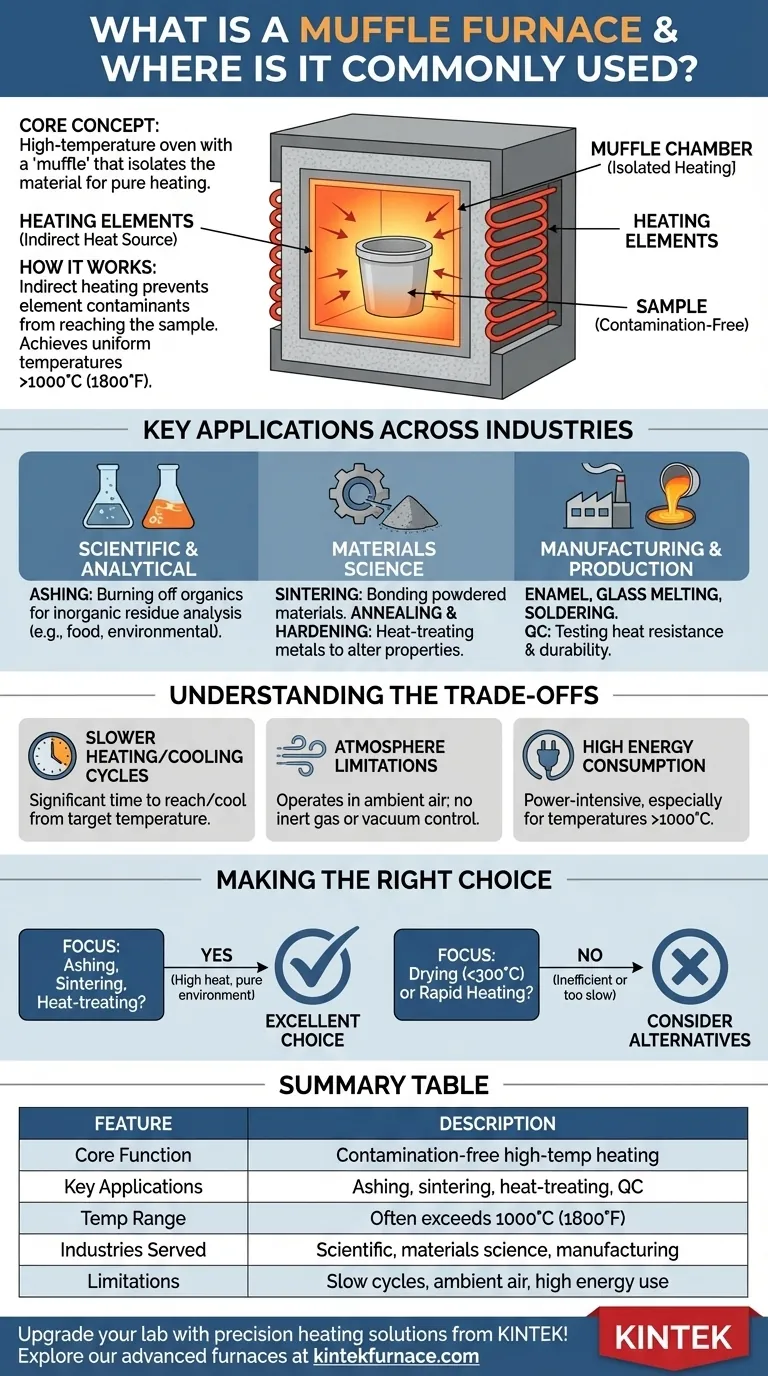
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that specializes in heating materials within a controlled, contamination-free environment. It is a fundamental piece of equipment in research labs and industrial settings, used for applications ranging from scientific analysis and materials testing to creating ceramics and heat-treating metals.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its design, which isolates the material being heated from the direct influence of the heating elements. This separation—the 'muffle'—is what guarantees a pure atmosphere, making it indispensable for processes where sample contamination is unacceptable.

How a Muffle Furnace Works
A standard oven heats a chamber, but a muffle furnace takes this a step further by building the chamber out of insulating material that contains hidden heating coils. This design is central to its function.
The Principle of the 'Muffle'
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated chamber that separates the workload from the heating elements. Think of it as cooking in a covered ceramic pot inside an oven, rather than placing food directly on a grill.
The heating elements heat the muffle chamber from the outside, and the chamber then radiates that heat evenly to the sample inside. This indirect heating prevents any contaminants from the heating elements from reaching the sample.
Achieving High, Uniform Temperatures
The chamber is constructed from high-density ceramic or other insulating materials that can withstand extreme temperatures while preventing heat loss.
This efficient insulation, combined with modern digital controllers, allows the furnace to achieve and maintain very precise and uniform temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C (1800°F).
Key Applications Across Industries
The muffle furnace's ability to provide pure, high-temperature heat makes it a versatile tool used in a wide array of fields.
For Scientific and Analytical Testing
This is one of the most common uses. In environmental science, food science, and chemistry, muffle furnaces are used for ashing.
Ashing is the process of burning off all organic material in a sample to precisely measure the weight of the inorganic residue (ash). This is critical for quality control and compositional analysis.
For Materials Science and Development
Researchers use muffle furnaces for sintering, which involves heating powdered materials until their particles bond to create a solid object, such as a technical ceramic.
It is also essential for annealing and hardening metals, processes that involve carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter a material's physical properties.
For Manufacturing and Production
In industrial settings, muffle furnaces are used for creating enamel coatings on metal, melting small batches of glass, and soldering components.
They also serve a vital quality control function, allowing manufacturers to test the heat resistance and durability of finished parts and materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is not the right tool for every heating task. Its design comes with specific limitations.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The same heavy insulation that makes a muffle furnace so efficient also means it takes a significant amount of time to reach its target temperature and to cool down. It is not suited for processes that require rapid temperature changes.
Atmosphere Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. While it prevents contamination from the heating elements, it does not control the gas atmosphere itself. Processes requiring an inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum demand specialized—and more complex—furnace models.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures over 1000°C requires a substantial amount of energy. These furnaces are power-intensive pieces of equipment, especially larger industrial units.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a muffle furnace depends entirely on whether your process requires its unique combination of high heat and a pure environment.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample (ashing): A muffle furnace is the industry-standard tool for this exact purpose.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating or sintering small metal and ceramic parts: The precise, uniform, and non-contaminating heat of a muffle furnace makes it an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is simply drying a sample or heating to low temperatures (below 300°C): A standard laboratory oven is a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-volume heating: You may need to consider alternative industrial ovens, as the heat-up and cool-down cycles of a muffle furnace can be slow.
Ultimately, understanding its core principle of isolated heating is the key to deploying a muffle furnace effectively in your lab or production line.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | High-temperature oven for contamination-free heating |
| Key Applications | Ashing, sintering, annealing, hardening, quality control |
| Temperature Range | Often exceeds 1000°C (1800°F) |
| Industries Served | Scientific research, materials science, manufacturing |
| Limitations | Slower heating/cooling, ambient air only, high energy use |
Upgrade your lab with precision heating solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















