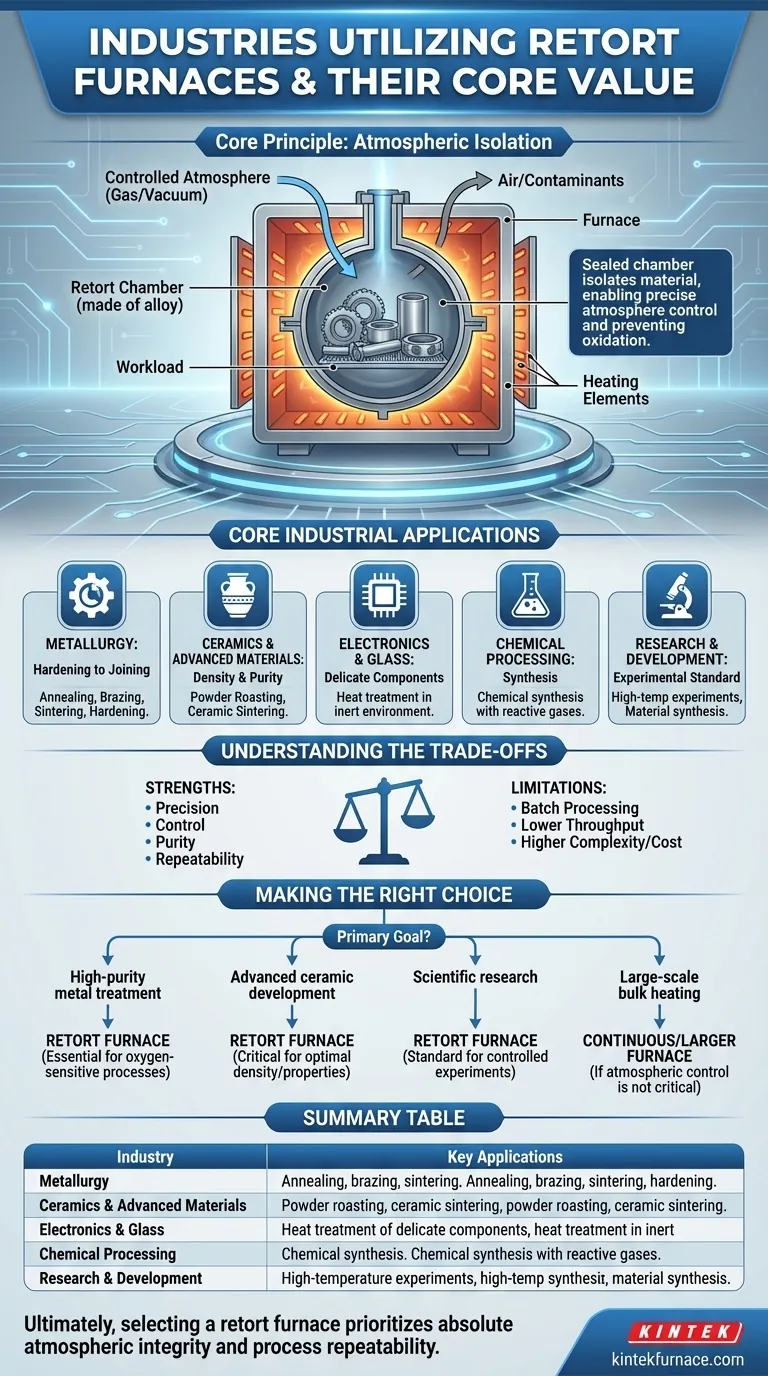
To be direct, retort furnaces are essential tools in industries that require precise high-temperature processing within a controlled atmosphere. The most common users are in the metallurgy, ceramics, electronics, chemical processing, and glass manufacturing sectors, as well as in advanced scientific research.
The core value of a retort furnace is not simply the heat it generates, but the sealed chamber—the "retort"—that isolates the material being processed. This design enables absolute control over the internal atmosphere, preventing unwanted reactions like oxidation and allowing for specific material transformations that are impossible in open air.
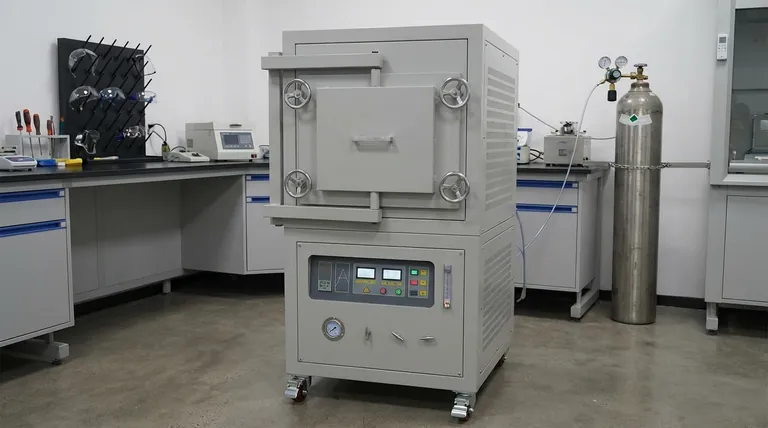

The Principle of Atmospheric Isolation
A retort furnace's unique capability stems from its fundamental design. Understanding this principle is key to seeing why it's so critical for certain industries.
What is the "Retort"?
The "retort" is a sealed container, typically made of metal alloy or ceramic, that holds the materials being heated.
This container is placed inside the furnace, but it remains separate from the heating elements and the outside air. This creates a pristine, isolated environment.
Why Control the Atmosphere?
By sealing the workload inside the retort, operators can purge the air and replace it with a specific gas or a vacuum.
This is critical for preventing oxidation when heating sensitive metals. It also allows for processes that require a reactive atmosphere, such as using hydrogen to remove oxides or introducing specific gases for chemical synthesis.
Core Industrial Applications
The ability to control the process atmosphere makes retort furnaces indispensable for a range of high-value applications.
In Metallurgy: From Hardening to Joining
The metallurgical industry relies on retort furnaces for treating metals and alloys that would be damaged by oxygen at high temperatures.
Key processes include annealing (softening metals), brazing (joining metals with a filler), sintering (fusing metal powders together), and hardening specialty steels.
In Ceramics & Advanced Materials: Achieving Density and Purity
Creating advanced ceramics and composites requires precise heat treatment. Retort furnaces are used for powder roasting and ceramic sintering.
The controlled atmosphere ensures uniform processing, removes binders without contamination, and helps achieve maximum material densification and strength.
In Electronics & Glass: For Delicate Component Manufacturing
Many electronic components and specialty glass products require heat treatment in an inert (non-reactive) environment to achieve their desired properties.
Retort furnaces provide the clean, controlled conditions needed for these sensitive manufacturing steps, preventing defects and ensuring product reliability.
In Research & Development: The Experimental Standard
For universities, scientific institutes, and corporate R&D labs, the retort furnace is a fundamental tool.
Its precise control over both temperature and atmosphere makes it ideal for high-temperature experiments, material synthesis, and developing the next generation of materials and processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a retort furnace is a specialized tool. Its strengths in control come with inherent limitations.
Precision Over Throughput
The focus on a perfectly sealed, controlled batch makes retort furnaces less suitable for high-volume, continuous processing. Industries that need to heat massive quantities of material quickly may opt for tunnel kilns or other continuous furnace designs.
Batch Processing by Design
The nature of loading, sealing, processing, and cooling a retort means it operates in batches. This workflow is different from a continuous furnace and must be factored into production planning.
Added Complexity and Cost
The systems required to manage the vacuum and gas atmospheres (pumps, flow controllers, safety interlocks) add a layer of complexity and cost compared to a simple furnace that operates in ambient air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing a furnace requires aligning the equipment's capability with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metal treatment: A retort furnace is essential for oxygen-sensitive processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramic development: The atmospheric control offered by a retort furnace is critical for achieving optimal density and material properties.
- If your primary focus is scientific research: A retort furnace is the standard for repeatable, high-temperature experiments where atmospheric variables must be eliminated or controlled.
- If your primary focus is large-scale bulk heating: You should investigate continuous or larger-capacity furnaces if a controlled atmosphere is not a critical requirement for your final product.
Ultimately, selecting a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize absolute atmospheric integrity and process repeatability.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Annealing, brazing, sintering, hardening of metals and alloys |
| Ceramics & Advanced Materials | Powder roasting, ceramic sintering for densification and purity |
| Electronics & Glass | Heat treatment of delicate components in inert atmospheres |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical synthesis with reactive gases |
| Research & Development | High-temperature experiments and material synthesis |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. If you need precise atmospheric control for your high-temperature processes, contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















