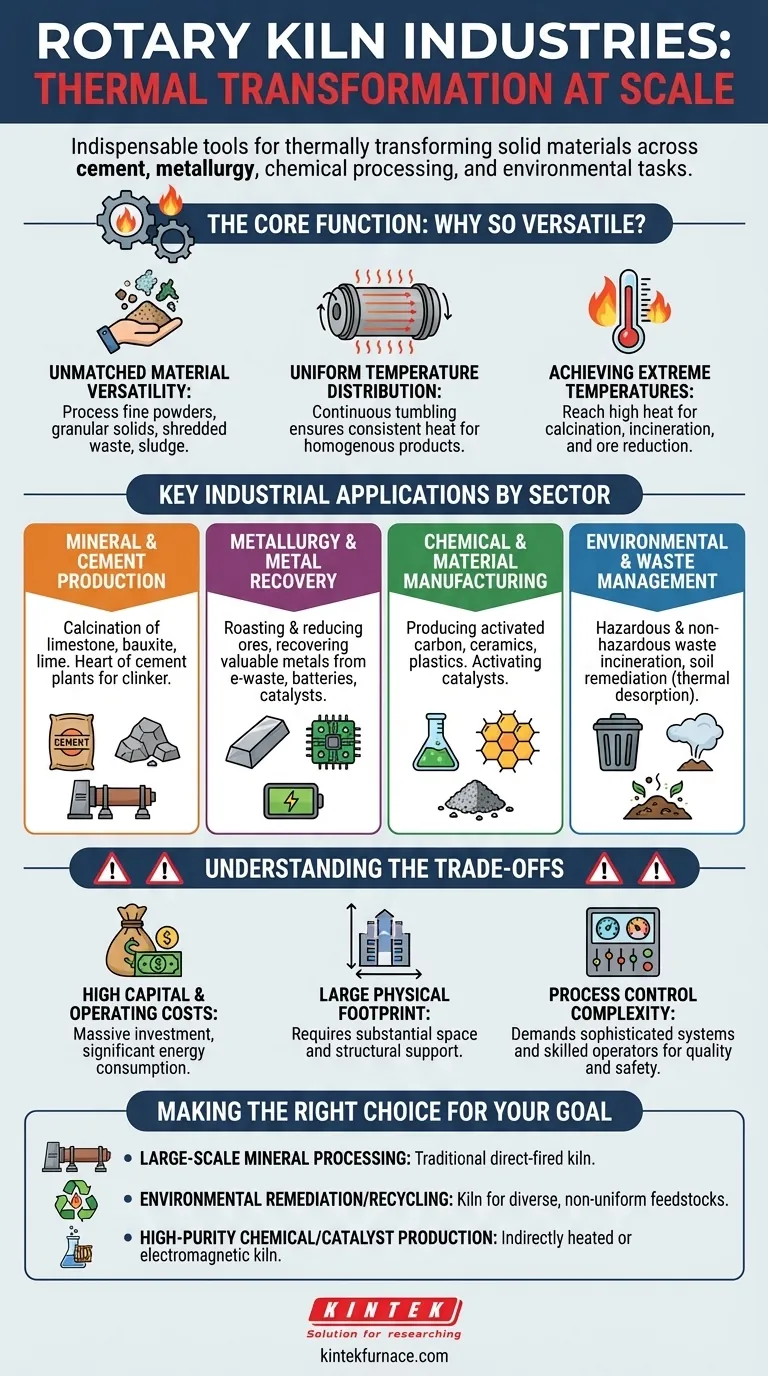
At their core, rotary kilns are indispensable tools for industries that need to thermally transform solid materials. They are most famously used in cement production, but their application extends across metallurgy for metal recovery, chemical processing for creating catalysts and activated carbon, and a wide array of environmental management tasks, including waste incineration and soil remediation.
The widespread adoption of rotary kilns is not due to a single application, but to their fundamental ability to apply precise, uniform, and high temperatures to an enormous variety of materials. This makes them the definitive solution for countless industrial processes involving heating, drying, and chemical change.

The Core Function: Why Rotary Kilns Are So Versatile
The value of a rotary kiln is rooted in three primary engineering advantages. Understanding these principles explains why they appear in so many different industries.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Rotary kilns can process a vast range of materials that other systems cannot. They excel at handling everything from fine powders and granular solids like minerals to heterogeneous materials like shredded waste, sewage sludge, and industrial by-products.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
The gentle rotation of the kiln drum continuously tumbles the material. This ensures every particle is exposed to the same heat, guaranteeing a consistent and homogenous final product, which is critical for applications like cement and catalyst manufacturing.
Achieving Extreme Temperatures
These systems are designed to reach and maintain the extremely high temperatures necessary for chemical reactions like calcination and incineration. This high-temperature capability is essential for producing cement, reducing ores, and destroying hazardous waste.
Key Industrial Applications by Sector
The kiln's core functions translate into a wide spectrum of uses. While the list is extensive, applications generally fall into four major categories.
Mineral and Cement Production
This is the most well-known application. Rotary kilns are the heart of cement plants, where they heat limestone and other materials to over 1400°C to create cement "clinker." They are also used to calcine (heat to drive off water and CO2) other materials like lime, bauxite, and various ores.
Metallurgy and Metal Recovery
In metallurgy, kilns are used to roast and reduce ores to extract metals. Critically, they are also a key technology for the circular economy, recovering valuable metals from e-waste, spent batteries, industrial red mud, and catalysts.
Chemical and Material Manufacturing
The chemical industry uses rotary kilns to produce or regenerate essential materials. This includes creating and reactivating activated carbon for purification, activating catalysts for chemical manufacturing, and processing specialty materials like ceramics and plastics.
Environmental and Waste Management
Rotary kilns are powerful tools for environmental protection. They are used for the high-temperature incineration of hazardous and non-hazardous waste, including sewage sludge and scrap tires. They are also used for thermal desorption, a process that cleans contaminated soil by heating it to vaporize pollutants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly capable, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Their industrial scale comes with significant considerations.
High Capital and Operating Costs
Rotary kilns are massive, heavy-duty machines that represent a significant capital investment. Their operation, whether fueled by gas, coal, or electricity (as with electromagnetic induction models), consumes a substantial amount of energy, leading to high operating costs.
Large Physical Footprint
These are not small pieces of equipment. A rotary kiln installation requires a very large physical footprint and significant structural support, making it a major infrastructure project.
Process Control Complexity
Achieving the uniform temperature that makes kilns so effective requires sophisticated process control systems. It demands skilled operators and continuous monitoring to maintain product quality and operational safety, especially when processing variable feedstocks like waste materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on the material you need to process and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale mineral processing (like cement or lime): A traditional, direct-fired rotary kiln is the established industry standard for its high throughput and proven reliability.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation or waste recycling: The kiln's unique ability to handle diverse, non-uniform feedstocks makes it ideal for neutralizing hazardous materials or recovering value from complex waste streams.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical or catalyst production: An indirectly heated or specialized electromagnetic induction kiln offers superior temperature precision and control over the internal atmosphere, preventing contamination.
Ultimately, understanding the core thermal capabilities of a rotary kiln allows you to leverage its power for nearly any material transformation challenge.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Primary Use | Key Material Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Cement & Mineral Production | Calcination, Clinker Production | Limestone, Bauxite, Lime |
| Metallurgy & Metal Recovery | Ore Roasting, Metal Extraction | Metal Ores, E-Waste, Spent Catalysts |
| Chemical & Material Manufacturing | Catalyst Activation, Material Synthesis | Activated Carbon, Ceramics, Plastics |
| Environmental & Waste Management | Hazardous Waste Incineration, Soil Remediation | Industrial Waste, Sewage Sludge, Contaminated Soil |
Leverage the Power of Precision Thermal Processing
Facing a material transformation challenge? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, built on exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, can provide the precise, uniform heating your process demands.
Whether your application aligns with large-scale mineral processing, high-purity chemical production, or complex environmental remediation, our diverse product line—including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and sophisticated Vacuum & Atmosphere Systems—is complemented by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique requirements.
Let's discuss how we can engineer a thermal solution for you. Contact our experts today to explore the possibilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















