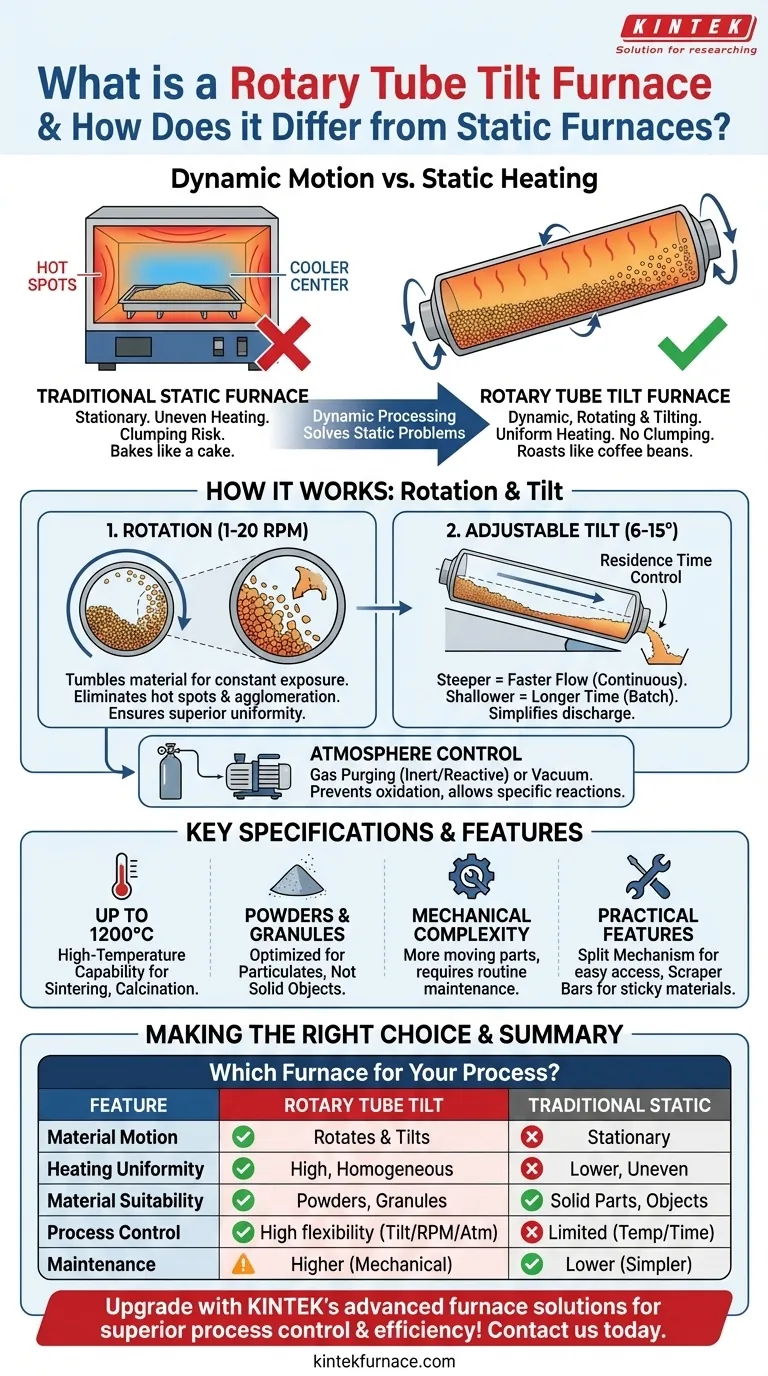
At its core, a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is a dynamic thermal processing system designed specifically for powders, granules, and other particulate materials. Unlike a traditional static furnace that heats stationary items, this furnace uses a constantly rotating and tilting tube. This continuous motion is the key difference, ensuring every particle is uniformly heated, mixed, and processed.
The primary advantage is not just heating, but active material handling. A static furnace bakes material like a cake, while a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace roasts it like coffee beans, guaranteeing every surface gets consistent exposure and preventing clumping or hot spots.

How Dynamic Processing Solves Static Problems
The fundamental challenge with heating powders or granules in a static furnace is non-uniformity. The material at the edges gets hotter than the material in the center, leading to inconsistent product quality, agglomeration (clumping), and inefficient energy use. A Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace directly solves these issues through its two primary functions: rotation and tilt.
The Role of Rotation: Achieving True Uniformity
The slow, constant rotation of the furnace tube forces the material to gently tumble. This movement continuously exposes new particles to the heat source.
This action eliminates hot spots and ensures that thermal energy is transferred evenly throughout the entire batch. The result is superior temperature uniformity, which is critical for sensitive processes like calcination or material synthesis where precise conditions are paramount.
Rotation also physically breaks up potential clumps, preventing agglomeration and ensuring the final product remains a free-flowing powder.
The Function of Tilt: Controlling Residence Time
The ability to tilt the furnace tube provides precise control over how long the material spends in the heated zone, a factor known as residence time.
A steeper angle results in a faster flow-through, ideal for continuous processing or drying. A shallower angle increases the residence time, allowing for more thorough thermal treatment in batch processes.
This tilt function also makes discharging the material incredibly simple and efficient, as the product can be poured out smoothly once the process is complete.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
These furnaces are designed for flexibility. They typically support gas purging to introduce inert or reactive gases, or they can operate under a vacuum. This allows for a wide range of chemical reactions and material treatments in a controlled atmospheric environment, preventing unwanted oxidation or contamination.
Key Operational Specifications
The design of a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is optimized for control and efficiency. Understanding its key specifications reveals its capabilities.
Low RPM Rotation (1-20 RPM)
The rotation speed is intentionally low. This ensures gentle handling of delicate materials while still providing the thorough mixing needed for uniform heat exposure.
Adjustable Tilt Angle (6-15 Degrees)
This specific range of tilt offers fine-tuned control over material flow and residence time, allowing operators to adapt the process to different materials and desired outcomes.
High-Temperature Capability (Up to 1200°C)
With a maximum operating temperature of 1200°C, these furnaces are suitable for a vast majority of industrial and laboratory applications, including sintering, thermal decomposition, and carbonization.
Practical Design Features
Many models include a split mechanism, which allows the furnace to be opened for easy loading and unloading of the processing tube. Internal scraper bars can also be included to assist with mixing sticky materials and prevent them from adhering to the tube walls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this furnace is a specialized tool. Its advantages come with considerations that make it different from a general-purpose static furnace.
Mechanical Complexity
The addition of a motor for rotation and a mechanism for tilting introduces more moving parts compared to a simple box furnace. This inherently means there is a greater need for routine maintenance to ensure long-term reliability.
Material Suitability
This furnace is purpose-built for powders, granules, and small particulates. It is not suitable for processing large, solid objects or components that cannot be tumbled.
Process Integration
While offering both batch and continuous operation, integrating a rotary furnace into a continuous production line requires more sophisticated feeding and collection systems compared to simply loading a tray into a static furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision between a static and a rotary tube tilt furnace depends entirely on the nature of your material and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, homogeneous powders: The superior mixing and uniform heating of a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of solid parts or objects: A traditional static furnace is more practical, cost-effective, and easier to operate.
- If your primary focus is precise process control and flexibility: The adjustable rotation, tilt, and atmosphere control of a rotary furnace offer unparalleled command over the processing environment.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace requires you to think beyond temperature and consider the physical dynamics of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace | Traditional Static Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Material Motion | Rotates and tilts for continuous mixing | Stationary, no movement |
| Heating Uniformity | High, eliminates hot spots and clumping | Lower, prone to uneven heating |
| Material Suitability | Powders, granules, small particulates | Solid parts, objects, or stationary items |
| Process Control | Adjustable rotation, tilt, and atmosphere for flexibility | Limited to temperature and time settings |
| Maintenance | Higher due to mechanical complexity | Lower, fewer moving parts |
| Applications | Calcination, sintering, material synthesis | Simple heat treatment, baking |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Tube Tilt Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with powders, granules, or other materials, our solutions ensure uniform heating, efficient mixing, and superior process control. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















