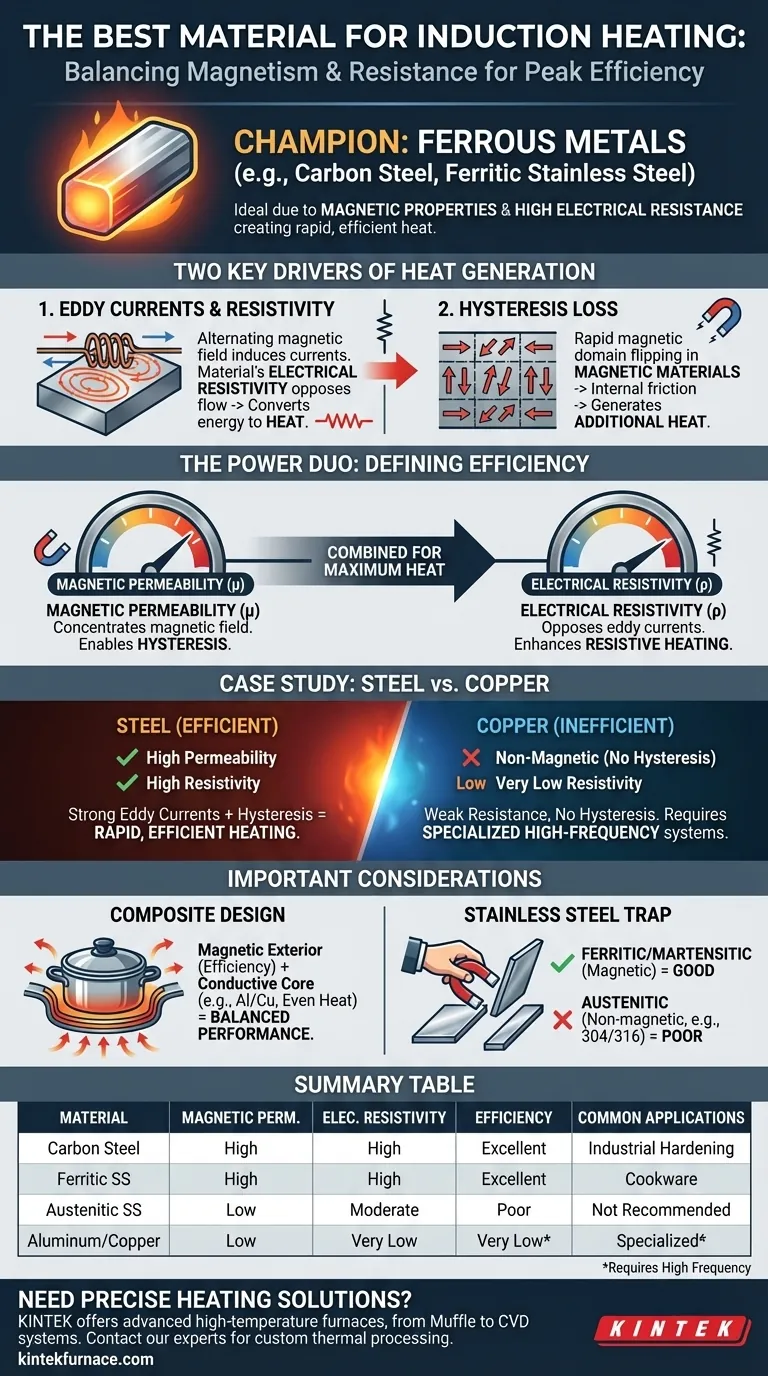
For most applications, the best materials for induction heating are ferrous metals like carbon steel and certain grades of stainless steel. These materials are ideal because their magnetic properties and higher electrical resistance work together to generate heat quickly and efficiently when exposed to an induction field. While other conductive materials can be heated, they are often far less effective.
The "best" material isn't a single metal, but rather a material with the right balance of two key properties: high magnetic permeability and high electrical resistivity. Ferrous metals excel in this regard, making them the default choice for efficient induction heating.

How Induction Heating Actually Works
To understand why some materials are better than others, you must first understand the two heating mechanisms at play in the induction process. The system uses a coil to create a rapidly alternating magnetic field.
The Role of Eddy Currents
This alternating magnetic field induces small, circular electrical currents within the conductive material placed inside it. These are known as eddy currents.
The Importance of Electrical Resistance
The material's natural opposition to the flow of these eddy currents is its electrical resistivity. This resistance converts the electrical energy of the currents directly into heat. Higher resistance means more heat is generated for the same amount of current.
The Power of Hysteresis
For magnetic materials (like iron and steel), there is a powerful secondary heating effect. The rapidly changing magnetic field forces the magnetic domains within the material to flip back and forth millions of times per second. This internal friction, called hysteresis loss, generates significant additional heat.
The Two Properties That Define "Best"
The efficiency of induction heating is almost entirely dependent on two intrinsic properties of the material itself.
Property 1: Magnetic Permeability
Magnetic permeability is a measure of a material's ability to support the formation of a magnetic field. Materials with high permeability, like iron, concentrate the magnetic field lines. This intensifies the eddy currents and enables the powerful hysteresis heating effect, making the process vastly more efficient.
Property 2: Electrical Resistivity
As mentioned, high electrical resistivity is crucial. It ensures that the energy from the induced eddy currents is converted into heat rather than flowing with little opposition.
Case Study: Steel vs. Copper
This is where the difference becomes clear.
Steel has high magnetic permeability and relatively high electrical resistivity. It benefits from both strong eddy currents and hysteresis, making it heat up extremely quickly and efficiently.
Copper, on the other hand, is non-magnetic (zero hysteresis heating) and has extremely low electrical resistivity. Eddy currents are induced, but they flow so easily that very little heat is generated. While copper can be heated with specialized high-frequency induction systems, it is far less energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is rarely about a single metric. You must balance heating efficiency with other practical considerations.
Efficiency vs. Heat Distribution
Carbon steel heats up incredibly fast but can develop hot spots because it doesn't conduct heat evenly across its surface. This is why high-end induction cookware often uses a composite design: a magnetic stainless steel exterior for efficient heating and an aluminum or copper core for superior, even heat distribution.
Why Some Stainless Steel Fails
Not all stainless steel is magnetic. Austenitic stainless steels (like the common 304 or 316 grades) are non-magnetic and perform very poorly for induction. You must use ferritic or martensitic grades (like the 400 series, e.g., 430 grade), which are magnetic. A simple test is to see if a magnet sticks to the material.
The Challenge with Non-Magnetic Metals
Materials like aluminum, brass, and copper are excellent thermal conductors, which is why they are used for traditional pots and pans. For induction, however, this low resistivity works against them. They require more power and higher frequencies to heat effectively, making the process less efficient and more costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" material is always the one that best serves your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid and efficient heating (e.g., industrial hardening, fast-boiling cookware): Choose a magnetic material with high resistivity, such as carbon steel or ferritic stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is uniform temperature (e.g., professional cooking, sensitive bonding): Use a composite material that pairs a magnetic exterior (like steel) with a highly conductive core (like aluminum or copper).
- If you must heat a non-ferrous material (e.g., brazing copper pipes, melting gold): Be prepared to use a specialized, high-frequency induction system and accept that the process will be inherently less energy-efficient.
Understanding the interplay between magnetism and resistance empowers you to select not just a good material, but the optimal material for your specific induction task.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Magnetic Permeability | Electrical Resistivity | Induction Heating Efficiency | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High | High | Excellent | Industrial Hardening, Fast Heating |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | High | High | Excellent | Cookware, Automotive Parts |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel (304, 316) | Low (Non-Magnetic) | Moderate | Poor | Not Recommended for Standard Induction |
| Aluminum | Low (Non-Magnetic) | Low | Low (Requires High Frequency) | Specialized Applications, Composite Cookware |
| Copper | Low (Non-Magnetic) | Very Low | Very Low (Requires High Frequency) | Brazing, Specialized Melting |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace for Your Material Research?
Choosing the right material is only half the battle. You need a heating system that can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability.
Whether you are working with ferrous metals, composites, or specialized non-ferrous materials, we can design a furnace solution that delivers the exact heating performance you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















