Rotary kiln furnaces are foundational technology in a wide range of heavy and advanced industries. They are most commonly used in metallurgy for metal processing, in chemical processing for creating compounds like catalysts and oxides, and in the production of advanced materials such as ceramics and battery components. Their value lies in their ability to continuously process materials at very high temperatures.
A rotary kiln is more than just a furnace; it is a dynamic chemical reactor. Its primary purpose is not merely to heat a substance, but to use precisely controlled high temperatures and a rotating environment to induce specific physical and chemical transformations in granular or powdered materials.
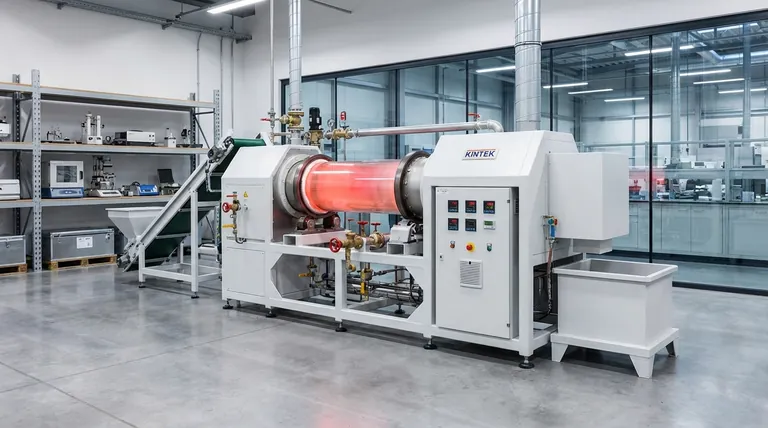

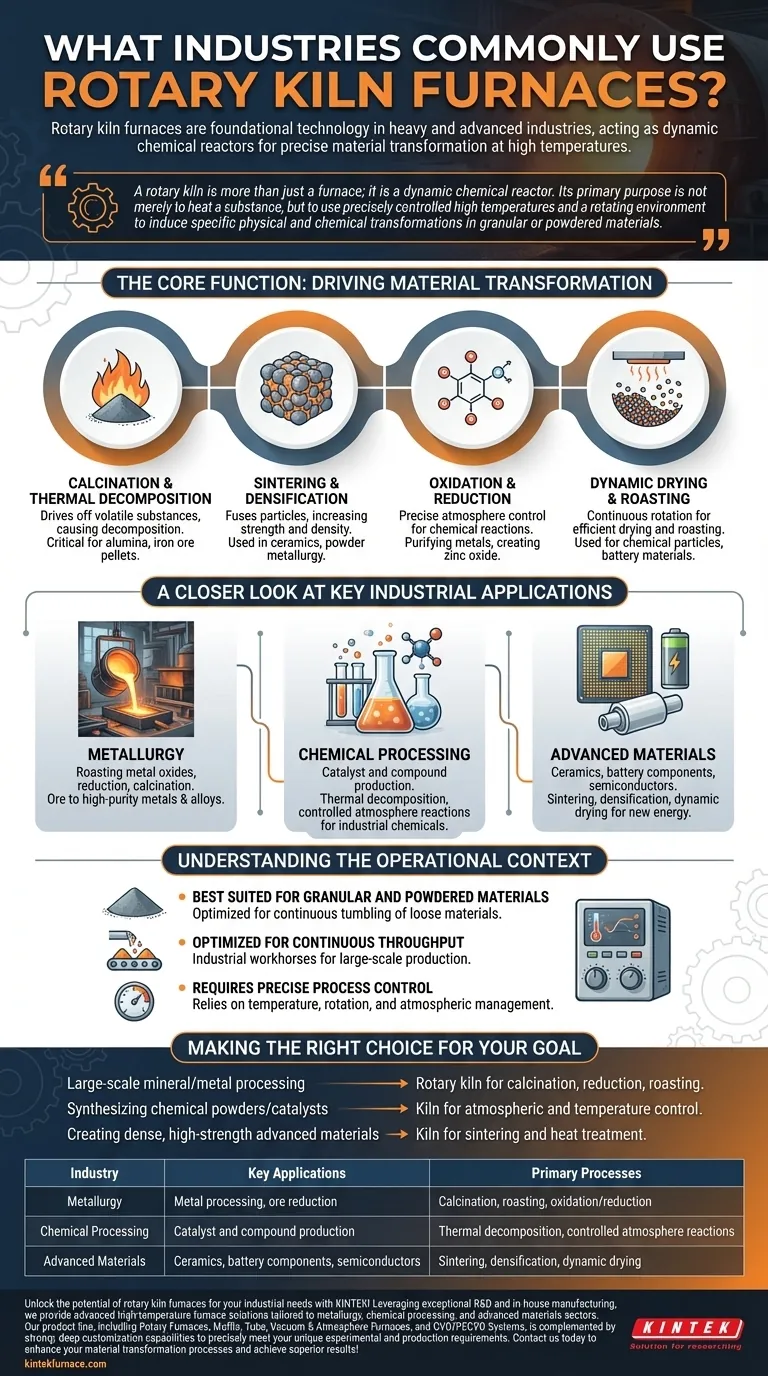
The Core Function: Driving Material Transformation
A rotary kiln excels at changing the fundamental nature of materials. The combination of heat, controlled atmosphere, and constant tumbling motion makes it uniquely effective for several key industrial processes.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a process that uses heat to drive off volatile substances (like water or CO₂) from a material, causing it to decompose or change its chemical state.
This is critical for producing materials like alumina from bauxite or manufacturing iron ore pellets before they enter a blast furnace.
Sintering and Densification
Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together, increasing a material's strength and density without melting it.
In ceramics, this process is used to fire products and create dense, uniform materials. In metallurgy, it is used to sinter metal powders into solid forms.
Oxidation and Reduction
Rotary kilns allow for precise control over the processing atmosphere, enabling specific chemical reactions.
Oxidation (adding oxygen) and reduction (removing oxygen) are vital in metallurgy for purifying metals from their ores. These reactions are also used to create chemical products like zinc oxide.
Dynamic Drying and Roasting
The continuous rotation ensures that every particle is exposed to heat, making rotary kilns highly efficient for drying and roasting powders and granules.
This is commonly used for chemical particles, abrasives, and materials used in lithium batteries.
A Closer Look at Key Industrial Applications
The versatility of these core functions means rotary kilns are indispensable across many sectors, each leveraging the technology for a specific outcome.
In Metallurgy: From Ore to Pure Metal
The metallurgical industry uses rotary kilns for roasting metal oxides and for reduction and calcination processes. This is a key step in producing high-purity metals and alloys from raw ore.
In Chemical Processing: Creating Essential Compounds
Rotary kilns are central to the production of many industrial chemicals. They are used to manufacture catalysts, silica gel, and other compounds that require high-temperature synthesis in a controlled, dynamic environment.
In Advanced Materials: For Ceramics and New Energy
The ability to improve material properties like density, strength, and corrosion resistance makes rotary kilns essential for advanced applications.
This includes firing ceramic products, preparing semiconductor materials, and developing components for new energy fields like solar cells and fuel cells.
Understanding the Operational Context
While powerful, rotary kilns are designed for a specific operational scale and material type. Understanding their intended use is key to leveraging their benefits.
Best Suited for Granular and Powdered Materials
The design of a rotary kiln is optimized for the continuous tumbling and throughput of loose materials. It is not designed to process large, single, solid objects.
Optimized for Continuous Throughput
These furnaces are industrial workhorses, built for continuous, large-scale production. They are less efficient for small, individual lab batches where a box or muffle furnace might be more appropriate.
Requires Precise Process Control
The value of a rotary kiln comes from the ability to precisely manage temperature, rotation speed, and atmospheric conditions. Achieving high-quality, consistent output depends on mastering these process controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln is driven entirely by the material transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is large-scale mineral or metal processing: A rotary kiln is the definitive tool for essential processes like calcination, ore reduction, and roasting.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing chemical powders or catalysts: The kiln's ability to control the atmosphere and temperature during continuous processing is a critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-strength advanced materials: The sintering and heat treatment capabilities of a rotary kiln are vital for achieving the desired final material properties.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's prevalence is a direct result of its unique ability to transform loose materials on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Metal processing, ore reduction | Calcination, roasting, oxidation/reduction |
| Chemical Processing | Catalyst and compound production | Thermal decomposition, controlled atmosphere reactions |
| Advanced Materials | Ceramics, battery components, semiconductors | Sintering, densification, dynamic drying |
Unlock the potential of rotary kiln furnaces for your industrial needs with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to metallurgy, chemical processing, and advanced materials sectors. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to enhance your material transformation processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















