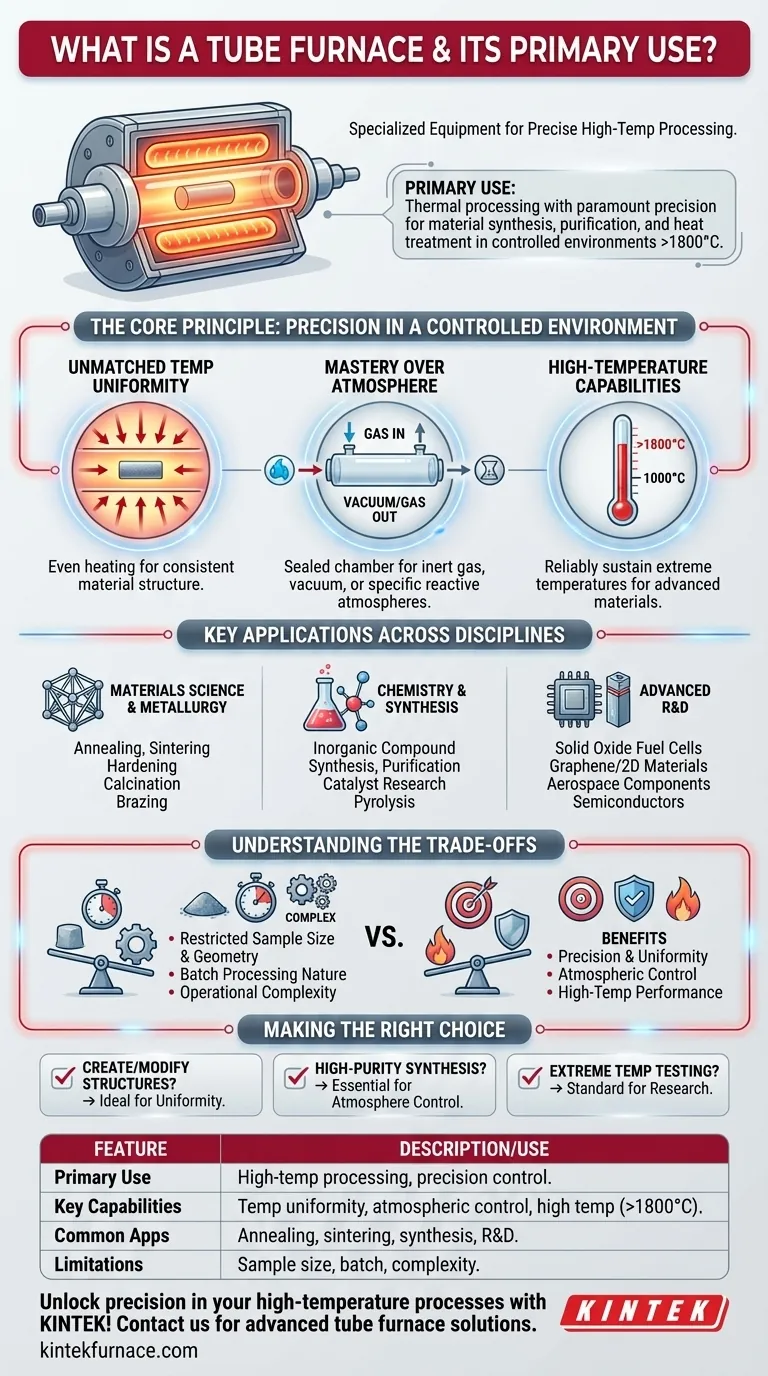
In essence, a tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory and industrial equipment designed to heat small samples to extremely high temperatures within a cylindrical chamber. Its primary use is for thermal processing where precision is paramount, enabling tasks like material synthesis, purification, and heat treatment in a tightly controlled environment that can exceed 1800°C.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its capacity to create a pristine and highly uniform thermal environment. It excels where the process demands absolute control over temperature profiles and atmospheric conditions, making it indispensable for advanced materials science and chemistry.
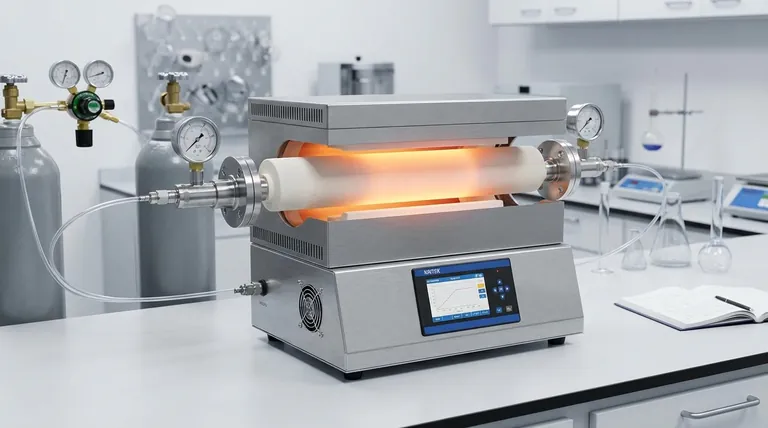

The Core Principle: Precision in a Controlled Environment
While many devices can heat a sample, a tube furnace is engineered for a level of control that standard ovens cannot match. This capability is built on a few key design principles.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber, or "tube," is the defining feature. Heating elements surround this tube, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides.
This uniform thermal exposure is critical for processes like annealing or crystal growth, where even minor temperature variations can compromise the final material's structural integrity.
Mastery Over the Atmosphere
The processing tube can be sealed at both ends, isolating the sample from the outside air.
This allows operators to create a specific atmosphere inside the tube. You can either pull a vacuum to remove reactive gases or introduce a flow of inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. This control is essential for synthesizing air-sensitive compounds or processing high-purity metals.
High-Temperature Capabilities
Tube furnaces are designed for applications that begin where conventional ovens leave off. Many models can reliably sustain temperatures from 1000°C to over 1800°C.
This high-temperature range is necessary for working with advanced ceramics, alloys, and composite materials, including sintering metallic powders or growing synthetic crystals.
Key Applications Across Disciplines
The combination of precision heating and atmospheric control makes the tube furnace a versatile tool in nearly every technical field that involves creating or testing materials.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
This is the most common domain for tube furnaces. They are used to fundamentally alter a material's physical properties.
Key processes include annealing (to increase ductility), sintering (to fuse powders into a solid mass), hardening, calcination, and brazing.
Chemistry and Synthesis
In chemistry, sample purity is paramount. The controlled atmosphere of a tube furnace prevents unwanted side-reactions and contamination.
It is used for the synthesis and purification of inorganic compounds, catalyst research, and processes like pyrolysis where material is thermally decomposed in an inert atmosphere.
Advanced Research and Development
Tube furnaces are integral to innovation in emerging technologies.
They are used in the development of solid oxide fuel cells, the production of graphene and other 2D materials, testing aerospace components, and fabricating next-generation semiconductors and batteries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its capabilities, a tube furnace is a specialized instrument, not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sample Size and Geometry
The primary limitation is throughput. The cylindrical chamber restricts the size and shape of the sample, making tube furnaces ideal for research-scale batches or small, high-value components, but poorly suited for bulk manufacturing.
Batch Processing Nature
Most tube furnace operations are batch processes. Loading, processing, cooling, and unloading a single sample or a small set of samples takes time. This contrasts with continuous furnaces used in large-scale industrial production.
Operational Complexity
Achieving precise results requires knowledge. Operators must understand how to program temperature profiles, manage gas flow rates, and handle samples at extreme temperatures. They are sophisticated tools that require more training than a simple lab oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Deciding whether a tube furnace is the appropriate tool comes down to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating or modifying material structures: A tube furnace is the correct choice for processes like annealing, sintering, or crystal growth where thermal uniformity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical synthesis: The ability to control the atmosphere makes a tube furnace essential for preventing contamination and unwanted oxidation.
- If your primary focus is testing material properties at extreme temperatures: The precise temperature control and high operational range make it the standard for catalyst research and developing advanced materials like ceramics and alloys.
Ultimately, selecting a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize precision and environmental control over sheer processing volume.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-temperature thermal processing with precision control for material synthesis, purification, and heat treatment |
| Key Capabilities | Temperature uniformity, atmospheric control (vacuum/inert gas), high-temperature operation (up to 1800°C) |
| Common Applications | Annealing, sintering, chemical synthesis, crystal growth, catalyst research, advanced materials development |
| Limitations | Restricted sample size, batch processing, operational complexity requiring training |
Unlock precision in your high-temperature processes with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced tube furnace solutions tailored for materials science, chemistry, and R&D labs. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















