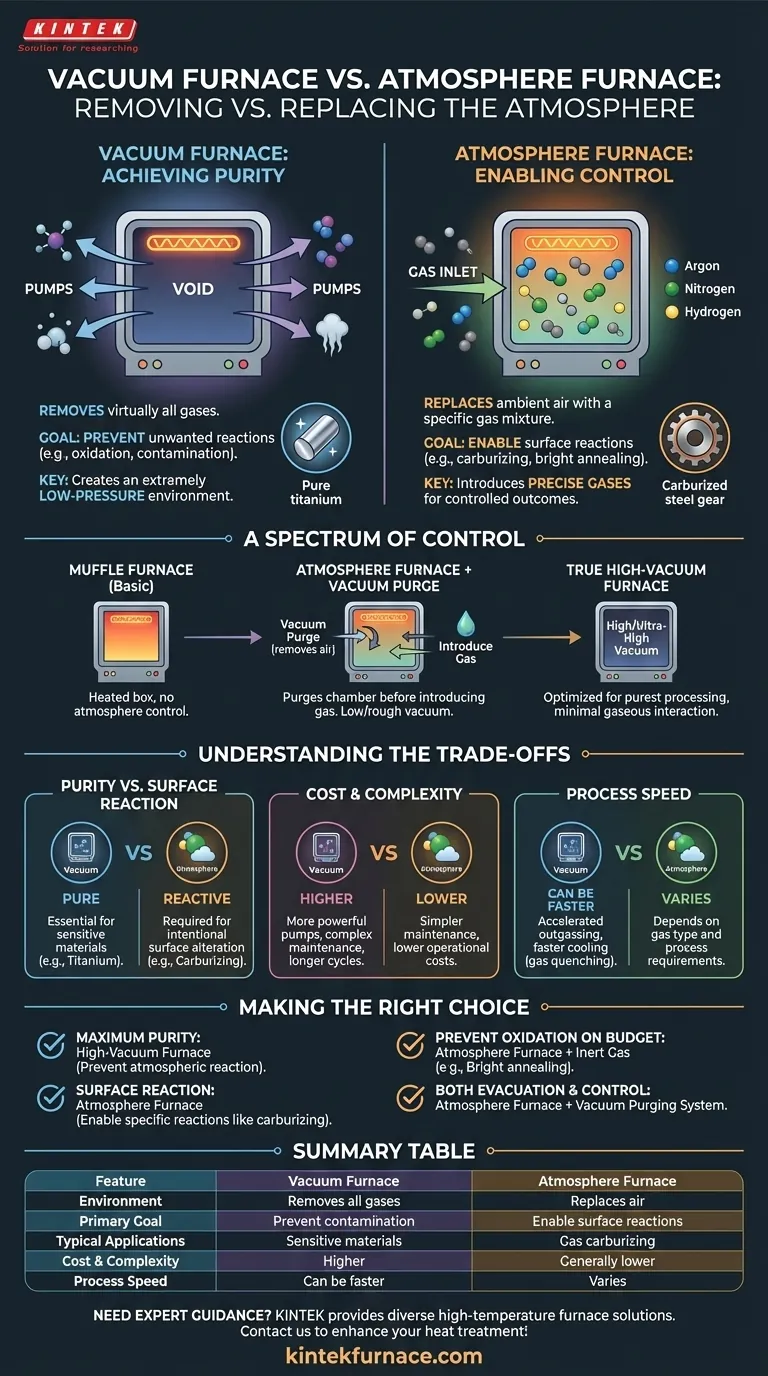
At its core, a vacuum furnace processes materials in an environment devoid of air to prevent contamination, while an atmosphere furnace replaces the air with a specific, controlled gas to enable or prevent certain reactions. The fundamental difference lies in whether you need to remove the atmosphere entirely for ultimate purity or replace it to achieve a specific chemical outcome.
The choice between a vacuum and an atmosphere furnace is not about which is "better," but which environment is required for your process. A vacuum furnace provides purity by creating a void, whereas an atmosphere furnace provides control by introducing a specific gas.
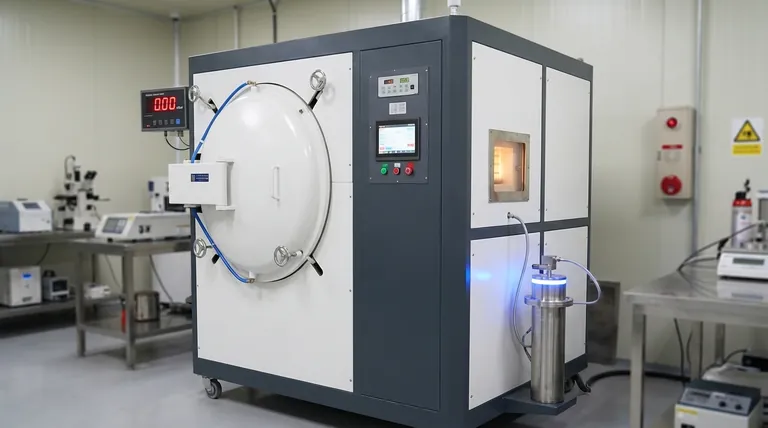

The Fundamental Difference: Removing vs. Replacing the Atmosphere
The primary distinction between these two technologies is how they manage the environment surrounding the material being heated. This single factor dictates their capabilities, applications, and limitations.
How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves Purity
A vacuum furnace uses one or more pumps to remove virtually all gases from a sealed chamber before heating begins. This creates an extremely low-pressure environment.
The primary goal is to prevent unwanted reactions. By removing oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, you eliminate the risk of oxidation, decarburization, and other forms of atmospheric contamination that can compromise a material's integrity at high temperatures.
How an Atmosphere Furnace Enables Control
An atmosphere furnace also starts with a sealed chamber, but its purpose is to replace the ambient air with a precise gas mixture. This is often called atmosphere-controlled heat treatment.
Commonly introduced gases include inert gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation, or reactive gases like hydrogen or methane to actively change the surface of the material, as seen in processes like gas carburizing.
A Spectrum of Control: Not Always a Binary Choice
The line between these furnace types can blur, as many modern systems incorporate features from both. Understanding this spectrum is key to selecting the right equipment.
The Muffle Furnace as a Foundation
At the simplest level, a muffle furnace is just a heated box with a closed chamber (the muffle) that separates the material from the heating elements. Basic muffle furnaces have no atmospheric control.
Atmosphere Furnaces with Vacuum Capability
Many atmosphere furnaces include a vacuum system. However, its purpose is typically to purge the chamber of air before introducing the desired gas mixture.
This ensures the controlled atmosphere is pure and not contaminated by residual air. These systems generally operate at a low or "rough" vacuum and are not designed for high-vacuum processing.
The True High-Vacuum Furnace
A dedicated vacuum furnace is engineered to achieve and maintain much lower pressures (high or ultra-high vacuum). Its entire design, from seals to pumping systems, is optimized for creating the purest possible processing environment, free from any gaseous interaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires a clear understanding of your material, your process goals, and your operational constraints.
Purity vs. Surface Reaction
The most critical factor is the desired outcome. If your material is highly sensitive to any impurity (e.g., titanium, refractory metals), a vacuum furnace is essential to preserve its chemical and mechanical properties.
If your goal is to intentionally alter the material's surface (e.g., hardening steel via carburizing), you explicitly need the reactive gases provided by an atmosphere furnace.
Cost and Complexity
Generally, atmosphere furnaces designed for low-pressure purging and gas backfilling can have lower operational costs and simpler maintenance requirements than high-vacuum systems.
High-vacuum furnaces are more complex instruments. They require more powerful and sophisticated pumping systems, more stringent maintenance, and often have longer cycle times due to the need to achieve and hold very low pressures.
Process Speed
For certain applications, a vacuum furnace can be faster. The vacuum environment can accelerate outgassing from the material and, in some designs, facilitate faster cooling cycles (gas quenching) without the risk of oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific environmental conditions your material requires during heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and preventing any atmospheric reaction: A dedicated high-vacuum furnace is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is enabling a specific surface reaction like carburizing or nitriding: An atmosphere furnace is the only technology that can provide the necessary reactive gases.
- If your primary focus is simply preventing oxidation on a budget (e.g., bright annealing): An atmosphere furnace backfilled with an inexpensive inert gas like nitrogen is the most cost-effective solution.
- If your process requires both an initial evacuation and a subsequent controlled gas environment: You need an atmosphere furnace equipped with a suitable vacuum purging system.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of whether your process needs to happen in nothing, or in something very specific.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Removes all gases for purity | Replaces air with specific gases for control |
| Primary Goal | Prevent contamination (e.g., oxidation) | Enable surface reactions (e.g., carburizing) |
| Typical Applications | Processing sensitive materials like titanium | Processes like gas carburizing or bright annealing |
| Cost & Complexity | Higher due to advanced vacuum systems | Generally lower and simpler |
| Process Speed | Can be faster with accelerated outgassing | Varies based on gas type and process requirements |
Need expert guidance on selecting the ideal furnace for your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your heat treatment processes with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















