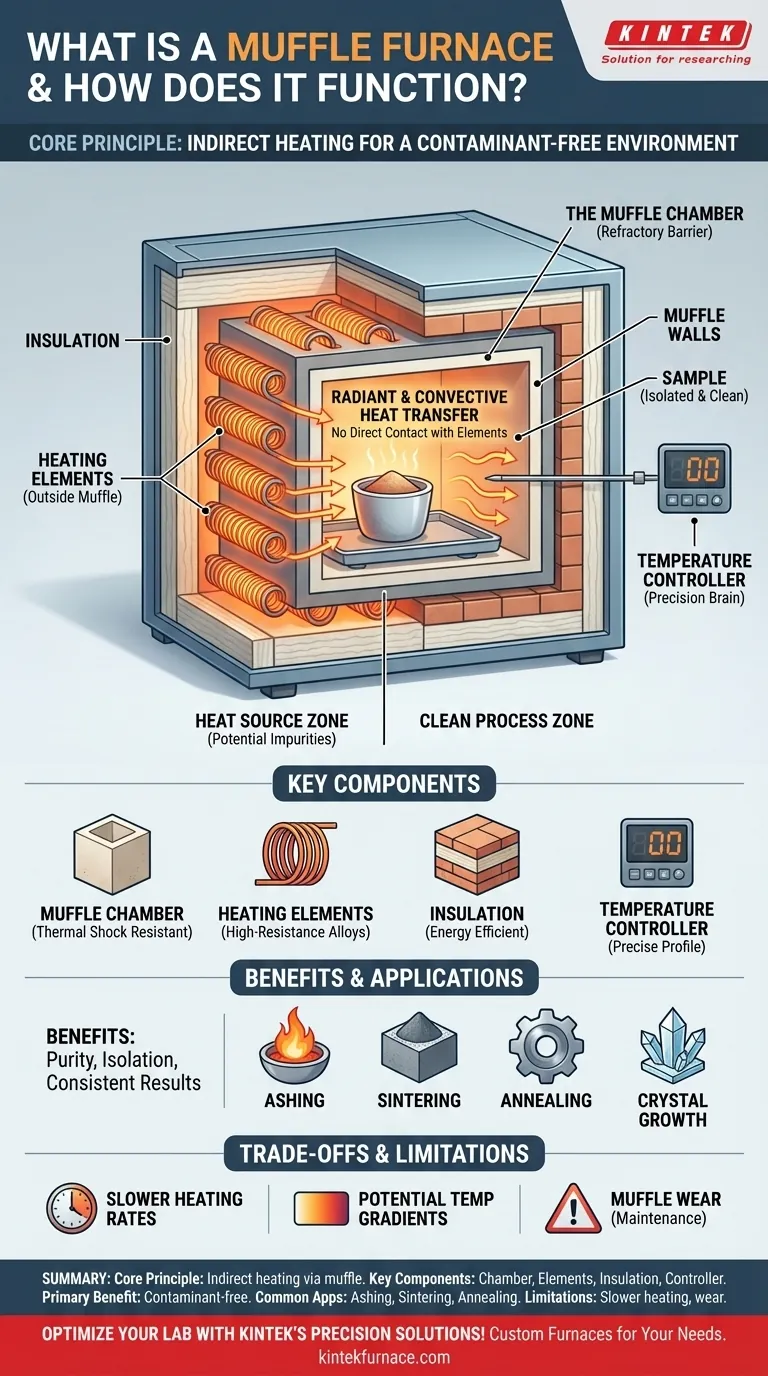
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature laboratory or industrial oven that heats materials inside an insulated chamber. Its defining feature is that the sample being heated is physically isolated from the heating elements themselves, a design that ensures a clean, controlled, and contaminant-free environment.
The critical concept to grasp is not just the high temperature, but the method of heating. A muffle furnace works on the principle of indirect heating, using a protective barrier (the "muffle") to separate the heat source from the sample, thereby guaranteeing process purity.
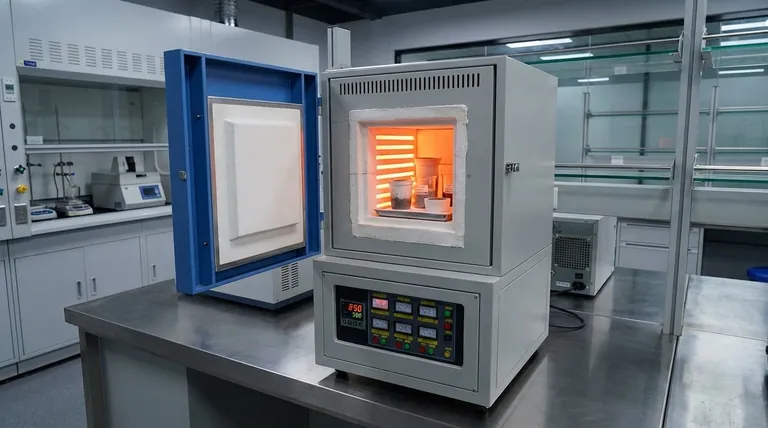

The Core Principle: Indirect Heating and Isolation
The unique value of a muffle furnace comes from its design, which prioritizes the integrity of the material being processed. This is achieved through a specific method of heat generation and transfer.
What is the "Muffle"?
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber or lining that encloses the workload. This chamber acts as a physical barrier.
It is typically made of a highly heat-resistant refractory material. The muffle separates the internal atmosphere where the sample sits from the heating elements and any potential contaminants.
How Heat is Generated and Transferred
Modern muffle furnaces use electrical resistance heating elements located outside the muffle chamber, often embedded within the furnace's insulation.
When energized, these elements generate intense heat. This thermal energy is transferred through the walls of the muffle into the main chamber via radiation and convection. The sample is heated indirectly, never coming into contact with the glowing-hot elements.
The Benefit: A Contaminant-Free Environment
This isolation is the primary reason for using a muffle furnace. For sensitive processes like chemical analysis or materials science, direct contact with heating elements can introduce trace impurities.
By separating the two, the furnace provides a chemically clean environment. This ensures that any changes to the sample are a result of the heat treatment alone, leading to accurate and repeatable results.
Key Components of a Modern Furnace
While designs vary, most muffle furnaces share a common architecture built for precision and durability at extreme temperatures.
The Muffle Chamber
This is the core workspace, constructed from materials that can withstand thermal shock and high temperatures, such as dense ceramics or specialized metal alloys.
Heating Elements
These are typically high-resistance coils or rods made from materials like Kanthal or silicon carbide, which can operate reliably at temperatures well over 1000°C.
Insulation
Multiple layers of high-grade ceramic fiber or firebrick line the furnace's outer casing. This insulation is critical for maintaining stable internal temperatures, improving energy efficiency, and keeping the exterior safe to touch.
Temperature Controller
A sophisticated digital controller is the brain of the furnace. It uses a thermocouple to measure the chamber's internal temperature and precisely adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to follow a specific heating profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the muffle furnace design is not without its compromises. Understanding these is key to using the tool effectively.
Slower Heating Rates
Because the heat must transfer indirectly through the muffle walls, the ramp-up time to the target temperature can be slower compared to direct-heating furnaces.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
Although designed for uniformity, the chamber's walls will inherently be hotter than its center. For highly sensitive work, strategic placement of the sample is important to ensure it receives even heating.
Muffle Wear and Tear
The muffle itself is subjected to extreme thermal stress during every cycle. Over time, it can crack or degrade, eventually requiring replacement. This is a key maintenance consideration for long-term operation.
When to Use a Muffle Furnace
The decision to use a muffle furnace hinges entirely on whether process purity is a critical requirement for your goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity and analysis: The furnace is essential for applications like ashing, where you must burn off organic matter without contaminating the inorganic residue.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: Its precise, high-temperature, and clean environment is ideal for sintering ceramics, annealing metals, or growing crystals.
- If your primary focus is simply rapid heating: A direct-fire oven or a simpler resistance furnace might be a more efficient and cost-effective choice if slight contamination is not a concern.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize sample integrity and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Indirect heating via a muffle barrier for sample isolation |
| Key Components | Muffle chamber, heating elements, insulation, temperature controller |
| Primary Benefit | Contaminant-free environment ensuring material purity |
| Common Applications | Ashing, sintering, annealing, crystal growth |
| Limitations | Slower heating rates, potential temperature gradients, muffle wear |
Optimize your lab's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures they meet your unique experimental needs for contaminant-free results. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















