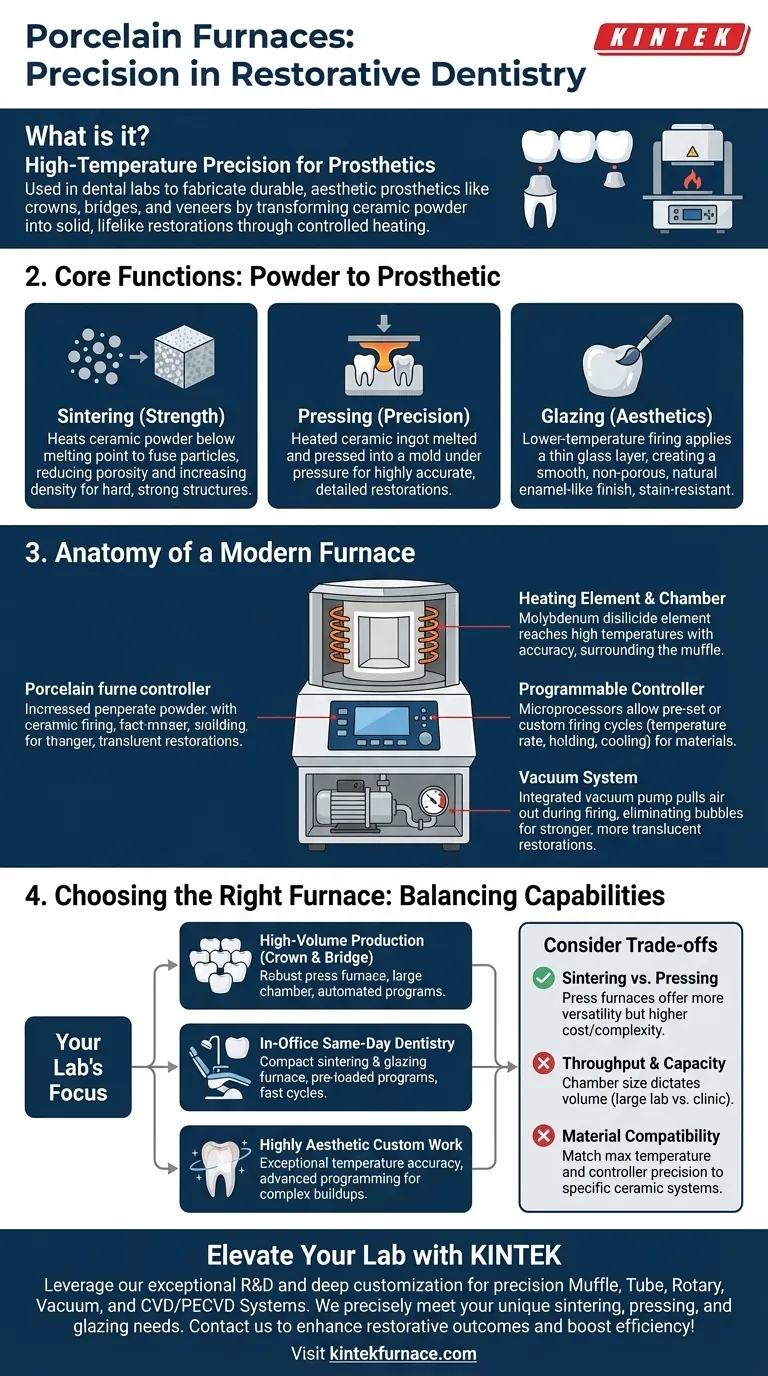
In the field of restorative dentistry, a porcelain furnace is a high-temperature oven used in dental laboratories to fabricate durable and aesthetic dental prosthetics. Its primary function is to transform dental ceramic materials, often in powder form, into solid, lifelike restorations like crowns, bridges, and veneers through a precisely controlled heating process.
A porcelain furnace is not merely a heater; it is a precision instrument essential for modern dentistry. It enables technicians to control the physical properties and aesthetic qualities of ceramic materials, turning raw powder into functional and natural-looking dental restorations.
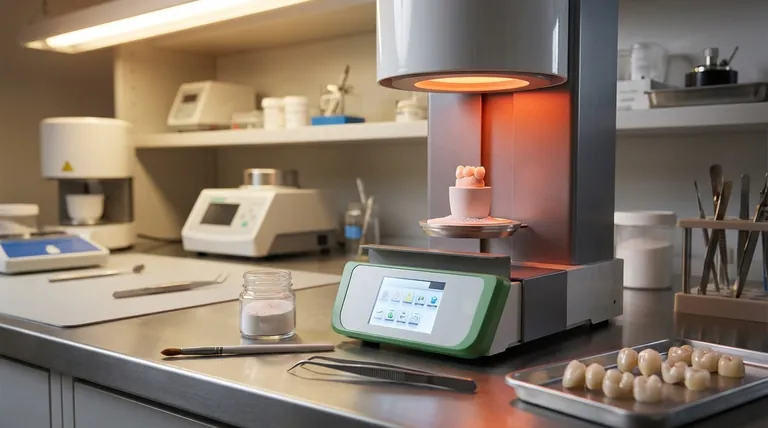

The Core Function: Transforming Powder into Prosthetics
A porcelain furnace executes several critical thermal processes. Each one is designed to manipulate the ceramic material at a molecular level to achieve a specific outcome for the final restoration.
Sintering: The Foundation of Strength
Sintering is the fundamental process. The furnace heats ceramic powder to a temperature just below its melting point.
This causes the individual particles to fuse, drastically reducing porosity and increasing the material's density. The result is a hard, strong structure that can withstand the forces of chewing.
Pressing: Achieving Anatomical Precision
Many modern furnaces also have pressing capabilities. In this process, a heated ceramic ingot is melted and then "pressed" into a mold under pressure.
This method is ideal for creating highly accurate and detailed restorations like full-contour crowns and inlays, ensuring a perfect fit for the patient.
Glazing: The Final Aesthetic Touch
Glazing is a final, lower-temperature firing cycle. A thin layer of glass is applied to the sintered restoration and fired.
This creates a smooth, non-porous, and lustrous surface that mimics the appearance of natural tooth enamel while also making the restoration more stain-resistant and biocompatible.
Anatomy of a Modern Porcelain Furnace
Understanding the key components of a furnace reveals why it is a piece of precision equipment rather than a simple oven.
The Heating Element and Chamber
The heart of the furnace is the heating element, often made from materials like molybdenum disilicide, which can reach and maintain extremely high temperatures with great accuracy. This element surrounds a muffle, or heating chamber, where the restorations are placed.
The Programmable Controller
Modern furnaces are governed by sophisticated microprocessors. Technicians can run pre-set programs for specific materials or create custom firing cycles to control the rate of temperature increase, holding times, and cooling.
The Vacuum System
A critical feature is the integrated vacuum pump. Firing ceramics under a vacuum pulls air out from between the ceramic particles before they fuse. This eliminates bubbles and porosity, resulting in a significantly stronger and more translucent restoration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capabilities with the specific needs of a dental lab or clinic. Not all furnaces are created equal.
Sintering vs. Pressing Capabilities
Some furnaces are designed exclusively for sintering and glazing, while others are combination "press" furnaces. A press furnace offers greater versatility but often comes at a higher cost and complexity.
Throughput and Capacity
The size of the heating chamber determines how many restorations can be fired at once. A high-volume production lab requires a furnace with a large capacity, whereas a smaller in-office clinic might prioritize a compact, faster unit for single crowns.
Material Compatibility
Different ceramic systems (e.g., zirconia, lithium disilicate) have unique firing requirements. The furnace's maximum temperature and the precision of its controller must be compatible with the materials you intend to use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the primary type of work your laboratory or practice performs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume crown and bridge production: A robust press furnace with a large firing chamber and repeatable, automated programs is the most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is in-office, same-day dentistry: A compact, user-friendly sintering and glazing furnace with pre-loaded programs for common material blocks is essential.
- If your primary focus is highly aesthetic, custom anterior work: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional temperature accuracy and advanced programming for complex, multi-layered buildups and custom glazing.
Ultimately, the porcelain furnace is the critical link that translates a technician's skill and advanced materials into a successful clinical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Heats ceramic powder below melting point | Fuses particles for strength and reduced porosity |
| Pressing | Melts and presses ceramic ingot into mold | Creates precise, detailed restorations like crowns |
| Glazing | Applies and fires a glass layer at low temperature | Adds smooth, stain-resistant, enamel-like finish |
| Component | Description | Benefit |
| Heating Element | Molybdenum disilicide for high temperatures | Ensures accurate, controlled heating cycles |
| Programmable Controller | Microprocessor for custom firing programs | Allows precise control of temperature and timing |
| Vacuum System | Removes air during firing | Eliminates bubbles for stronger, translucent results |
Elevate your dental lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs for sintering, pressing, and glazing dental ceramics. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your restorative dentistry outcomes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab



















