining: Use positive pressure to sustain the inert shield. |
| Applications | Heat treatment (prevents oxidation), food packaging (extends shelf life), chemical synthesis (ensures purity), electronics (improves solder joints). |
| Challenges | Costs of inert gases, system complexity, safety risks (e.g., asphyxiation). |
Take control of your processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions to meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing material integrity and process purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you implement the inert atmosphere principle effectively!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















