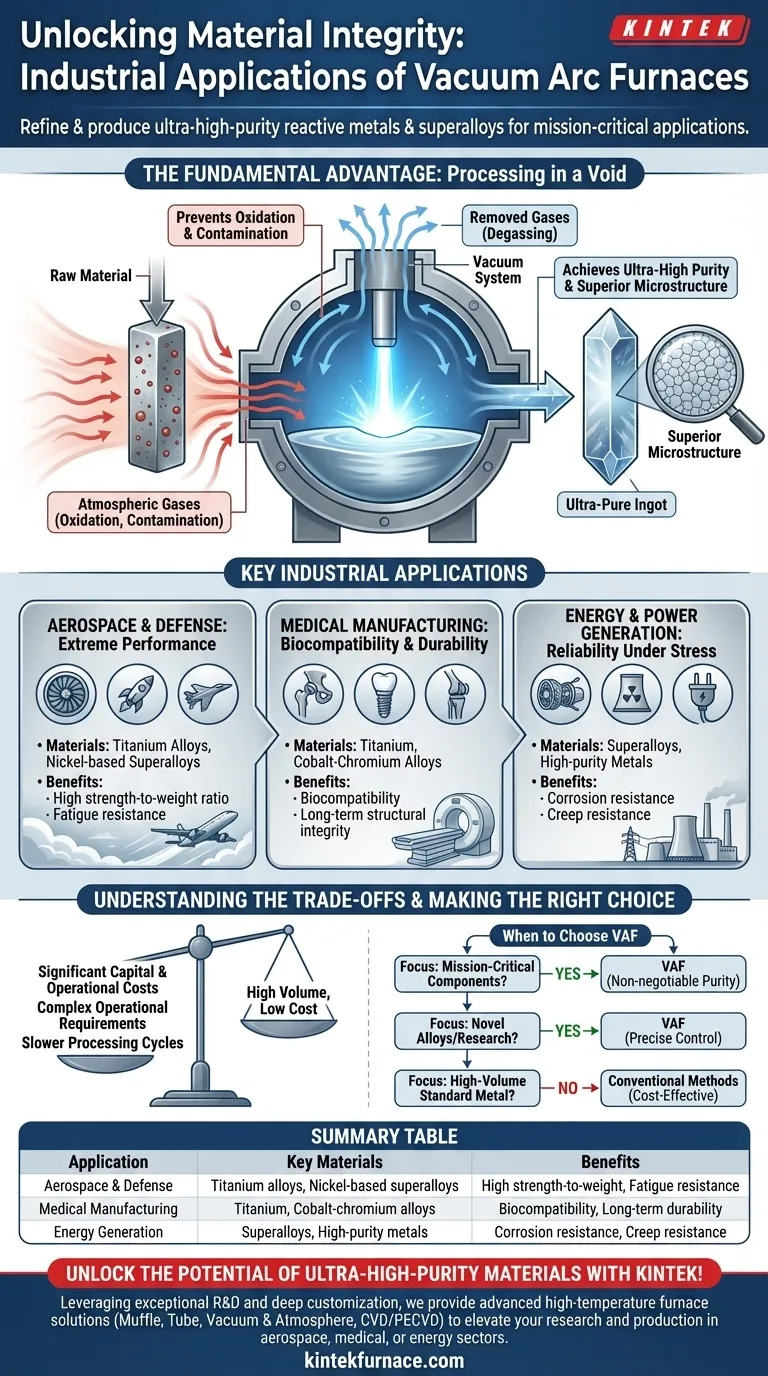
In short, vacuum arc furnaces are indispensable for industries where material failure is not an option. They are primarily used to refine and produce ultra-high-purity reactive metals and superalloys for critical applications in aerospace, defense, medical device manufacturing, and energy generation. This technology is chosen when the final product's strength, purity, and performance must be absolute.
The core value of a vacuum arc furnace isn't just heating metal—it's purifying it. By creating a vacuum, the furnace eliminates atmospheric gases that contaminate and weaken advanced alloys, allowing for the production of materials with properties unattainable through conventional methods.
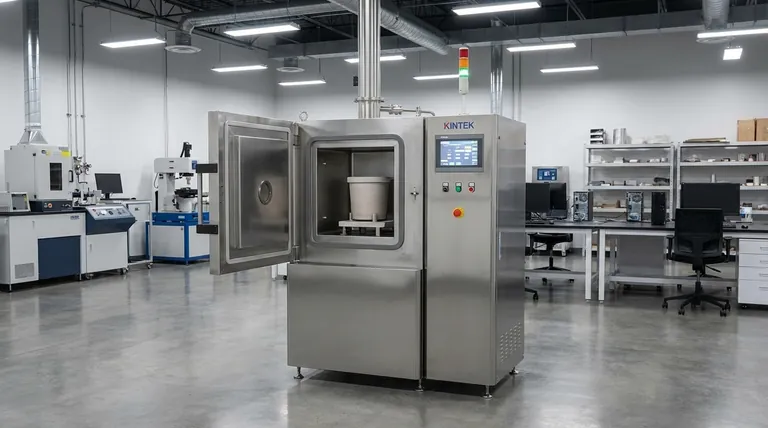

The Fundamental Advantage: Processing in a Void
To understand the applications of a vacuum arc furnace, you must first understand the problem it solves: contamination. When metals, especially reactive ones like titanium, are melted in the open air, they react with oxygen and nitrogen.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Atmospheric gases create oxides and other impurities that become trapped within the metal's structure. These impurities act as microscopic weak points, compromising the material's strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
A vacuum furnace removes the air, creating an environment where these unwanted chemical reactions cannot occur. This is the only way to produce the pristine, high-integrity metals required for demanding applications.
Removing Dissolved Gases (Degassing)
The vacuum doesn't just prevent contamination from entering; it also pulls existing impurities out. As the metal melts, the vacuum environment effectively boils off dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen that were trapped inside the raw material.
This process, known as degassing, is critical for preventing issues like hydrogen embrittlement, a condition that can cause catastrophic, brittle failure in high-strength components.
Achieving Ultra-High Purity and a Superior Microstructure
The combination of preventing oxidation and active degassing results in an exceptionally pure final product. Furthermore, the controlled melting and solidification process in a vacuum arc furnace creates a uniform, refined internal grain structure.
This superior microstructure is directly responsible for the enhanced mechanical properties—like extreme tensile strength and fracture toughness—that define these advanced materials.
Key Industrial Applications and Their Demands
The need for absolute material integrity drives the adoption of vacuum arc technology across several high-stakes industries.
Aerospace and Defense: The Need for Extreme Performance
Components in jet engines, rocket motors, and aircraft fuselages are subjected to incredible stress and extreme temperatures. There is zero margin for error.
Titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys refined in vacuum arc furnaces are essential for manufacturing turbine blades, landing gear, and critical structural components. Their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue are a direct result of the vacuum refining process.
Medical Manufacturing: The Requirement for Biocompatibility
When a material is placed inside the human body, it must be completely inert and exceptionally durable. Impurities can trigger an immune response or lead to mechanical failure of the implant.
Vacuum arc furnaces are used to produce the ultra-pure titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys for surgical implants like hip joints, knee replacements, and dental fixtures. The purity achieved ensures biocompatibility and the long-term structural integrity needed to last a lifetime.
Energy and Power Generation: Reliability Under Stress
Components in power plants, particularly in gas turbines and nuclear reactors, must operate reliably for decades under high heat, high pressure, and corrosive conditions.
The same superalloys and high-purity metals used in aerospace are applied here for turbine blades and critical nuclear reactor components. The purity and structural uniformity ensure resistance to creep and corrosion over long service lives.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, vacuum arc technology is not a universal solution. The decision to use it is driven by necessity, not convenience.
Significant Capital and Operational Costs
Vacuum arc furnaces are highly complex systems that represent a major capital investment. They also have high operational costs related to energy consumption, specialized maintenance, and the consumables required for the melting process.
Complex Operational Requirements
Operating a vacuum arc furnace is not a simple task. It requires highly skilled technicians who understand the intricate relationship between vacuum levels, arc stability, and melt parameters to achieve the desired material properties.
Slower Processing Cycles
Compared to conventional atmospheric furnaces, vacuum processes are inherently slower. Significant time is required to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level, run the controlled melt, and cool the ingot. This makes it a batch process unsuitable for high-volume, low-cost metal production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice to use a vacuum arc furnace is a function of the material properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is creating mission-critical components: The ultra-high purity, superior strength, and fatigue resistance provided by vacuum arc refining are non-negotiable for aerospace, medical, and nuclear applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standard metal production: A vacuum arc furnace is expensive overkill. Conventional atmospheric melting and casting methods are far more cost-effective for applications where material purity is not the primary driver.
- If your primary focus is developing novel alloys with unique properties: The precise control over alloy chemistry and purity makes a vacuum arc furnace an indispensable tool for materials science research and the production of next-generation alloys.
Choosing this technology means you are prioritizing ultimate material integrity above all other manufacturing considerations.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Materials | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Titanium alloys, Nickel-based superalloys | High strength-to-weight ratio, Fatigue resistance |
| Medical Manufacturing | Titanium, Cobalt-chromium alloys | Biocompatibility, Long-term durability |
| Energy Generation | Superalloys, High-purity metals | Corrosion resistance, Creep resistance |
Unlock the potential of ultra-high-purity materials for your critical applications with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering enhanced material integrity and performance. Don't let contamination compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can elevate your research and production in aerospace, medical, or energy sectors!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















