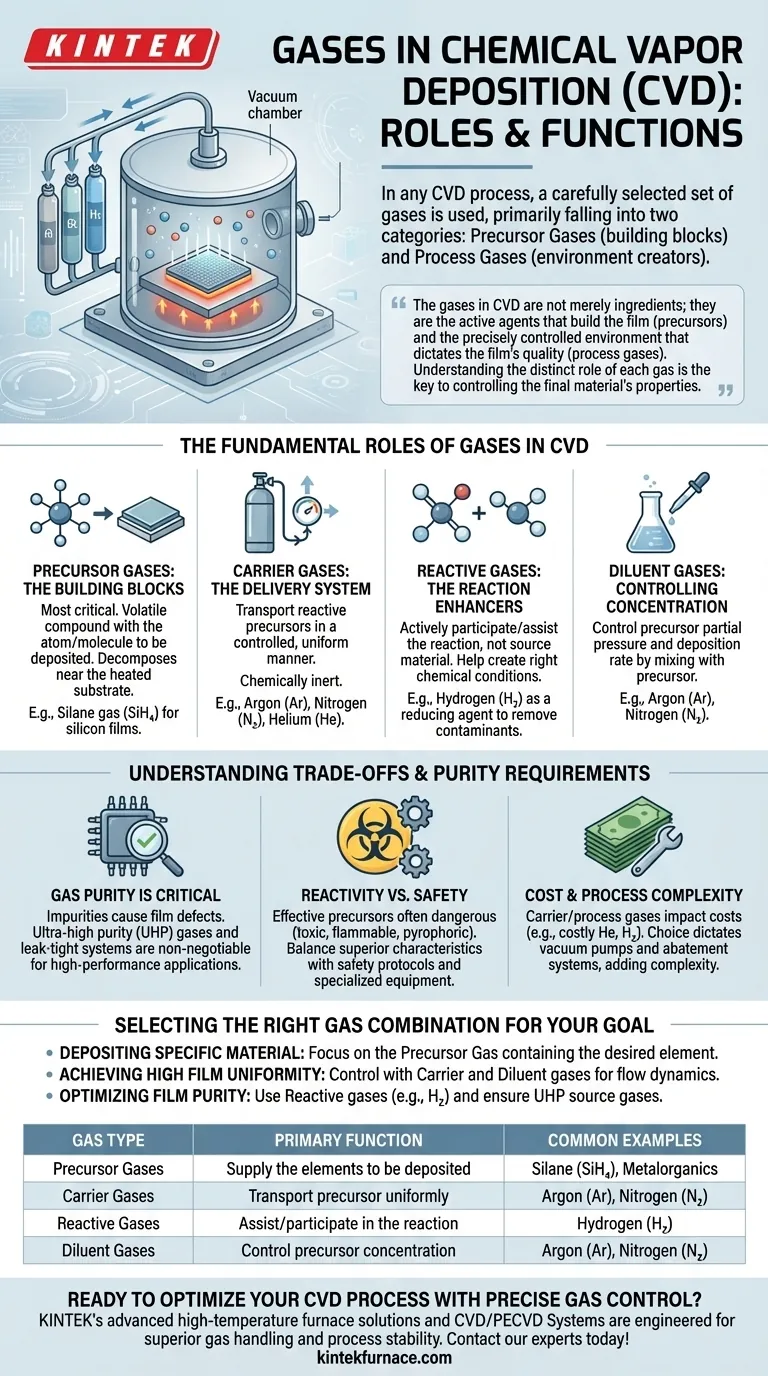
In any Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process, a carefully selected set of gases is used, primarily falling into two categories: precursor gases, which contain the elements to be deposited onto a surface, and process gases, such as hydrogen, argon, or nitrogen, which create the necessary environment for the reaction to occur efficiently and with high quality.
The gases in CVD are not merely ingredients; they are the active agents that build the film (precursors) and the precisely controlled environment that dictates the film's quality (process gases). Understanding the distinct role of each gas is the key to controlling the final material's properties.
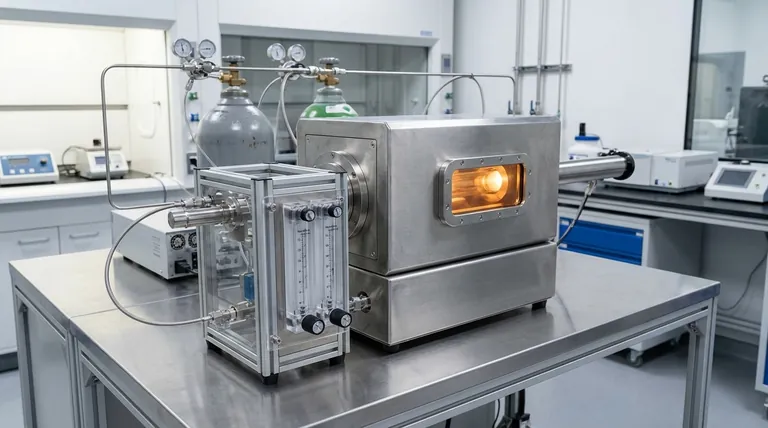

The Fundamental Roles of Gases in CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally a gas-phase process. A substrate is heated in a vacuum chamber while gases are introduced, which then react or decompose on the substrate's surface to form the desired thin film. Each gas has a highly specific job.
Precursor Gases: The Building Blocks
The most critical gas in any CVD recipe is the precursor. This is a volatile compound that contains the atom or molecule you intend to deposit.
When heated near the substrate, the precursor gas decomposes, leaving the desired element behind. For example, to deposit a silicon film, silane gas (SiH₄) is often used as a precursor.
Carrier Gases: The Delivery System
Precursor gases are often highly reactive and need to be transported to the substrate in a controlled, uniform manner. This is the job of a carrier gas.
These gases are chemically inert, meaning they do not participate in the primary reaction. Common examples include argon (Ar), nitrogen (N₂), and sometimes helium (He). Their purpose is to carry the precursor molecules and ensure a stable, consistent flow over the substrate.
Reactive Gases: The Reaction Enhancers
Some gases are added to actively participate in or assist the chemical reaction. They are not the source of the deposited material but help create the right chemical conditions.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a classic example. It can act as a reducing agent, removing unwanted elements (like oxygen or carbon) from the growing film and ensuring a purer final product. It can also help "catalyze" or enhance the surface reaction rate.
Diluent Gases: Controlling Concentration
In many processes, the precursor gas is too concentrated on its own, which could lead to a deposition rate that is too fast and difficult to control.
Inert gases like argon and nitrogen also serve as diluents. By mixing the precursor with a large volume of a diluent gas, you can precisely control the precursor's partial pressure, which in turn controls the deposition rate and film uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Purity Requirements
The choice of gases is a balance of performance, safety, and cost. Each decision has direct consequences for the process and the final product.
The Critical Role of Gas Purity
Impurities in the source gases are a primary cause of film defects. Even trace amounts of water or oxygen (measured in parts per billion) can contaminate the process, leading to poor film quality or device failure.
Therefore, using ultra-high purity (UHP) gases and maintaining a leak-tight vacuum system are non-negotiable for high-performance applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
Reactivity vs. Safety
The most effective precursor gases are often the most dangerous. Many are highly toxic, flammable, or pyrophoric (igniting spontaneously in air).
Engineers must weigh the superior deposition characteristics of a specific precursor against the significant safety protocols, specialized equipment, and handling procedures it requires.
Cost and Process Complexity
Carrier and process gases also impact the bottom line. While argon and nitrogen are relatively inexpensive and abundant, other gases like helium or hydrogen can be more costly.
The choice of gas also dictates the type of vacuum pumps and exhaust gas treatment (abatement) systems required, adding further layers of cost and complexity to the overall CVD system.
Selecting the Right Gas Combination for Your Goal
The optimal gas mixture depends entirely on the material you are depositing and the properties you want to achieve. Use the role of each gas as your guide.
- If your primary focus is depositing a specific material: Your first and most important decision is the selection of the precursor gas that contains the desired element.
- If your primary focus is achieving high film uniformity: Your control levers are the carrier and diluent gases, which dictate flow dynamics and precursor concentration across the substrate.
- If your primary focus is optimizing film purity: Your attention must be on using reactive gases like hydrogen to remove contaminants and ensuring all source gases are of ultra-high purity.
Ultimately, mastering CVD is mastering the precise control and interaction of these essential gases.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Gases | Supply the elements to be deposited | Silane (SiH₄), Metalorganics |
| Carrier Gases | Transport precursor uniformly | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N₂) |
| Reactive Gases | Assist/participate in the reaction | Hydrogen (H₂) |
| Diluent Gases | Control precursor concentration | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N₂) |
Ready to optimize your CVD process with precise gas control? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered for superior gas handling and process stability. Our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities allow for deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring high-purity, uniform films. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using a CVD system? Optimize Carbon Nanotube Growth for Thermal Conductivity
- What is the function of a PECVD system in the passivation of UMG silicon solar cells? Enhance Efficiency with Hydrogen
- Why is a high-precision PECVD system required in ACSM? Enable Low-Temperature Atomic-Scale Manufacturing
- What is the necessity of high-bias gas ion cleaning? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion
- Why Use PECVD for Monolithic Integrated Chip Isolation Layers? Protect Your Thermal Budget with High-Quality SiO2



















