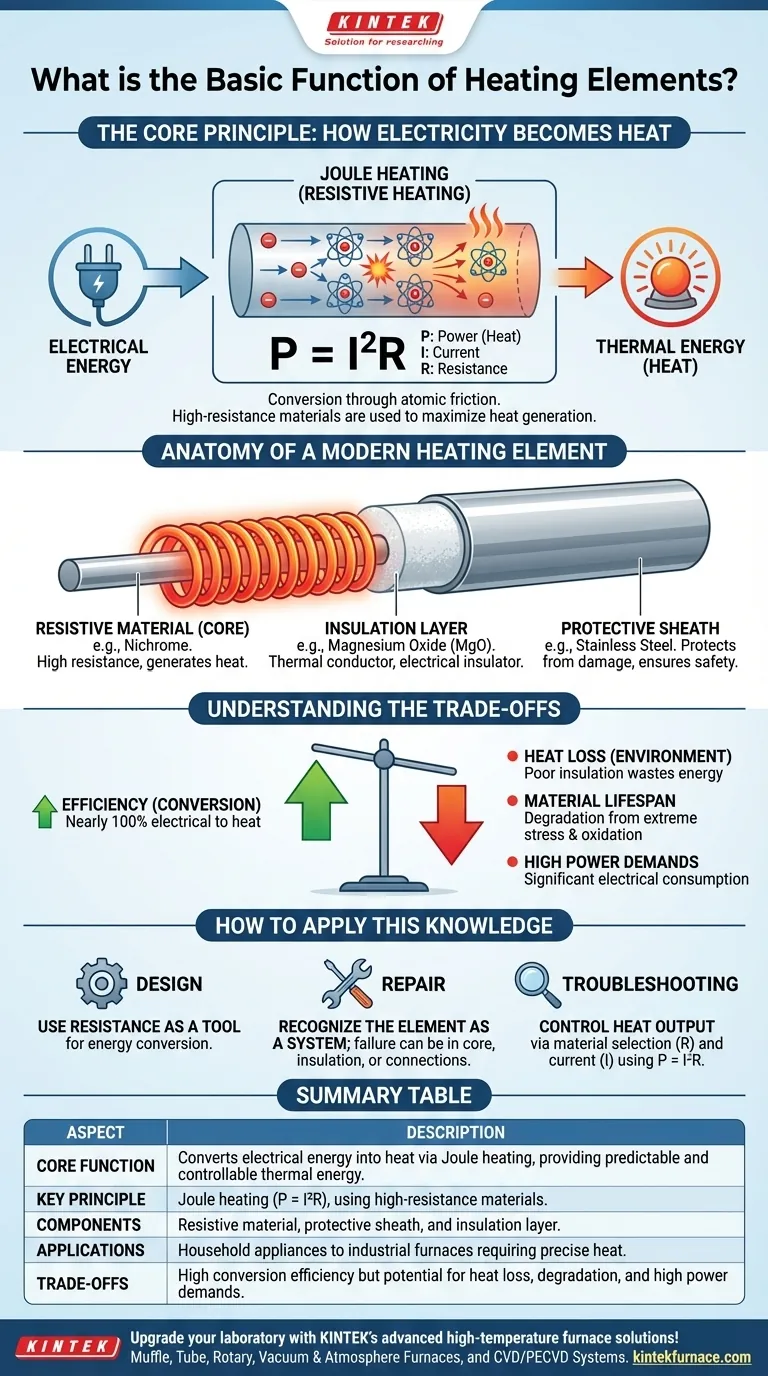
At its most fundamental level, a heating element is a component designed to convert electrical energy into heat. It accomplishes this through a process called Joule heating, where the material's natural resistance to the flow of an electrical current generates thermal energy. This simple principle is the foundation for countless devices, from household toasters to complex industrial furnaces.
The core function of a heating element is not just to produce heat, but to do so in a predictable and controllable way. It harnesses the power of electrical resistance to provide on-demand thermal energy, offering the power of fire with the precision of electricity.
The Core Principle: How Electricity Becomes Heat
The conversion of electricity to heat is a fundamental process in physics. Heating elements are specifically engineered to maximize this effect for practical use.
Introducing Joule Heating
The scientific principle behind a heating element is known as Joule heating, or resistive heating. When an electric current flows through a conductor, the moving electrons collide with the atoms within that material.
These countless microscopic collisions create friction on an atomic scale. This friction manifests as a rise in temperature, transforming the electrical energy into thermal energy, or heat.
The Critical Role of Resistance
Every material has some electrical resistance, which is its natural opposition to the flow of current. While materials like copper are chosen for low resistance to transmit power efficiently, heating elements are made from materials with high resistance.
This high resistance is deliberate. According to Joule's first law (P = I²R), the heat generated (Power) is proportional to the square of the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R). By using a high-resistance material, a significant amount of heat can be generated with a manageable electric current.
The Goal: Controlled, On-Demand Heat
The true function of a heating element is to provide the convenience of fire with the control of an electrical circuit. It allows heat to be applied precisely where needed and can be switched on or off instantly, a level of control that combustion cannot match.
Anatomy of a Modern Heating Element
A functional heating element is more than just a resistive wire. It is a system of components working together to deliver heat safely and efficiently.
The Resistive Material (The Core)
This is the heart of the element, often a wire or ribbon made from a nickel-chrome alloy (Nichrome) or similar material. It is chosen specifically for its high electrical resistance and its ability to withstand repeated high-temperature cycles without degrading quickly.
The Protective Sheath
The resistive core is almost always housed within a protective outer tube, or sheath. This sheath, often made of stainless steel or another durable metal, protects the core from moisture, corrosion, and physical damage. It also ensures user safety.
The Insulation Layer
Between the core and the sheath lies a critical layer of insulation, typically compacted magnesium oxide (MgO) powder. This material is a thermal conductor but an electrical insulator. It efficiently transfers heat from the core to the sheath while preventing the electric current from shorting out.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the function of a heating element involves inherent compromises that are important to understand.
Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
A heating element is nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat. However, the overall efficiency of the appliance depends on how well that heat is directed. Poor insulation or design can lead to significant heat loss to the surrounding environment, wasting energy.
Material Lifespan and Degradation
The very act of generating intense heat puts materials under extreme stress. Over time, the resistive core can oxidize and become brittle, eventually leading to failure. The constant expansion and contraction from heating and cooling also contributes to material fatigue.
High Power Demands
Generating substantial heat requires a significant amount of electrical power. This is why devices like electric ovens, water heaters, and industrial furnaces are among the highest energy consumers in a home or factory, impacting both utility costs and electrical circuit capacity.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the function of a heating element is useful in several contexts, from basic troubleshooting to system design.
- If your primary focus is basic electronics: See resistance not as a flaw, but as a deliberate and powerful tool for converting one form of energy (electrical) into another (thermal).
- If your primary focus is repairing an appliance: Recognize the element as a system where failure can occur in the resistive core, the insulation, or the electrical connections, not just the part that glows red.
- If your primary focus is designing a system: Remember that heat output is governed by the formula P = I²R, making the selection of material resistance and the control of current your primary levers for achieving a target temperature.
Ultimately, the simple conversion of electricity to heat through resistance is one of the most versatile and essential technologies in our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Converts electrical energy into heat via Joule heating, providing predictable and controllable thermal energy. |
| Key Principle | Joule heating (P = I²R), where high-resistance materials generate heat from electric current. |
| Components | Resistive material (e.g., Nichrome), protective sheath, and insulation layer (e.g., magnesium oxide). |
| Applications | Household appliances (toasters), industrial furnaces, and other devices requiring precise heat. |
| Trade-offs | High efficiency in conversion but potential for heat loss, material degradation, and high power demands. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our heating technologies can enhance your research and industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















