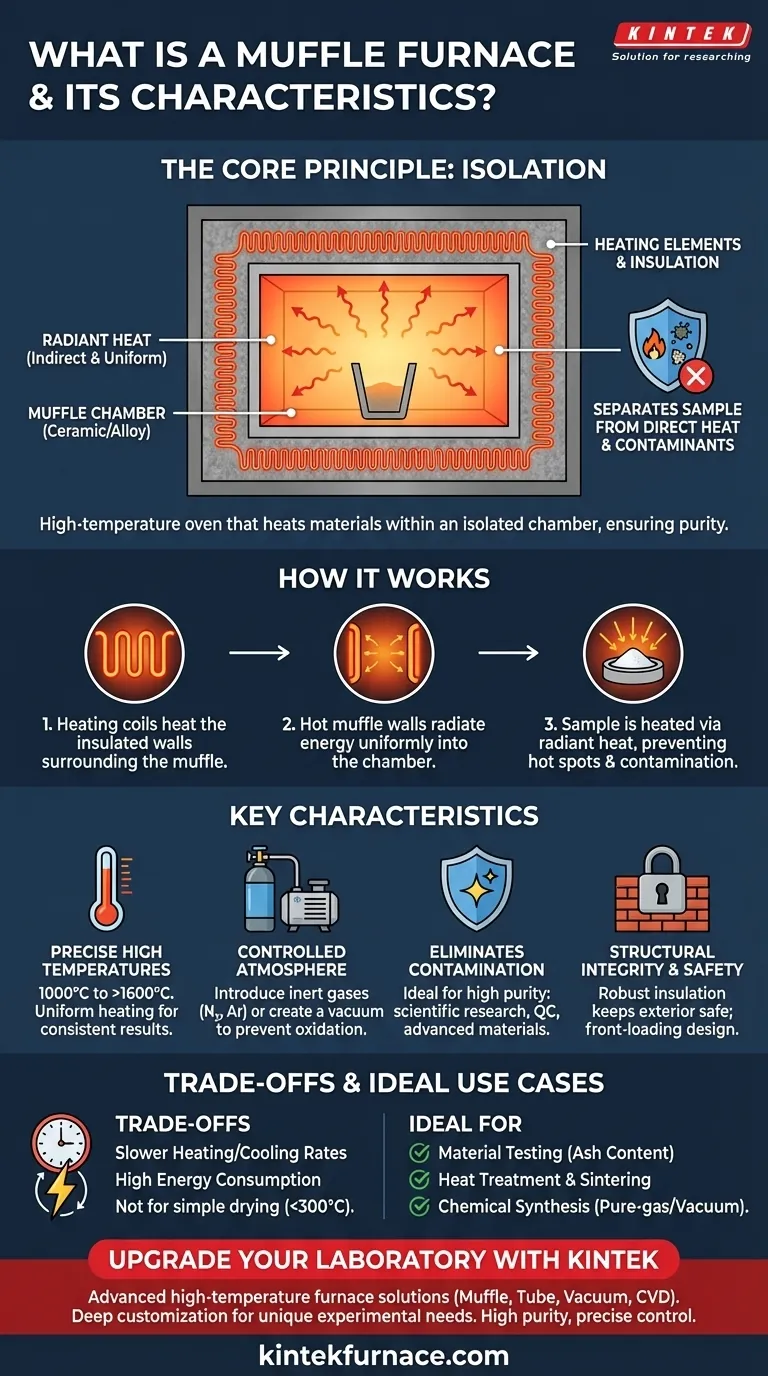
At its core, a muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven that heats materials within an isolated chamber. This design intentionally separates the material being heated from the direct heat source and any potential contaminants, such as fuel byproducts or combustion gases. This principle of isolation is what makes it indispensable for applications demanding high purity and precise thermal processing in laboratory and industrial settings.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is not just its high heat, but its principle of isolation. By creating a barrier between the sample and the heating elements, it guarantees that the only variable affecting the material is a pure, precisely controlled temperature.
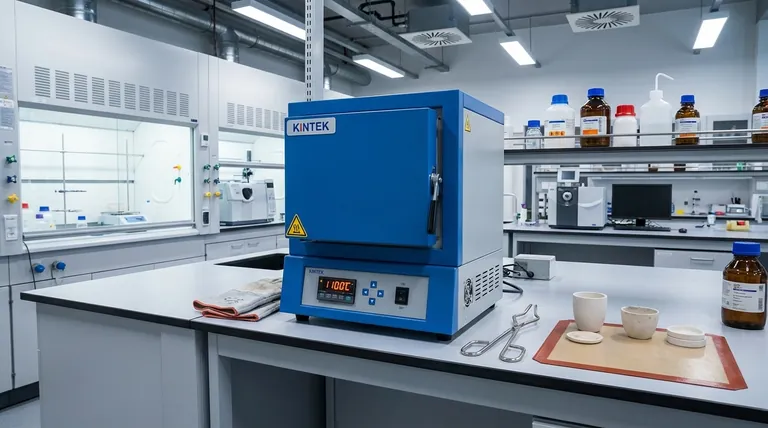

The Fundamental Principle: Heating Through Isolation
The name "muffle furnace" directly describes its function. The "muffle" is the core of its design—a specialized chamber that shields the contents from the outside environment and the heat source itself.
What is the "Muffle"?
The muffle is the internal chamber, typically made of high-temperature resistant ceramic or alloy, that contains the sample. This chamber is enclosed by insulation and heating elements.
The design ensures that the sample is never in direct contact with the heating coils or, in older designs, an open flame.
How Heat is Transferred
In modern electric muffle furnaces, heating coils are embedded within the surrounding insulation. These coils heat the walls of the muffle chamber to a very high temperature.
The hot walls then transfer this energy to the sample inside primarily through radiant heat. This indirect method provides extremely uniform heating, preventing the hot spots that can occur with direct contact.
The Benefit: Eliminating Contamination
This isolation is the furnace's most critical advantage. By separating the sample, you prevent byproducts from fuel, combustion, or even microscopic flakes from the heating element itself from corrupting the material.
This level of purity is non-negotiable for scientific research, quality control testing, and advanced materials processing.
Key Characteristics of a Muffle Furnace
The unique design of a muffle furnace gives rise to several key operational characteristics that define its use cases.
Precise and Uniform High Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are engineered for extreme heat, with many models capable of reaching and sustaining temperatures from 1000°C to over 1600°C (1832°F to 2912°F).
The radiant heating method ensures that this temperature is applied uniformly across the entire sample, which is critical for consistent results in material treatments and analyses.
Controlled Atmosphere
Because the muffle chamber is a sealed, isolated environment, it allows for precise control over the atmosphere surrounding the sample.
Users can introduce specific inert gases (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation or even create a vacuum. This makes muffle furnaces ideal for sensitive chemical reactions and advanced material sintering.
Structural Integrity and Safety
These furnaces are built with robust, multi-layered insulation, such as firebricks and ceramic fibers. This not only retains heat for energy efficiency but also keeps the exterior of the unit at a safe temperature for operators.
The common front-loading, box-type design provides easy and safe access to the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific operational considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Slower Heating and Cooling Rates
The heavy insulation required to safely contain extreme temperatures also means the furnace has high thermal mass. As a result, it heats up and cools down much more slowly than a conventional oven.
This must be factored into process times, as a cycle can take several hours from start to finish.
Significant Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures well over 1000°C is an energy-intensive process. Muffle furnaces require a substantial amount of electrical power, especially during the initial heat-up phase.
Not for All Heating Tasks
For simple applications like drying glassware or low-temperature heating where contamination is not a concern, a muffle furnace is overkill. A standard laboratory oven is far more energy-efficient and faster for these tasks.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
Your choice between a muffle furnace and another heating device depends entirely on your requirements for temperature, purity, and atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is material testing or analysis: A muffle furnace is essential for determining properties like ash content, where all organic material must be burned away without leaving behind contaminants.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment or sintering: The uniform high heat and controlled atmosphere are critical for processes like hardening metals, firing ceramics, or fusing powdered materials into a solid mass.
- If your primary focus is chemical synthesis: A muffle furnace is necessary when reactions must occur at high temperatures in a specific, pure-gas atmosphere or vacuum.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or low-temperature heating: A standard laboratory oven is a more energy-efficient and responsive choice for tasks below ~300°C.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when the absolute integrity of your sample in a pure, high-heat environment is non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Principle of Isolation | Separates sample from heat source and contaminants for high purity. |
| Heating Method | Uses radiant heat from hot chamber walls for uniform temperature distribution. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 1000°C to over 1600°C, suitable for extreme heat applications. |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows introduction of inert gases or vacuum to prevent oxidation. |
| Safety and Design | Features robust insulation and front-loading box design for operator safety. |
| Common Applications | Material testing (e.g., ash content), heat treatment, sintering, and chemical synthesis. |
| Limitations | Slower heating/cooling rates and higher energy consumption compared to standard ovens. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for high purity, precise temperature control, and uniform heating. Don't let contamination or inefficient processes hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration



















