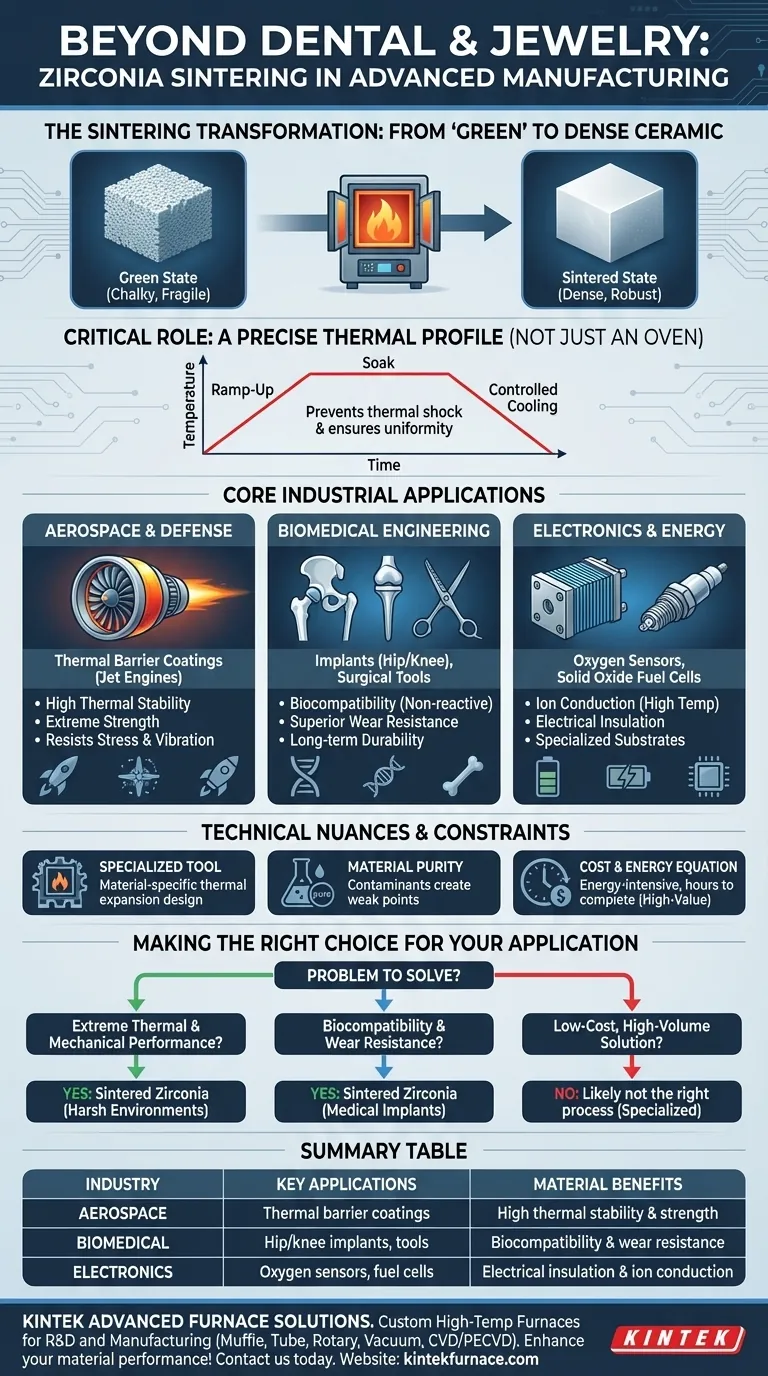
Beyond the dental lab and jeweler's bench, zirconia sintering furnaces are critical tools in a range of advanced manufacturing sectors. These industries, including aerospace, electronics, and biomedical engineering, leverage the unique properties of sintered zirconia—namely its exceptional strength, thermal resistance, and biocompatibility—for high-performance, mission-critical components.
The presence of a zirconia sintering furnace in a facility signals a focus not just on a piece of equipment, but on a material transformation process. It indicates a need to unlock the extreme performance characteristics of ceramic materials, where conventional metals or plastics would fail.
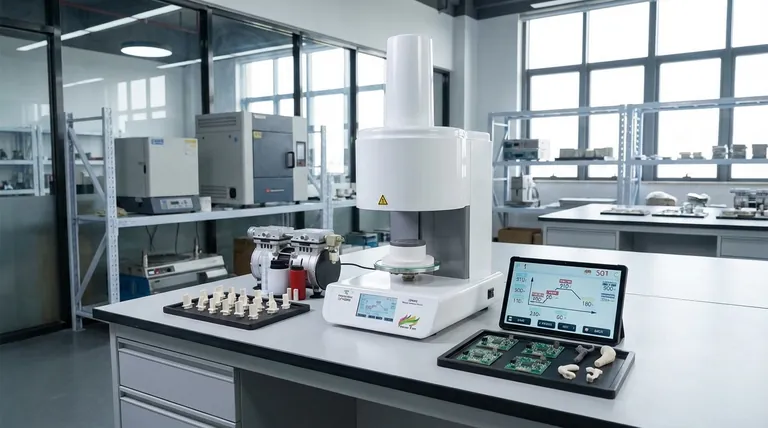

Why Zirconia Requires Sintering
To understand the furnace's role, you must first understand the material. Zirconia components do not start as a solid block; they begin as a compressed powder.
The Transformation from "Green" to Dense
In its initial, pre-sintered form—often called the "green state"—a zirconia part is chalky and fragile. It has the desired shape but lacks the structural integrity required for any functional application.
Sintering is the thermal process that transforms this weak part into a fully dense, robust ceramic. The furnace heats the material to a high temperature, below its melting point, causing the individual zirconia particles to fuse together.
The Critical Role of the Thermal Profile
A zirconia sintering furnace is more than just a high-temperature oven. It executes a precise, pre-programmed thermal profile. This includes a controlled temperature ramp-up, a specific "soak" time at peak temperature, and a carefully managed cooling phase to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
Core Industrial Applications
The adoption of zirconia sintering is driven entirely by the final properties of the sintered part. Different industries leverage different aspects of this versatile material.
Aerospace and Defense: Resisting Extreme Environments
In aerospace, materials must withstand incredible stress, vibration, and temperature gradients. Sintered zirconia's high thermal stability and strength make it an ideal material for thermal barrier coatings on jet engine turbine blades, protecting the underlying metal alloys from extreme heat.
Biomedical Engineering: Biocompatibility and Durability
Beyond dental crowns, zirconia's biocompatibility (it does not react with bodily tissues) and superior wear resistance make it a choice material for advanced medical implants. This includes components for hip and knee replacements, where long-term durability is paramount.
Electronics and Energy: Insulation and Ion Conduction
Zirconia is an excellent electrical insulator but, when doped with certain elements, becomes an effective ion conductor at high temperatures. This unique duality makes it essential for manufacturing oxygen sensors (used in automotive exhaust systems), solid oxide fuel cells, and insulating substrates for specialized electronic circuits.
Understanding the Technical Nuances
While powerful, the zirconia sintering process is not a universal solution and comes with specific constraints that define its use.
A Specialized Tool, Not a Generic Oven
You cannot simply use any high-temperature furnace for zirconia. Zirconia-specific furnaces are designed for the material's unique thermal expansion properties, ensuring uniform heating and cooling to achieve consistent density and prevent catastrophic failure of the part.
Material Purity is Essential
The performance of a sintered zirconia component is highly sensitive to the purity of the initial powder. Contaminants can create weak points in the final ceramic structure, leading to premature failure in a critical application like an engine or a medical implant.
The Cost and Energy Equation
Sintering is an energy-intensive process that can take many hours to complete. This cost and time investment means it is almost exclusively reserved for high-value components where the performance requirements justify the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to explore this technology depends entirely on the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme thermal and mechanical performance: Sintered zirconia is a leading candidate for components that must operate in harsh, high-temperature environments where metals would deform or degrade.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and wear resistance: This material is an excellent choice for medical implants or surgical instruments that require long-term stability and non-reactivity within the human body.
- If your primary focus is finding a low-cost, high-volume solution: Zirconia sintering is likely not the right process, as its energy, time, and equipment costs are geared toward specialized, high-performance applications.
Ultimately, the decision to use a zirconia sintering furnace is a decision to work with one of the most capable technical ceramics available today.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Material Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Thermal barrier coatings for turbine blades | High thermal stability and strength |
| Biomedical | Hip and knee implants, surgical tools | Biocompatibility and wear resistance |
| Electronics | Oxygen sensors, fuel cells, insulating substrates | Electrical insulation and ion conduction |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. If you're in aerospace, biomedical, or electronics and need reliable zirconia sintering solutions, contact us today to enhance your material performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations
- Why is proper ventilation important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Lab
- What is the purpose of dental sintering furnaces? Transform Zirconia into Durable, High-Quality Dental Restorations
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- How has the sintering process innovated dental zirconia applications? Boost Strength, Precision, and Efficiency



















