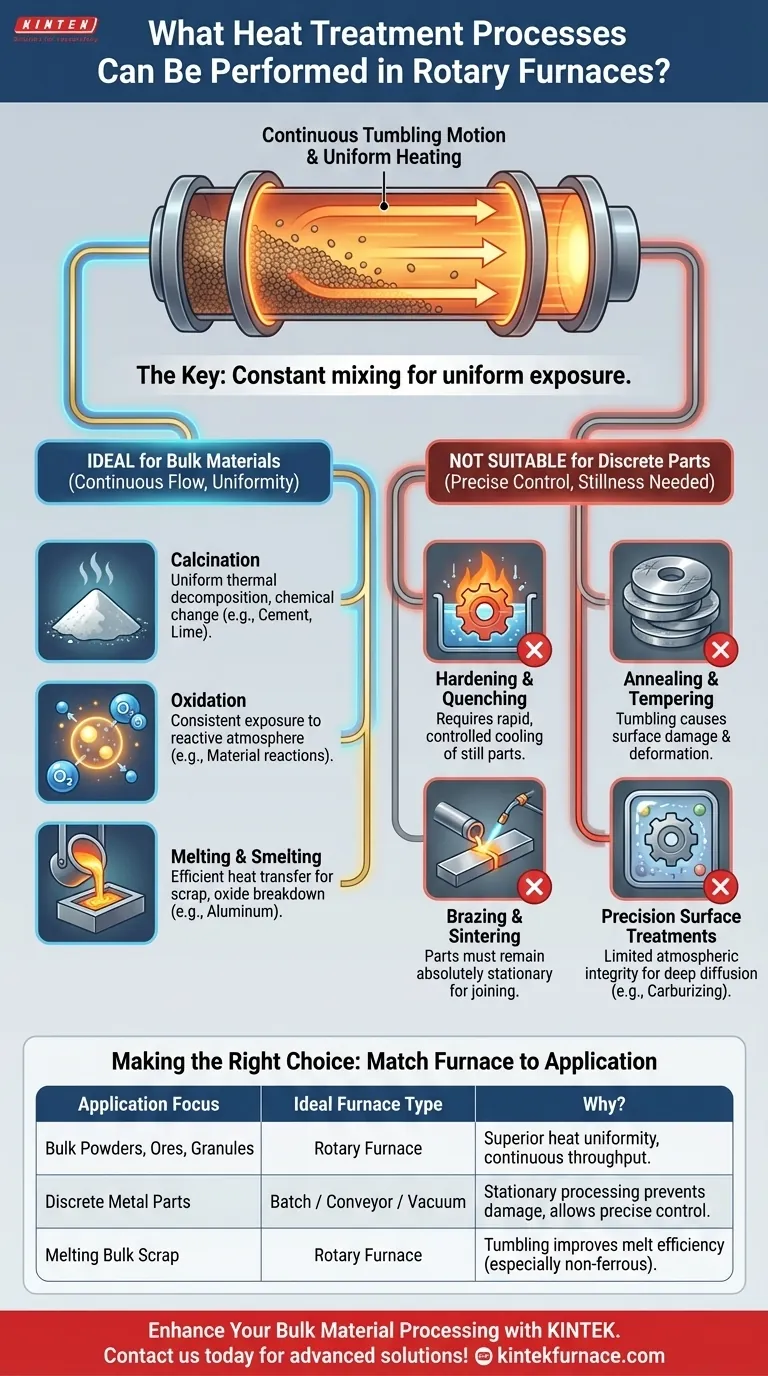
Rotary furnaces are specialized tools designed primarily for the continuous, high-temperature thermal processing of bulk materials. Their unique rotational design makes them exceptionally effective for processes like calcination, oxidation, and melting, where uniform exposure of every particle to heat and atmosphere is critical for the final product's quality.
The key to understanding a rotary furnace is its continuous tumbling motion. This makes it ideal for uniformly treating bulk powders, granules, and ores, but fundamentally unsuitable for processes that require precise part orientation, controlled atmospheres, or rapid quenching, such as hardening or brazing.
Core Processes of a Rotary Furnace
The design of a rotary furnace, a slowly rotating cylindrical tube, dictates its primary applications. It excels where constant mixing of the material is a benefit, not a drawback.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a thermal treatment process used to bring about a chemical change, such as removing volatile components or driving off carbon dioxide from ores. The constant tumbling ensures every particle reaches the target temperature, resulting in a complete and uniform reaction. This is fundamental in the cement, lime, and mineral processing industries.
Oxidation
Oxidation involves heating a material in an oxygen-rich environment to induce a chemical reaction. In a rotary furnace, this process benefits from the continuous exposure of new material surfaces to the process atmosphere, ensuring a thorough and consistent reaction throughout the entire batch.
Melting and Smelting
For certain applications, like melting aluminum scrap, rotary furnaces are highly effective. The tumbling action helps break up the oxide layer on the surface of the metal and improves heat transfer, leading to a more efficient melting process compared to static furnaces.
Why Rotary Furnaces Excel at These Processes
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace is a direct result of its mechanical design, which offers distinct advantages for specific material types and goals.
Uniform Heating Through Constant Mixing
The single most important feature is the gentle tumbling of the material as the furnace rotates. This action constantly circulates the material, eliminating hot spots and ensuring that the entire charge is heated uniformly.
High Throughput for Bulk Materials
Unlike a batch furnace that must be loaded and unloaded, a rotary furnace can operate continuously. Raw material is fed into one end and the processed material is discharged from the other, making it ideal for large-scale industrial production of powders, granules, and small, irregular solids.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern rotary furnaces are equipped with advanced control systems that can maintain precise temperature profiles along the length of the tube. This allows for multi-stage processes within a single piece of equipment, further enhancing efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Processes Not Suited for Rotary Furnaces
Equally important is understanding what a rotary furnace cannot do. Its core strength—constant motion—is a critical weakness for many common heat treatment processes.
Hardening and Quenching
Hardening processes like quenching require a part to be heated to a specific temperature and then cooled with extreme rapidity. The slow, continuous discharge and tumbling action of a rotary furnace make it impossible to transfer parts into a quench bath with the speed and control required to achieve the desired metallurgical properties.
Annealing and Tempering of Finished Parts
While these processes involve heating and slow cooling, the tumbling action can cause surface damage, scratching, or deformation to finished or semi-finished parts. Batch or conveyor furnaces that keep parts stationary are far superior for these tasks.
Brazing and Sintering
Brazing requires a filler metal to join two precisely aligned components, while sintering fuses powder into a solid shape. Both processes demand that the parts remain absolutely still. The tumbling motion of a rotary furnace would destroy the assembly or the part's intended geometry.
Precision Surface Treatments
Processes like carburizing or nitriding require a highly controlled and sealed atmosphere to diffuse elements into a part's surface to a precise depth. The seals on a rotary furnace are generally not designed for the level of atmospheric integrity required for these precision surface engineering tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology is critical to achieving your production goals efficiently and cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders, ores, or granules (e.g., calcination): A rotary furnace is the ideal choice due to its superior heat uniformity and capacity for continuous throughput.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating discrete metal parts (e.g., hardening, annealing, brazing): A batch, conveyor, or vacuum furnace is the correct tool, as the rotary motion is detrimental to these processes.
- If your primary focus is melting bulk scrap or loose material: A rotary furnace is a strong candidate, especially for non-ferrous metals where mixing improves melt efficiency.
Choosing the right furnace begins with matching the equipment's core mechanical action to your specific material form and process requirements.

Summary Table:
| Process | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Cement, lime, mineral processing | Uniform thermal decomposition, high throughput |
| Oxidation | Material oxidation reactions | Consistent exposure to atmosphere, thorough reaction |
| Melting/Smelting | Aluminum scrap melting | Efficient heat transfer, oxide layer breakdown |
Ready to enhance your bulk material processing? Contact KINTEK today to explore our advanced rotary furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for calcination, oxidation, and more. Get in touch now to discuss how we can boost your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















