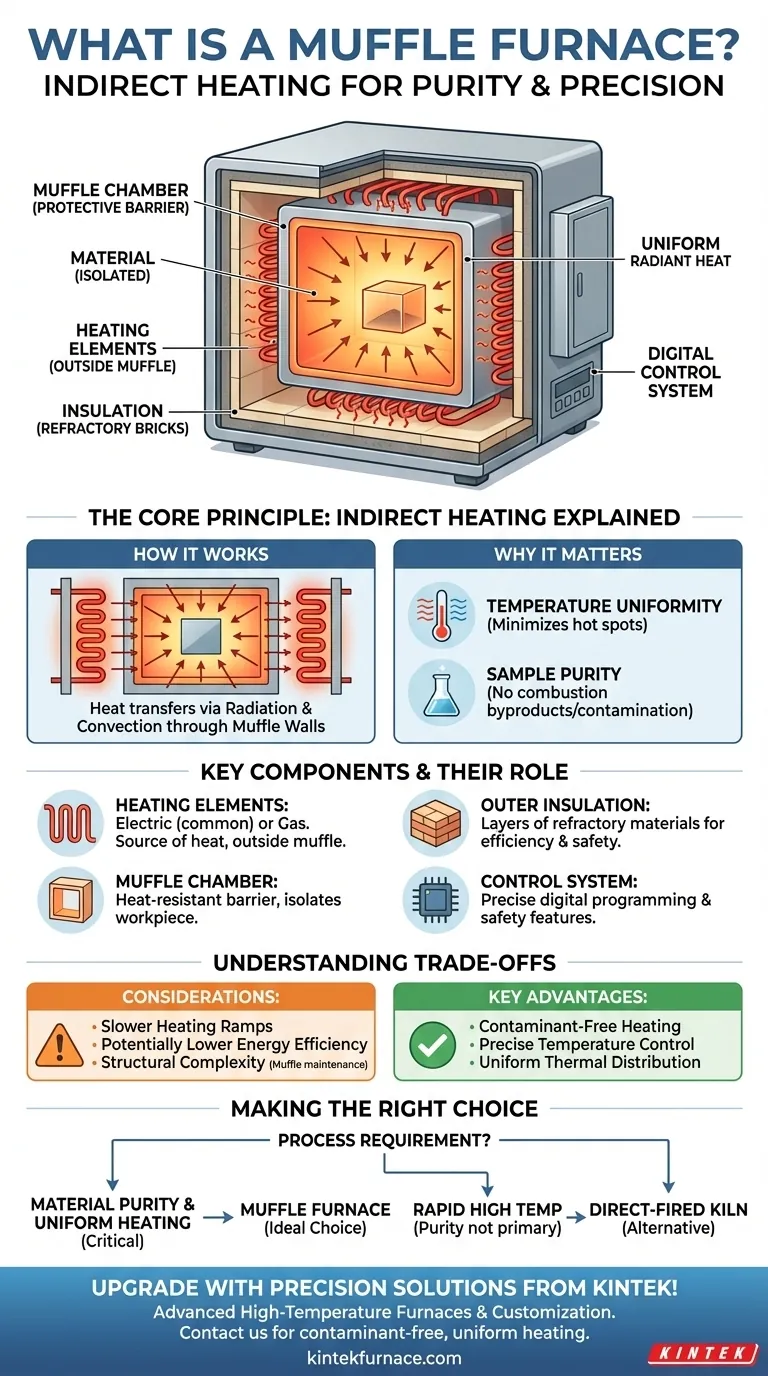
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that uses an indirect heating method. It contains a primary chamber, the "muffle," which isolates the material being heated from the actual heating elements. This design ensures that the material is not contaminated by byproducts of combustion or direct contact with the heat source.
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of a separating barrier—the muffle—to provide highly uniform, contaminant-free heating. This makes it essential for processes where material purity and consistent thermal treatment are critical.

The Core Principle: Indirect Heating Explained
A muffle furnace, also known as a box or chamber furnace, operates on a simple but crucial principle. Unlike a simple oven where the heat source might directly interact with the contents, a muffle furnace creates a controlled and isolated environment.
What is the "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is an enclosed chamber, typically made of a high-temperature, heat-resistant ceramic or metallic alloy. It acts as a protective barrier, forming a box within the larger furnace structure.
The heating elements, whether they are electric coils or gas burners, are positioned outside of this muffle chamber.
How Heat is Transferred
The heating elements heat the space surrounding the muffle. This heat is then transferred through the muffle's walls into the inner chamber via radiation and convection.
Because the heat radiates inward from all sides of the muffle, it creates an exceptionally uniform temperature zone inside. A sophisticated control system monitors and adjusts the temperature to ensure precision.
Why This Matters: Uniformity and Purity
This indirect heating method provides two primary advantages. First, it ensures temperature uniformity, minimizing hot spots that could damage sensitive materials.
Second, it guarantees sample purity. By isolating the workpiece from the heating elements and any potential fuel combustion byproducts, the furnace prevents chemical contamination. This is vital for analytical chemistry, materials science, and quality control applications.
Key Components of a Modern Muffle Furnace
While designs vary, most muffle furnaces share a common architecture built around the indirect heating principle.
Heating Elements
The most common method uses electrical resistance coils, which offer precise control and a clean operating environment. However, some industrial-scale furnaces may be heated by natural gas, propane, or oil.
The Inner Muffle Chamber
This is the central component that defines the furnace. It contains the workpiece and shields it from the external heating elements, ensuring the integrity of the thermal process.
Outer Casing and Insulation
To reach and maintain temperatures that can exceed 1800°C (3272°F), the furnace is heavily insulated. The outer body is lined with layers of refractory bricks and other insulating materials to contain the intense heat safely and efficiently.
Control System and Safety Features
A digital controller is the brain of the furnace, allowing for precise temperature programming. Modern units include critical safety mechanisms like over-temperature protection, which shuts the system down if it exceeds a set limit, and circuit breakers to prevent electrical faults.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the muffle furnace design is not without its considerations. Understanding these helps in selecting the right tool for a specific task.
Slower Heating Ramps
Because the heat must transfer indirectly through the muffle walls, these furnaces can sometimes have a slower rate of temperature increase compared to direct-fired kilns.
Energy Efficiency
The added layer of the muffle and the need to heat the space around it can make these furnaces slightly less energy-efficient than direct-heating designs. However, high-quality insulation mitigates this effect significantly.
Structural Complexity
The muffle itself is a component that can degrade over time with extreme thermal cycling. It represents an additional point of maintenance or eventual failure compared to simpler furnace designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a muffle furnace depends entirely on the requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is material purity: A muffle furnace is the correct choice, as it prevents any contamination from the heat source.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform heating: The indirect heating method is ideal for treating sensitive materials that cannot tolerate temperature variations or hot spots.
- If your primary focus is simply reaching high temperatures rapidly: A direct-fired kiln might be a more efficient option, provided that potential contamination and slight temperature gradients are not a concern for your process.
Understanding that the muffle's purpose is separation empowers you to choose the right heating technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Indirect heating via a muffle chamber to isolate materials from heat source, ensuring purity and uniform temperature. |
| Key Advantages | Contaminant-free heating, precise temperature control, and uniform thermal distribution for sensitive applications. |
| Common Uses | Analytical chemistry, materials science, quality control, and processes requiring high-temperature purity. |
| Considerations | Slower heating rates, potential energy inefficiency, and structural complexity requiring maintenance. |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision heating solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for contaminant-free, uniform heating. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















