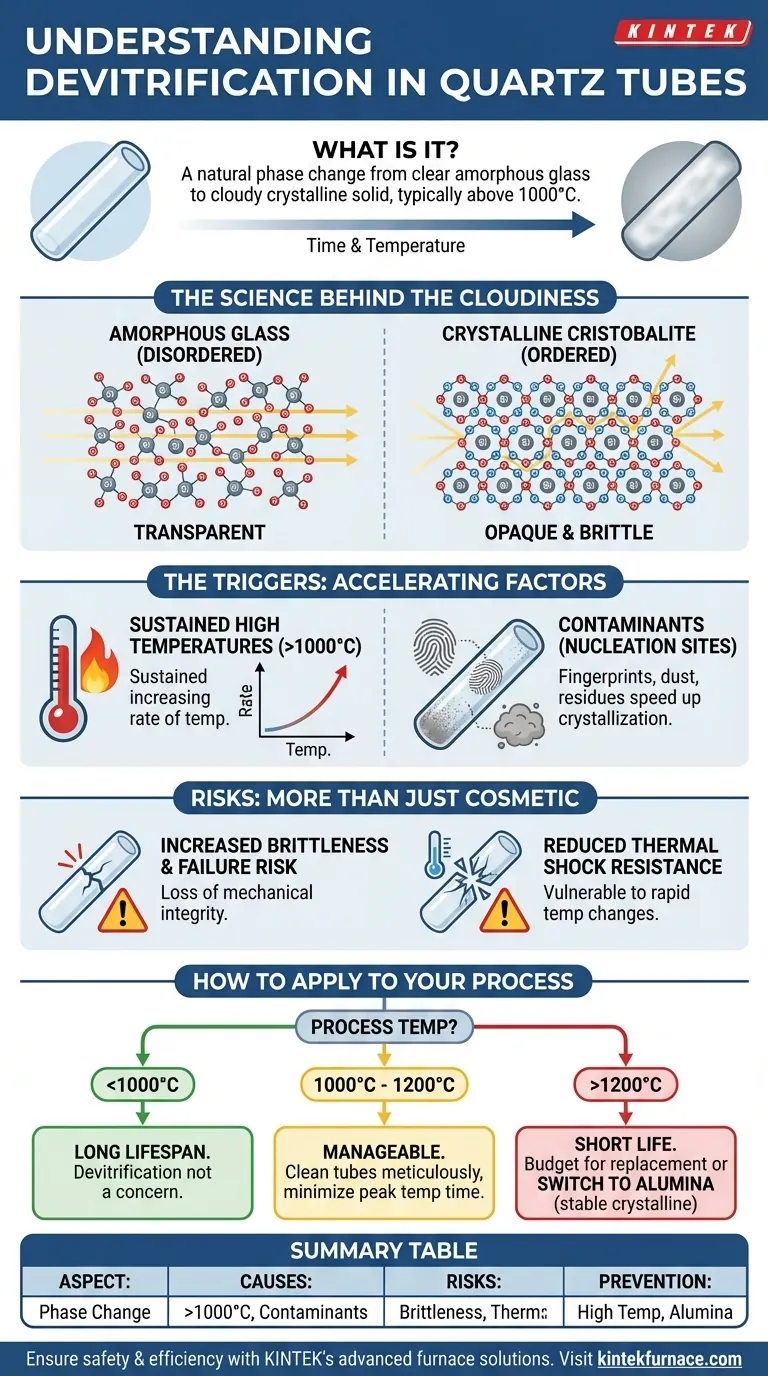
In the context of high-temperature tube furnaces, devitrification is a natural process where a clear quartz glass tube begins to turn opaque and cloudy. This is not a manufacturing defect but an inherent characteristic of quartz when subjected to temperatures typically exceeding 1000°C for extended periods.
Devitrification is a phase change from a disordered, glassy state to an ordered, crystalline state. While it appears as a simple cosmetic change, its true impact is a significant increase in brittleness, making the quartz tube far more susceptible to failure from thermal shock or mechanical stress.

The Science Behind Devitrification
To understand how to manage devitrification, we must first understand what is happening at a molecular level.
From Amorphous Glass to Crystalline Solid
Quartz glass used for furnace tubes has an amorphous structure. This means its silicon and oxygen atoms are arranged in a disordered, non-repeating pattern, which allows light to pass through easily, making it transparent.
When heated to high temperatures, these atoms gain enough energy to rearrange themselves into a more stable, ordered, and repeating pattern. This new structure is a crystalline form of silica known as cristobalite.
Why This Causes Opacity
The new crystalline structure is not a single, perfect crystal but rather a collection of many small crystal grains. The boundaries between these grains scatter light instead of letting it pass through.
This light-scattering effect is what we observe as cloudiness or opacity. The once-transparent tube becomes translucent or fully opaque.
The Triggers: What Accelerates the Process?
Devitrification is inevitable at high temperatures, but its rate is heavily influenced by two key factors.
Sustained High Temperatures
The primary driver is heat. The process typically begins to be noticeable above 1000°C and accelerates significantly as the temperature approaches the upper service limit of quartz (around 1200-1300°C).
Longer exposure times at these temperatures will result in more extensive devitrification.
The Critical Role of Contaminants
Even trace amounts of contaminants on the surface of the quartz can act as nucleation sites, drastically speeding up the crystallization process.
Common culprits include fingerprints (which leave behind alkali salts), dust, and residues from materials being processed. These impurities lower the energy required for the glass-to-crystal transition to begin.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The visual cloudiness is only a symptom. The real dangers of devitrification are mechanical and pose a significant risk to your process and equipment.
Increased Brittleness and Risk of Failure
The cristobalite crystal structure is inherently more brittle than the original amorphous glass. A devitrified tube loses its mechanical integrity and can fracture easily from minor impacts or stress that a new tube would withstand.
Reduced Thermal Shock Resistance
Most critically, the devitrified tube becomes highly vulnerable to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling can cause micro-cracks to form and propagate along the crystal grain boundaries, leading to catastrophic failure of the tube.
Why Quartz is Used Despite This Flaw
Quartz is chosen for its exceptional purity, excellent thermal stability (up to a point), and chemical inertness. It provides a clean, non-reactive environment for sensitive processes. However, this performance comes with the unavoidable trade-off of devitrification at its upper temperature limits. For temperatures consistently above 1200°C, a different material like an alumina ceramic tube is often a better choice, as it is already a stable crystalline material.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your operational strategy should be based on your specific temperature and longevity requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tube lifespan below 1100°C: Meticulously clean the tube before every use to remove all contaminants, and avoid holding it at peak temperature longer than necessary.
- If you must operate consistently near or above 1200°C: Recognize that quartz tube life will be very short. You should budget for frequent replacements or switch to an alumina tube, which is designed for these temperatures.
- If your process remains safely below 1000°C: Devitrification is not a practical concern, and you can expect a long service life from your quartz tube.
Understanding the material science of your equipment is the key to ensuring reliable and safe operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Definition | Phase change from amorphous to crystalline state (cristobalite) in quartz tubes, causing opacity and brittleness. |
| Primary Causes | Sustained temperatures >1000°C and contaminants (e.g., fingerprints, dust) acting as nucleation sites. |
| Main Risks | Increased brittleness, reduced thermal shock resistance, leading to potential tube failure. |
| Prevention Tips | Clean tubes thoroughly, minimize high-temperature exposure, consider alumina tubes for >1200°C operations. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Tube Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our products can help prevent issues like devitrification and enhance your experimental outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















