The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is not one single value, but a specification that varies significantly by model. While many standard furnaces for general lab work operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), high-performance models designed for advanced materials processing can reliably reach maximum temperatures of 1700°C to 1800°C (3092°F to 3272°F).
The critical insight is not the absolute maximum temperature possible, but understanding that muffle furnaces are built in distinct temperature tiers. Your choice depends entirely on matching the furnace's capability to the specific heat-treatment requirements of your material or process.

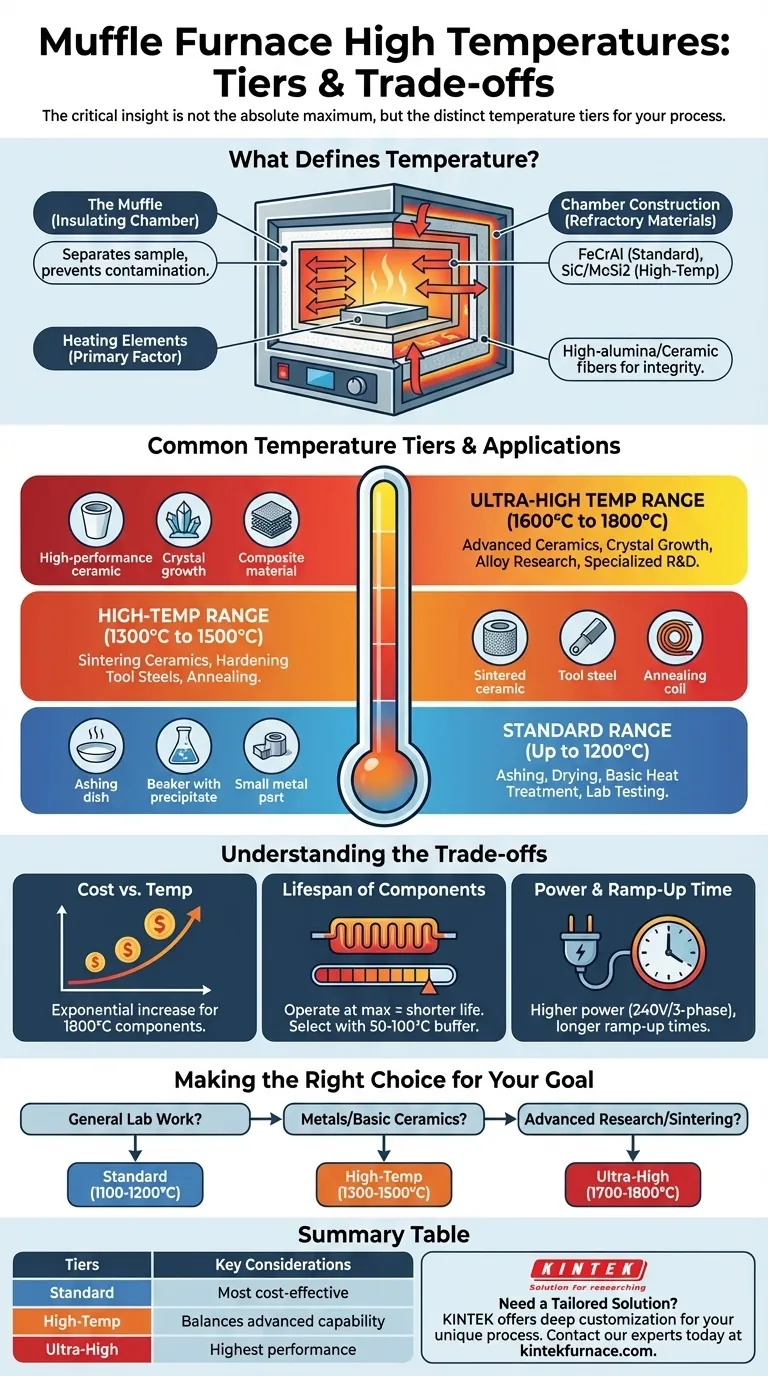
What Defines a Muffle Furnace's Temperature?
A muffle furnace achieves high, uniform temperatures by using electric heating elements to heat a chamber that is isolated from the sample being processed. The maximum achievable temperature is a direct result of its core components and design.
The Role of the Muffle
The defining feature is the "muffle"—an insulating outer chamber, often made of high-purity ceramic or firebrick.
This design separates the material being heated from the heating elements. This prevents contamination from any byproducts and ensures a clean, controlled heating environment.
Heating Elements and Insulation
The type of heating element is the primary factor determining a furnace's maximum temperature.
Standard furnaces (up to ~1200°C) often use iron-chrome-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys. High-temperature models require more exotic elements like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) to reach 1800°C without rapid degradation.
Chamber Construction
The internal chamber must be constructed from refractory materials that can withstand the target temperatures. High-alumina firebricks and advanced ceramic fibers are used to provide structural integrity and excellent thermal insulation, allowing the furnace to reach and maintain its setpoint efficiently.
Common Temperature Tiers and Applications
Muffle furnaces are generally categorized into tiers based on their maximum operating temperature. Understanding these tiers helps align the equipment with the task.
Standard Range (Up to 1200°C)
This is the most common and versatile range. These furnaces are the workhorses of general-purpose laboratories.
Typical applications include ashing food or chemical samples, drying precipitates, heat-treating small steel parts, and conducting basic materials testing.
High-Temperature Range (1300°C to 1500°C)
This tier bridges the gap between general lab work and more specialized industrial or research processes.
These furnaces are used for sintering some ceramics, more advanced metal heat treatments like hardening tool steels, and annealing processes that require temperatures beyond the standard range.
Ultra-High Temperature Range (1600°C to 1800°C)
This is the domain of advanced materials science and specialized production. These furnaces are a significant investment and are used for demanding applications.
This includes firing high-performance ceramics like zirconia, growing crystals, and conducting research on novel alloys and composite materials that have very high melting points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace isn't just about choosing the highest number. Higher temperatures come with significant trade-offs in cost, longevity, and operational requirements.
Cost vs. Temperature
The relationship between maximum temperature and cost is exponential. The specialized heating elements and advanced refractory materials required for 1800°C operation are significantly more expensive than those used in a 1200°C furnace.
Lifespan of Components
Consistently operating a furnace at its absolute maximum temperature will shorten the life of its heating elements and insulation. For longevity, it is wise to select a furnace with a maximum temperature at least 50°C to 100°C higher than your typical operating temperature.
Power and Ramp-Up Time
Higher temperature furnaces require more power to operate, often necessitating 240V or three-phase electrical service. They may also have longer ramp-up times, with some models requiring an hour or more to reach their maximum temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace based on your most frequent and demanding application, building in a small buffer for component longevity.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work like ashing or drying: A standard 1100°C to 1200°C furnace offers the best balance of cost and capability.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating metals or basic ceramic work: Target a furnace with a maximum temperature between 1300°C and 1500°C to handle a wider range of materials.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or high-temperature sintering: You will need an ultra-high temperature furnace capable of reaching 1700°C to 1800°C.
By understanding these temperature tiers and their intended uses, you can select a furnace that precisely meets your technical needs without overpaying for unnecessary capacity.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Tier | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Standard (Up to 1200°C) | Ashing, Drying, Basic Heat Treatment | Most cost-effective, versatile for general lab work |
| High-Temp (1300°C - 1500°C) | Sintering Ceramics, Hardening Tool Steels | Balances advanced capability with cost |
| Ultra-High (1600°C - 1800°C) | Advanced Ceramics, Crystal Growth, Alloy Research | Highest performance for specialized R&D and production |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace Tailored to Your Specific Process?
Selecting the right muffle furnace is critical for your research or production outcomes. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions for diverse laboratories.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. We ensure your furnace precisely meets your unique temperature and application requirements, from standard ashing to ultra-high-temperature sintering.
Let's discuss your project requirements and build the ideal solution for you.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration



















