At its core, a continuous furnace is an industrial heating system designed for high-volume manufacturing. Unlike a traditional batch furnace where parts are loaded and unloaded in static groups, a continuous furnace uses a conveyor, belt, or rotary system to move products uninterrupted through a heated chamber for rapid and consistent thermal processing.
The fundamental trade-off of a continuous furnace is exchanging higher initial cost and complexity for unparalleled efficiency, consistency, and cost-effectiveness in medium to high-volume production environments.
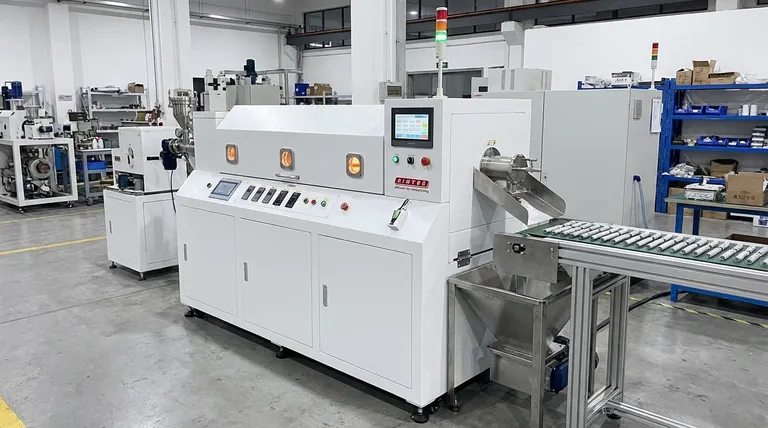

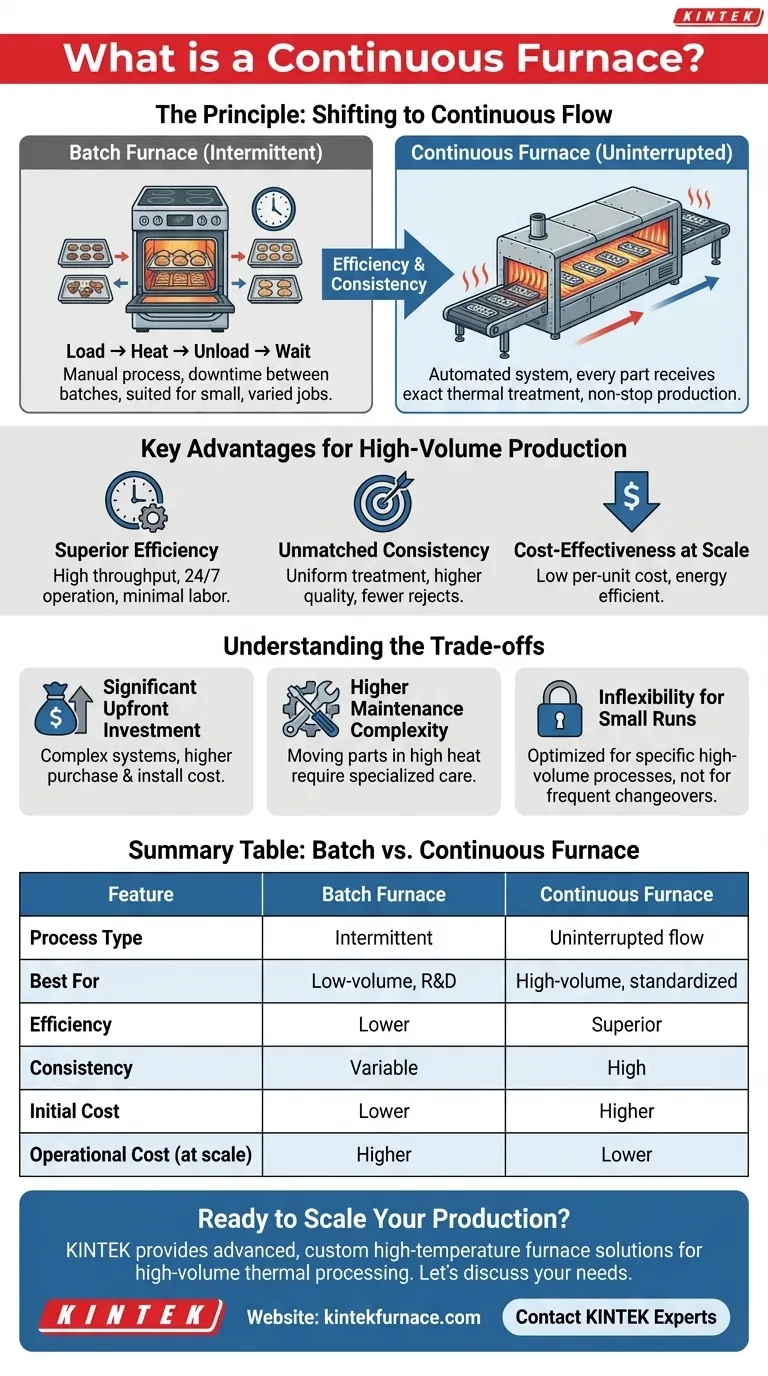
The Principle: Shifting from Batches to a Continuous Flow
The primary difference between industrial furnaces lies in how they handle material. A continuous furnace represents a shift in manufacturing philosophy from intermittent processing to a constant, automated flow.
The Batch Furnace Analogy
Think of a home oven as a batch furnace. You place a tray of items inside, heat them for a set time, remove the tray, and then load the next one. This process is manual, has downtime between batches, and is best suited for small, varied jobs.
The Continuous Furnace Model
Now, imagine a commercial pizza oven with a conveyor belt. You place uncooked pizzas on one end, and they travel through the oven to emerge perfectly cooked on the other side. This is the principle of a continuous furnace—an automated system that ensures every single part receives the exact same thermal treatment in a non-stop production line.
Key Advantages of a Continuous System
The design of a continuous furnace delivers specific, powerful benefits for manufacturers operating at scale. These advantages are the primary drivers for its adoption.
Superior Production Efficiency
By eliminating the manual loading and unloading steps of batch processing, a continuous furnace dramatically increases throughput. The system is designed for 24/7 operation with minimal labor, making it the backbone of many high-volume production lines.
Unmatched Process Consistency
Because every part travels along the same path at the same speed through precisely controlled temperature zones, process variation is nearly eliminated. This results in higher product quality, fewer rejects, and more predictable outcomes for processes like curing, drying, or heat-treating.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
While the initial investment is significant, the per-unit processing cost is extremely low in a high-volume setting. The energy efficiency is often better than a batch furnace (which must be reheated after opening), and the reduced labor requirements provide substantial long-term savings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A continuous furnace is a specialized piece of equipment, not a universal solution. Its benefits come with clear and important limitations that must be considered.
Significant Upfront Investment
Continuous furnaces are complex systems with integrated material handling, making them significantly more expensive to purchase and install than batch furnaces of a similar capacity.
Higher Maintenance Complexity
The presence of moving parts—conveyors, belts, and drive systems—operating in a high-heat environment introduces more potential points of failure. Maintenance requires specialized knowledge and a rigorous preventative schedule to ensure reliability.
Inflexibility for Small Runs
These furnaces are optimized for a specific process and product type. They are not suited for low-volume, high-mix manufacturing where frequent changeovers would negate all of their efficiency advantages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to invest in a continuous furnace hinges entirely on your production goals and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace is the definitive choice for achieving maximum efficiency and process control.
- If your primary focus is R&D, custom work, or low-volume manufacturing: A more flexible and lower-cost batch furnace is the more appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is scaling from medium to high volume: A continuous furnace represents a strategic investment that can unlock significant cost savings and production capacity.
Choosing the right thermal processing technology is about aligning the equipment's capabilities with your specific manufacturing strategy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Intermittent (load, heat, unload) | Uninterrupted flow (conveyor/belt) |
| Best For | Low-volume, R&D, varied jobs | High-volume, standardized production |
| Efficiency | Lower (downtime between batches) | Superior (24/7 operation) |
| Consistency | Variable (batch-to-batch differences) | High (uniform treatment for every part) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Operational Cost | Higher per unit at scale | Lower per unit at scale |
Ready to Scale Your Production with a High-Temperature Furnace Solution?
If your goal is to achieve high-volume, consistent thermal processing with maximum efficiency, the right furnace technology is critical. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, custom high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratory and industrial needs.
Our product line includes:
- Continuous Furnaces for high-throughput production lines
- Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces
- CVD/PECVD Systems
Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique production requirements, whether you are scaling from medium to high volume or optimizing an existing process.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK continuous furnace can transform your manufacturing efficiency and consistency.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency for Your Materials
- How does the heating process work in rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Uniform Heat for Powders and Granules
- What are some common applications of rotary tube furnaces? Unlock Efficient Bulk Material Processing
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces contribute to material science and chemical engineering? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















