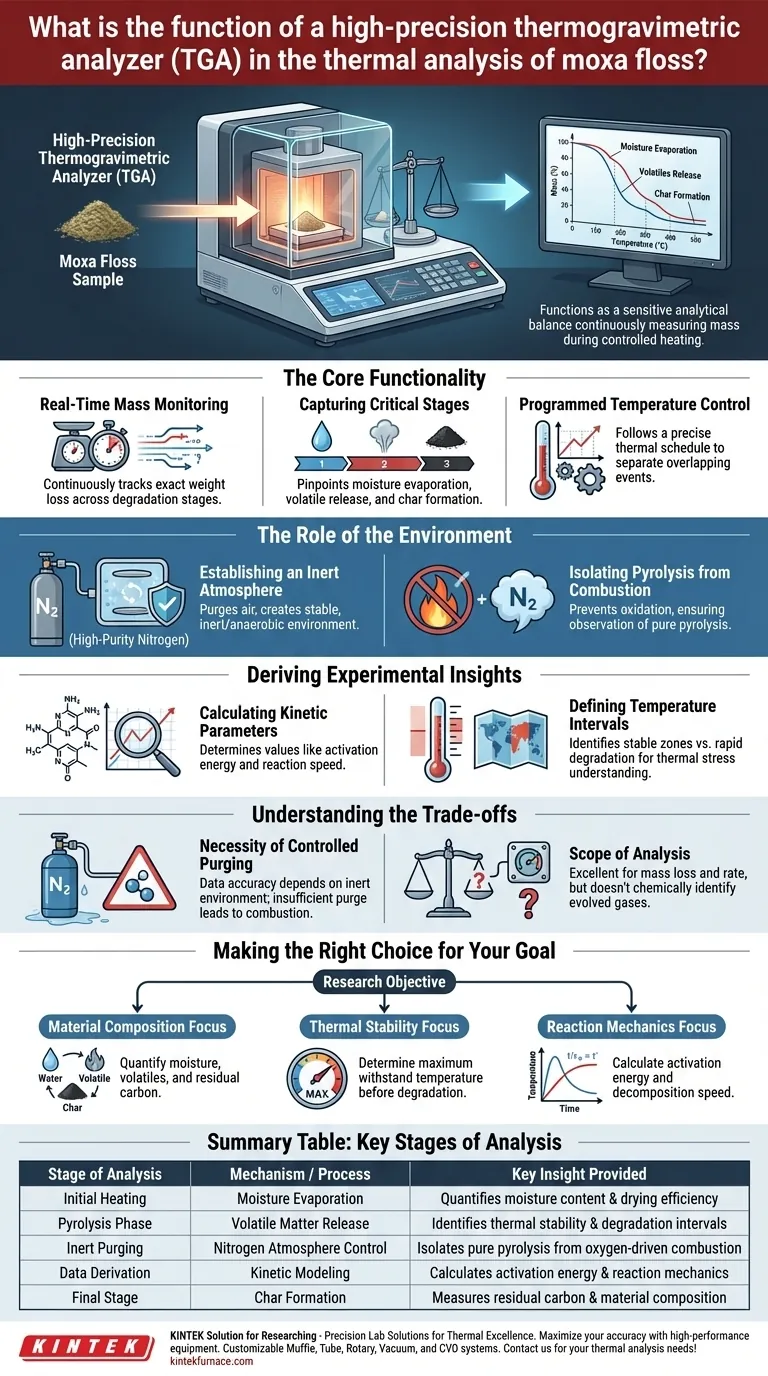
A high-precision thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) functions as a sensitive analytical balance that continuously measures the mass of a moxa floss sample while it is heated under a specific temperature program. By monitoring these weight changes in real-time, the instrument detects and quantifies physical and chemical transitions, including moisture evaporation, the release of volatiles, and the final formation of char.
The analyzer provides the essential baseline data required to characterize the thermal degradation behavior of moxa floss. It transforms raw mass-loss data into actionable insights regarding thermal stability and reaction kinetics.

The Core Functionality
Real-Time Mass Monitoring
The primary mechanism of the TGA is the continuous tracking of mass change. As the moxa floss is heated, the analyzer records the exact weight loss associated with different degradation stages.
Capturing Critical Stages
The device allows researchers to pinpoint exactly when specific changes occur. It accurately captures the distinct phases of moisture evaporation, the rapid release of volatile matter, and the residual stage of char formation.
Programmed Temperature Control
The analysis is not performed at a static temperature but follows a precise programmed thermal schedule. This controlled heating rate is crucial for separating overlapping thermal events, allowing for a clear differentiation between the various components of the moxa floss.
The Role of the Environment
Establishing an Inert Atmosphere
To ensure the data reflects the material's intrinsic properties, high-purity nitrogen is often introduced into the furnace chamber. This purges the air and creates a stable, inert, or anaerobic environment.
Isolating Pyrolysis from Combustion
The protective nitrogen atmosphere prevents the moxa floss from undergoing oxidation or combustion. This ensures the experiment observes a "pure" pyrolysis process, allowing for an accurate analysis of thermal stability without the interference of oxygen-driven burning.
Deriving Experimental Insights
Calculating Kinetic Parameters
Beyond simple weight loss, the data provided by the TGA is used to calculate complex reaction kinetic parameters. Researchers use this data to determine values such as activation energy, which describes the energy barrier that must be overcome for thermal decomposition to occur.
Defining Temperature Intervals
The analyzer helps identify specific temperature intervals where moxa floss is stable versus where it degrades rapidly. This mapping is vital for understanding how the material behaves under different thermal stress conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Controlled Purging
The accuracy of the data is entirely dependent on the quality of the inert environment. If the nitrogen purge is insufficient or interrupted, oxygen may enter the chamber, leading to unwanted combustion and invalidating the pyrolysis data.
Scope of Analysis
While the TGA is excellent for determining how much mass is lost and at what rate, it primarily measures physical weight changes. It provides data on thermal stability, but on its own, it does not chemically identify the specific gases being evolved during the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To get the most out of your thermal analysis data, tailor your focus to your specific research objective:
- If your primary focus is material composition: Analyze the mass loss steps to quantify moisture content, volatile components, and residual carbon (char).
- If your primary focus is thermal stability: Examine the specific temperature intervals to determine the maximum temperature the moxa floss can withstand before degrading.
- If your primary focus is reaction mechanics: Utilize the time and temperature data to calculate the activation energy and understand the speed of the decomposition reaction.
By strictly controlling the atmosphere and temperature, the high-precision thermogravimetric analyzer converts physical sample changes into precise, quantifiable scientific data.
Summary Table:
| Stage of Analysis | Mechanism / Process | Key Insight Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Heating | Moisture Evaporation | Quantifies moisture content & drying efficiency |
| Pyrolysis Phase | Volatile Matter Release | Identifies thermal stability & degradation intervals |
| Inert Purging | Nitrogen Atmosphere Control | Isolates pure pyrolysis from oxygen-driven combustion |
| Data Derivation | Kinetic Modeling | Calculates activation energy & reaction mechanics |
| Final Stage | Char Formation | Measures residual carbon & material composition |
Precision Lab Solutions for Thermal Excellence
Maximize your research accuracy with KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory equipment. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique thermal analysis requirements. Whether you are investigating the kinetic parameters of biomass or conducting complex pyrolysis studies, our systems offer the reliability and control your lab deserves.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing capabilities? Contact KINTEK today and let our experts design the perfect solution for your research goals!
Visual Guide
References
- Yukun Feng, Zhaoyi Zhuang. Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere. DOI: 10.3390/fuels6020048
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Ultra High Vacuum CF Observation Window Flange with High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a graphite plate in microwave cladding? Ensure Purity & Thermal Uniformity for HEA Synthesis
- Why is a stainless steel crucible selected for melting AM60 magnesium alloy? Ensure Alloy Purity and Safety
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity
- What is the role of a vacuum pass-box and a high-capacity vacuum pump? Ensuring Safety in Battery Recycling
- What processes can a circulating water vacuum pump provide negative pressure conditions for? Essential Lab Techniques Explained
- What are the components of the circulating water vacuum pump and their functions? Discover Oil-Free Vacuum Solutions
- What are the advantages of using a Type B thermocouple for 1600°C slag reduction? Precision in Ultra-High Heat
- What is the function of a graphite crucible with a threaded lid? Key to Successful Mg3Sb2 Synthesis













