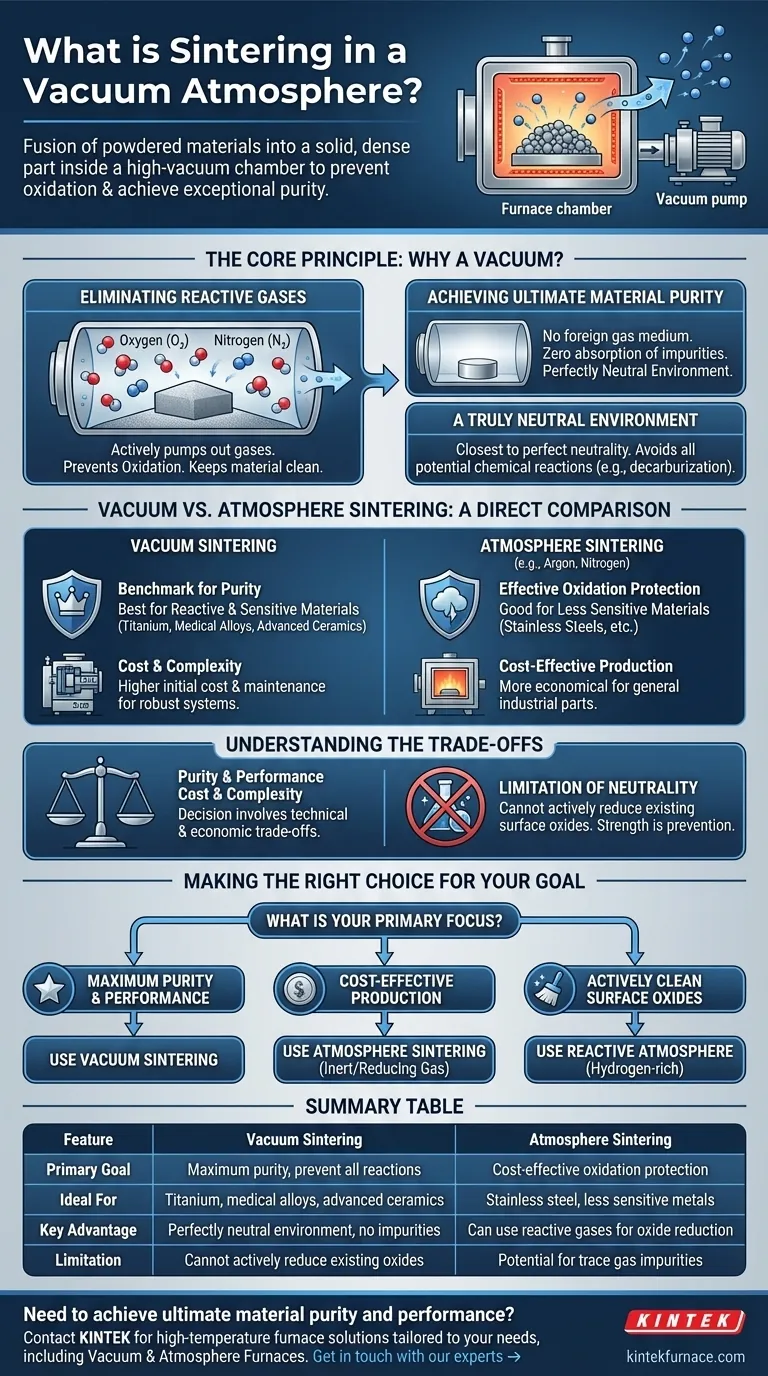
In essence, vacuum sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat to fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense part inside a high-vacuum chamber. This is done below the material's melting point to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions, resulting in an object with exceptionally high purity and superior material properties.
The core purpose of using a vacuum is to create the most neutral atmosphere possible. By removing virtually all gases, you eliminate the risk of the material reacting with its environment, which is critical for sensitive and high-performance applications.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum?
Sintering fundamentally relies on atomic diffusion at high temperatures. The choice of atmosphere during this process directly controls the final chemistry and integrity of the component. A vacuum is not just an empty space; it is an active engineering choice.
Eliminating Reactive Gases
The primary enemy of many metals and ceramics at high temperatures is oxygen. A vacuum furnace actively pumps out oxygen and other reactive gases from the chamber before heating begins.
This complete removal of atmospheric gases prevents oxidation, ensuring the material's surface and internal structure remain clean and uncompromised.
Achieving Ultimate Material Purity
Unlike atmosphere sintering, which introduces an inert or reducing gas (like argon or nitrogen), a vacuum introduces nothing. This absence of a medium is the key to its effectiveness.
Because no foreign gas molecules are present, there is virtually zero chance of them being absorbed into the material. This is crucial for applications where even trace impurities can degrade performance, such as in medical implants or aerospace components.
A Truly Neutral Environment
While inert gases like argon are mostly non-reactive, they are not perfectly neutral. At the high temperatures required for sintering, even inert gases can have subtle interactions with certain sensitive materials.
A vacuum is the closest achievable state to a perfectly neutral environment. It is the ideal choice when any potential for chemical reaction, such as decarburization (carbon loss) or carburization (carbon gain), must be avoided.
Vacuum vs. Atmosphere Sintering: A Direct Comparison
Choosing between a vacuum and a controlled gas atmosphere depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
The Purity Factor
Vacuum sintering is the benchmark for purity. It is the process of choice for highly reactive or sensitive materials like titanium alloys, refractory metals, and certain advanced ceramics.
Atmosphere sintering is highly effective for protecting most metals from gross oxidation but may leave behind trace impurities from the gas itself. It is widely used for less sensitive materials like stainless steels.
The Application and Material
A vacuum environment is essential for parts where material integrity is paramount. This includes components that must withstand extreme stress, temperature, or corrosive environments.
Atmosphere sintering is a robust and often more cost-effective method for a broad range of industrial parts where the absolute highest purity is not the primary design driver.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single process is universally superior. The decision to use vacuum sintering involves clear technical and economic trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex and expensive to build, operate, and maintain than most atmosphere furnaces due to the need for robust vacuum chambers and high-performance pumps.
When a Lower Vacuum Suffices
Not all applications require a high vacuum. Low-vacuum furnaces are a practical compromise for annealing, brazing, and sintering materials like stainless steel, where removing the bulk of the oxygen is sufficient to achieve the desired properties.
The Limitation of "Neutrality"
Sometimes, the sintering atmosphere is intended to be reactive. For example, a hydrogen-rich atmosphere is often used to actively reduce surface oxides on metal powders. A vacuum cannot perform this function; its strength lies in prevention, not active chemical reduction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering environment is a critical decision that directly impacts component performance, lifespan, and cost. Your choice should be guided by the material's sensitivity and your end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: Use vacuum sintering, especially for reactive materials like titanium, medical-grade alloys, or advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production for less sensitive metals: Use atmosphere sintering with an inert or reducing gas like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is to actively clean surface oxides: Use a reactive atmosphere containing hydrogen, as a vacuum can only prevent further oxidation, not reverse it.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering environment is about precisely controlling the material's final properties from the atomic level up.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Sintering | Atmosphere Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximum purity, prevent all reactions | Cost-effective oxidation protection |
| Ideal For | Titanium, medical alloys, advanced ceramics | Stainless steel, less sensitive metals |
| Key Advantage | Perfectly neutral environment, no impurities | Can use reactive gases (e.g., hydrogen) for oxide reduction |
| Limitation | Cannot actively reduce existing oxides | Potential for trace gas impurities |
Need to achieve ultimate material purity and performance?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique sintering requirements. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet the demands of sensitive materials like titanium alloys and advanced ceramics.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum sintering solutions can enhance your component's integrity and lifespan.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery



















