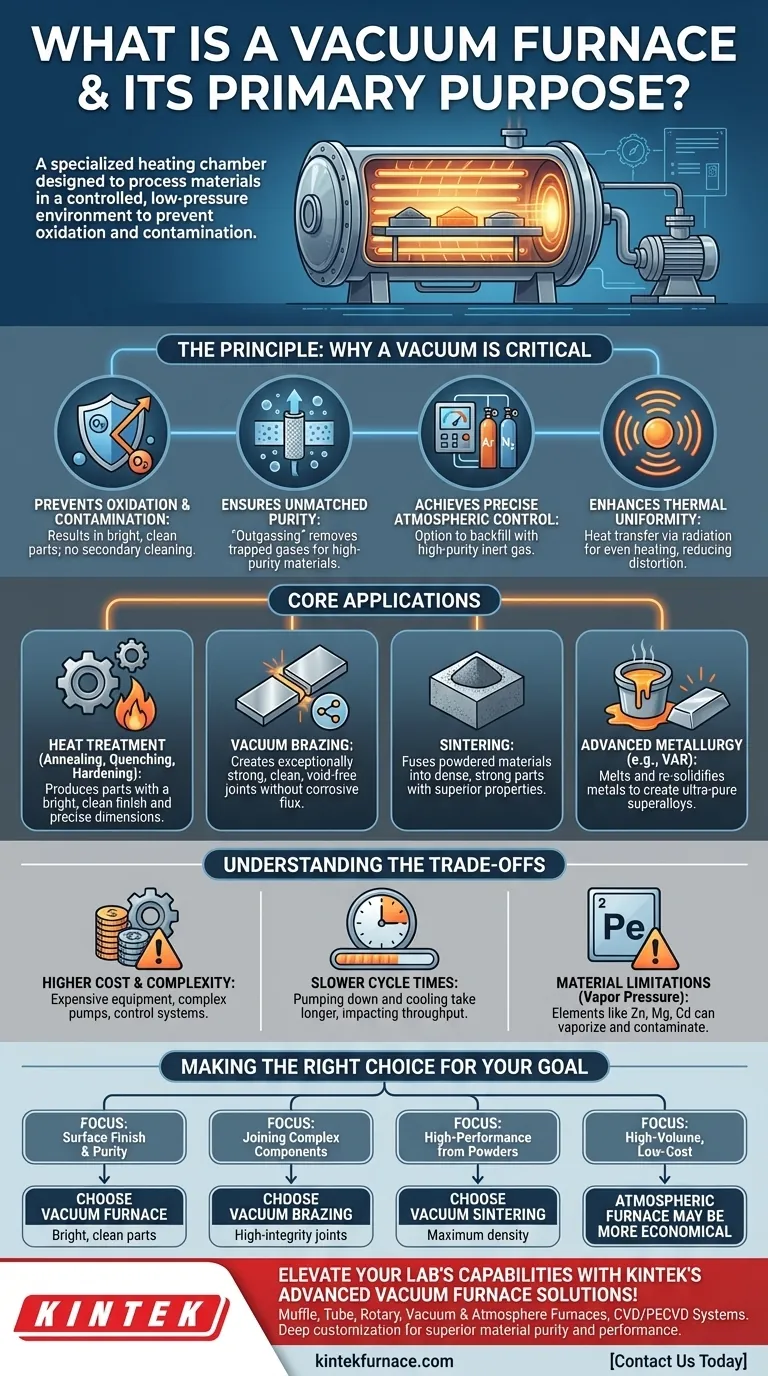
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized heating chamber designed to process materials in a controlled, low-pressure environment. Its primary purpose is to perform thermal processes like heat treatment, brazing, and sintering without the risk of oxidation or contamination from atmospheric gases. This results in cleaner parts, superior material properties, and the ability to perform processes that are impossible in open air.
The defining advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the atmosphere it removes. By eliminating reactive gases, it ensures that the material's integrity is preserved from start to finish, enabling a higher level of quality and performance.

The Principle: Why a Vacuum is the Critical Element
Understanding a vacuum furnace requires shifting focus from the heat to the environment. The vacuum itself is the key enabling technology that delivers several distinct advantages over traditional atmospheric furnaces.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit of removing air is the prevention of oxidation. At high temperatures, metals react with oxygen to form scale and discoloration on the surface.
A vacuum environment eliminates this reaction, resulting in bright, clean parts that often require no secondary cleaning. This also prevents contamination from other atmospheric gases that could negatively affect the material's properties.
Ensuring Unmatched Purity
A vacuum does more than just protect the material's surface. It actively helps purify the material itself by drawing out trapped gases and other volatile impurities from within the workpiece.
This process, known as outgassing, is critical for producing high-purity, dense materials with superior mechanical and thermal properties, especially in demanding applications like aerospace and medical implants.
Achieving Precise Atmospheric Control
Creating a vacuum provides a perfectly clean slate. Once the chamber is evacuated, operators have the option to backfill it with a specific, high-purity inert gas like Argon or Nitrogen.
This gives you absolute control over the material's environment, allowing for specialized processes where a specific inert atmosphere is more beneficial than a pure vacuum.
Enhancing Thermal Uniformity
In a vacuum, heat transfer via convection is eliminated. Heat is transferred almost entirely through radiation, which can result in more uniform heating of the part. This precise and even heating helps prevent thermal stress and distortion, particularly in parts with complex geometries.
Core Applications of Vacuum Furnaces
The unique environment of a vacuum furnace makes it indispensable for several high-value industrial processes.
Heat Treatment (Annealing, Quenching, Hardening)
Standard heat treatments performed under vacuum produce parts with a bright, clean finish. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering benefit from the lack of surface oxidation, preserving the precise dimensions and surface integrity of the finished component.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing is a process for joining two pieces of metal. Vacuum brazing is highly valued because it creates exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints without the need for corrosive flux. This makes it the preferred method for critical components in the aerospace, medical, and semiconductor industries.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (like metals or ceramics) into a solid mass using heat. Vacuum sintering prevents oxidation of the fine powders and promotes better bonding, resulting in parts that are denser, stronger, and have higher performance characteristics.
Advanced Metallurgy and Melting
For the most demanding applications, furnaces like the Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) furnace are used. These systems melt and re-solidify metals under a deep vacuum to remove impurities and create ultra-pure superalloys used in jet engines and power generation turbines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Its advantages come with clear trade-offs.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. They require sophisticated vacuum pumps, control systems, and maintenance routines.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level, running the thermal cycle, and cooling the system often takes longer than an equivalent atmospheric process. This can impact overall throughput.
Material Limitations (Vapor Pressure)
Some elements, such as zinc, magnesium, cadmium, and lead, have a high vapor pressure. At high temperatures under vacuum, these elements can "boil off" or vaporize from the alloy. This can damage the material being processed and contaminate the inside of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on the required outcome for your material and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and purity: Use a vacuum furnace to produce bright, clean parts that eliminate the need for post-process cleaning or acid pickling.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or sensitive components: Use vacuum brazing for fluxless, high-integrity joints required in mission-critical applications.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance parts from powders: Use vacuum sintering to achieve maximum density and superior mechanical properties for items like medical implants or carbide tools.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost heat treatment: An atmospheric furnace may be a more economical choice if a small amount of surface oxidation is acceptable for the application.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize material integrity and final quality over process simplicity and initial cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Process materials in a low-pressure environment to prevent oxidation and contamination, enabling cleaner parts and superior properties. |
| Key Advantages | Prevents oxidation, ensures purity via outgassing, allows precise atmospheric control, and enhances thermal uniformity. |
| Common Applications | Heat treatment (e.g., annealing), vacuum brazing, sintering, and advanced metallurgy (e.g., VAR). |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and complexity, slower cycle times, and material limitations due to vapor pressure. |
Elevate your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior material purity, performance, and efficiency. Ready to transform your thermal processes? Contact us today to discuss how we can help achieve your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















