At its core, a Muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that provides an exceptionally clean and controlled heating environment. Unlike a simple furnace where a substance might be exposed to flames or combustion byproducts, a Muffle furnace uses an insulated outer chamber—the "muffle"—to isolate the material from the heating elements. This design is essential for laboratory and industrial processes like ashing, heat-treating metals, or chemical analysis, where sample contamination would compromise the results.
The key takeaway is that a Muffle furnace's value comes from separation. By placing the heating source outside an insulated inner chamber, it ensures the material inside is heated uniformly and without contamination from the elements themselves.
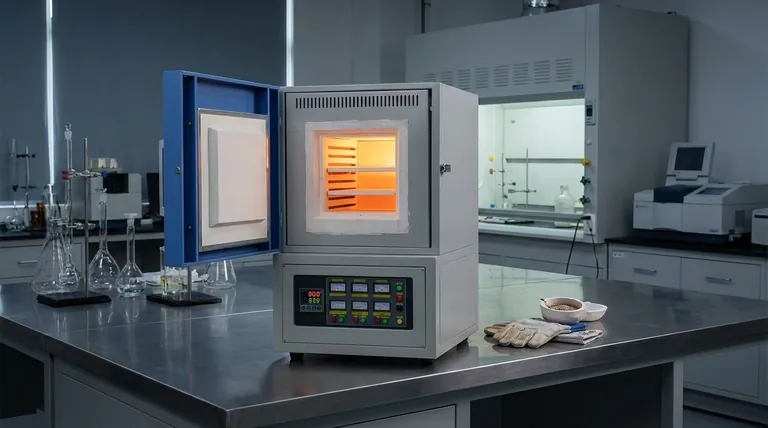

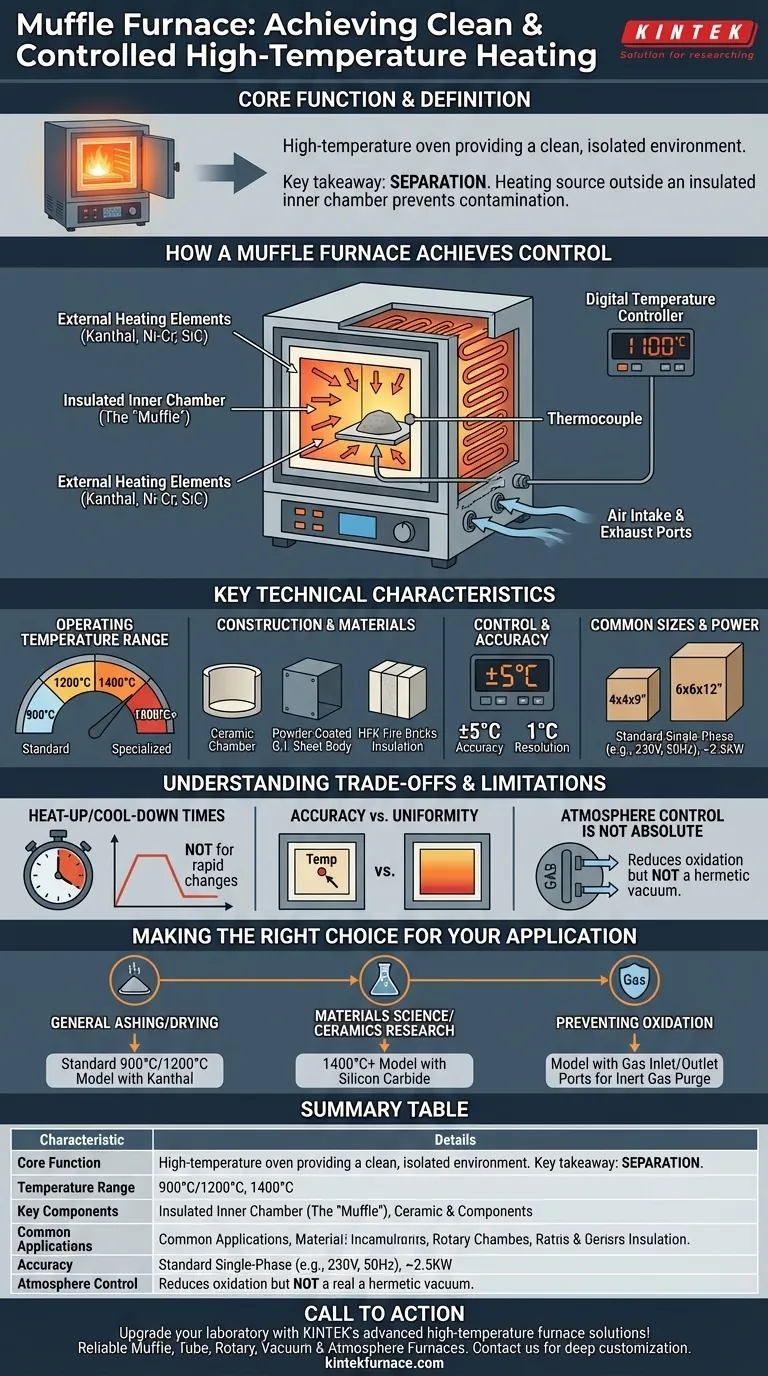
How a Muffle Furnace Achieves a Controlled Environment
The defining characteristic of a Muffle furnace is its design, which is engineered for thermal precision and purity. Several components work together to achieve this.
The Insulated Inner Chamber (The "Muffle")
The heart of the furnace is the inner chamber, which forms a barrier between the sample and the heat source. This chamber is typically constructed from high-grade, chemically inert ceramic or quartz materials that can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading or reacting with the sample.
External Heating Elements
Heating elements are strategically placed around the outside of the muffle chamber. This arrangement prevents any direct contact or contamination between the elements and the contents of the furnace. Common materials for heating elements include Kanthal wire, nickel-chromium, or, for very high temperatures, silicon carbide rods.
Precision Temperature Control Loop
A Muffle furnace operates on a closed-loop control system. A sensor, typically a thermocouple (like a J-type or K-type), constantly measures the temperature inside the chamber. This reading is sent to a digital temperature controller, which compares it to the desired setpoint and adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements to maintain a stable temperature.
Managing the Internal Atmosphere
Many Muffle furnaces include air intake and exhaust ports. These allow an operator to introduce specific gases (like nitrogen or argon) to create an inert atmosphere or to safely vent fumes produced during a process.
Key Technical Characteristics
While designs vary, most lab-grade Muffle furnaces share a common set of technical specifications that define their performance.
Operating Temperature Range
Standard benchtop models typically operate at maximum temperatures of 900°C, 1200°C, or 1400°C. More specialized industrial models can reach 1800°C or higher, depending on the heating elements and insulation used.
Construction and Materials
The furnace's construction directly impacts its durability and performance. A typical unit features an inner chamber made of high-grade ceramic, a body made from powder-coated galvanized iron (G.I.) sheet, and heavy insulation, often using HFK fire bricks in the door.
Control and Accuracy
Modern furnaces use a digital controller with an LED display. A standard accuracy rating is ±5°C, with a resolution (the smallest temperature increment) of 1°C. This level of precision is suitable for most laboratory applications.
Common Sizes and Power
Benchtop models come in various chamber sizes, such as 4x4x9 inches or 6x6x12 inches. They are typically designed to run on standard single-phase power (e.g., 230V, 50Hz) and may draw around 2.5KW.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
A Muffle furnace is a powerful tool, but it's important to understand its practical limitations to ensure it is used correctly.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Times
The heavy ceramic insulation required to reach and maintain high temperatures also holds heat very effectively. Consequently, Muffle furnaces have long heat-up and cool-down cycles. They are not designed for rapid temperature changes.
Temperature Accuracy vs. Uniformity
Accuracy (±5°C) refers to how close the temperature at the thermocouple is to the setpoint. Uniformity refers to the temperature consistency across the entire chamber, which can vary. For highly sensitive processes, understanding the temperature gradient within the chamber is critical.
Atmosphere Control is Not Absolute
While gas ports allow for atmosphere modification, a standard Muffle furnace is not a hermetically sealed vacuum chamber. It can reduce oxidation but may not be suitable for applications that require a truly oxygen-free environment, which demands a specialized vacuum furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general ashing, drying, or basic heat treatment: A standard 900°C or 1200°C model with Kanthal heating elements is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is materials science or ceramics research: You will need a model rated for 1400°C or higher, likely equipped with more robust silicon carbide heating elements.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of a sample: Choose a model with well-designed gas inlet and outlet ports for purging with an inert gas.
Understanding these core principles ensures you select a tool that precisely matches your technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Provides clean, controlled high-temperature heating with isolation from heating elements |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1400°C for standard models, higher for specialized units |
| Key Components | Insulated inner chamber (muffle), external heating elements, digital temperature controller |
| Common Applications | Ashing, heat-treating metals, chemical analysis, materials research |
| Accuracy | Typically ±5°C with 1°C resolution |
| Atmosphere Control | Includes air intake/exhaust ports for gas introduction, but not fully sealed |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for contamination-free, uniform heating. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity



















